MySQL数据操作: DML
在MySQL管理软件中,可以通过SQL语句中的DML语言来实现数据的操作,包括
1.使用INSERT实现数据的插入
2.UPDATE实现数据的更新
3.使用DELETE实现数据的删除
4.使用SELECT查询数据以及。
创建一个表:
create table t1(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name char(12) not null,
age int not null,
sex enum('male','female') default 'male'
);
插入数据 insert
1. 插入完整数据(顺序插入) 语法一: insert into 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3…字段n) values(值1,值2,值3…值n);
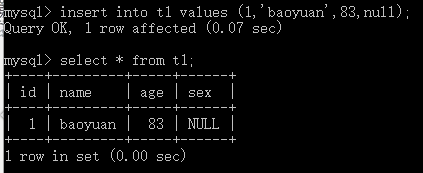
语法二: insert into 表名 values (值1,值2,值3…值n); 例:insert into t1 values (1,'baoyuan',83,null);
2. 指定字段插入数据
语法: insert into 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3…) values (值1,值2,值3…);
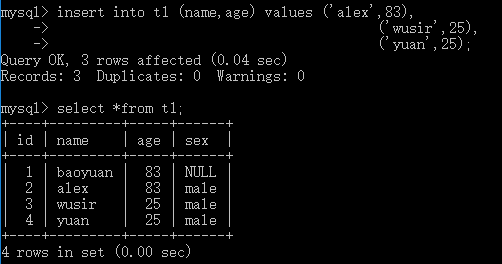
例:insert into t1 (name,age) values ('alex',83); 3. 插入多条记录 语法: insert into 表名 values (值1,值2,值3…值n), (值1,值2,值3…值n), (值1,值2,值3…值n);
例:insert into t1 (name,age) values ('alex',83),
('wusir',25),
('yuan',25);
4. 插入查询结果
语法:
insert into 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3…字段n)
select (字段1,字段2,字段3…字段n) from 表2
where …;
删除数据delete
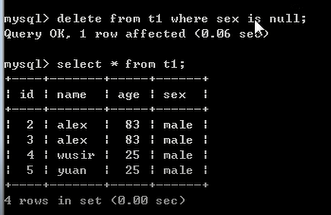
语法: delete from 表名 where 条件;
例:delete from t1 where sex = 'male'; #所有的男士都删掉
delete from t1 where name = 'alex' and sex = 'male'; #名字=alex,男士都删掉
更新数据update
语法: update 表名 set 字段1=值1, 字段2=值2, where 条件;
例: update 表 set age = 84 where name = alex;
update 表 set age = null where name = alex;
update 表 set age = 84,
sex = 'female'
where id = 1;
示例:
update mysql.user set password=password(‘123’)
where user=’root’ and host=’localhost’; #修改密码
所有的用户信息都在mysql的user表中
如果我们需要删除用户或者修改用户的密码,也可以使用数据的删改来操作user表
查询数据select
单表查询
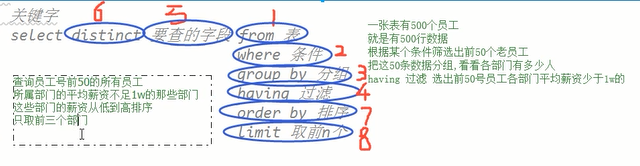
select distinct 要查的字段 from 表 #distinct 去重
where 条件
group by 分组
having 过滤
order by 排序
limit 取前n个
词法分析
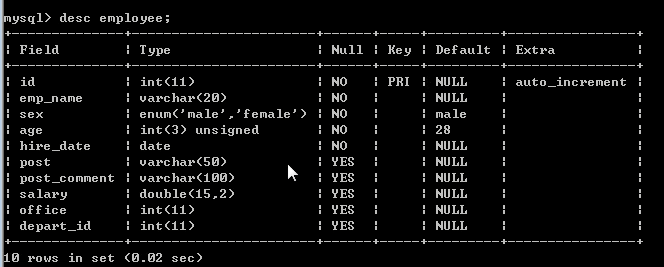
company.employee
员工id id int
姓名 emp_name varchar
性别 sex enum
年龄 age int
入职日期 hire_date date
岗位 post varchar
职位描述 post_comment varchar
薪水 salary double
办公室 office int
部门编号 depart_id int
#创建表
create table employee(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
emp_name varchar(20) not null,
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', #大部分是男的
age int(3) unsigned not null default 28,
hire_date date not null,
post varchar(50),
post_comment varchar(100),
salary double(15,2),
office int, #一个部门一个屋子
depart_id int
);
简单查询
查询所有的字段\单个字段\给字段重命名\给字段去重 select * from 表; select 字段名1,字段名2 from 表; select distinct 字段名1 from 表; select 字段名 as 新的临时名字 from 表;
查询数据的四则运算
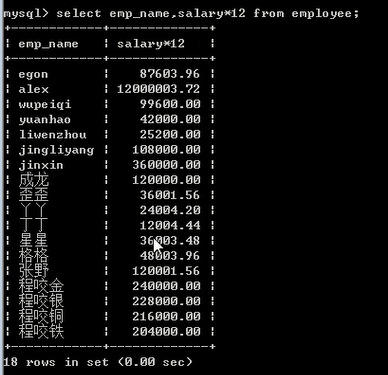
select emp_name,salary*12 from 表; #salary*12 + - * / 都可以
select emp_name,salary*12 as annua_salary from employee;
定义显示格式
concat/concat_ws
CONCAT() 函数用于连接字符串
now() 获取当前时间
user() 获取当前用户
password('密码') 摘要密码
concat('','','','')
concat_ws('拼接符号','','','')
GROUP_CONCAT(字段名) 一定适合group by 连用的
count 计数器
sum
max
min
avg
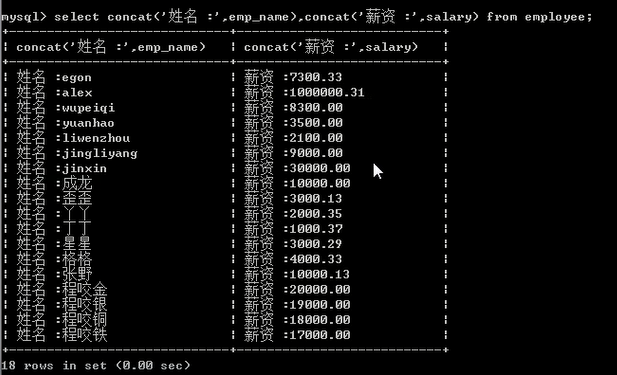
select concat('姓名 :',emp_name,', 薪资 :',salary) from employee;
select concat('姓名 :',emp_name),concat('薪资 :',salary) from employee;
select concat_ws(':',emp_name,salary) from employee;
select concat_ws(':',emp_name,salary) as annual_salary from employee;
case语句
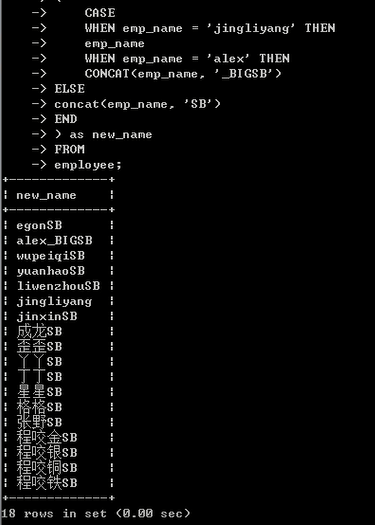
SELECT
( # if条件判断
CASE # 一个if条件判断句的开始
WHEN emp_name = 'jingliyang' # if
THEN emp_name # then if条件成立之后做的事儿
WHEN emp_name = 'alex' # # elif 另一个条件
THEN CONCAT(emp_name,'_BIGSB') #
ELSE # else
concat(emp_name, 'SB') # 没有then 直接就是上述条件不满足都走这个分支
END # end 就表示这个case语句结束了
) as new_name
FROM
employee;
where字句中可以使用
1. 比较运算符:> < >= <= <> !=
2. between 80 and 100 值在10到20之间 范围
3. in(80,90,100) 值是10或20或30 范围
4.like
# 通配符
# '%' 表示任意长度任意字符
# '_' 表示一个任意字符
薪资在8000-10000之间的男人
select * from employee where salary between 8000 and 10000 and sex = 'male';
找到所有的 operation部门或者teacher部门
select * from employee where post = 'operation' or post = 'teacher';
select * from employee where post in ('operation','teacher');
多表查询