本人学号:201771010138
姓名:邹丰蔚
《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十六周学习总结
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握线程概念;
(2) 掌握线程创建的两种技术;
(3) 理解和掌握线程的优先级属性及调度方法;
(4) 掌握线程同步的概念及实现技术;
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:

l 在elipse IDE中调试运行ThreadTest,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握线程概念;
l 掌握用Thread的扩展类实现线程的方法;
l 利用Runnable接口改造程序,掌握用Runnable接口创建线程的方法。
class Lefthand extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("You are Students!"); try{ sleep(500); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error.");} } } } class Righthand extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); try{ sleep(300); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error.");} } } } public class ThreadTest { static Lefthand left; static Righthand right; public static void main(String[] args) { left=new Lefthand(); right=new Righthand(); left.start(); right.start(); } }
利用Runnable接口改造程序后:
class Lefthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("You are Students!"); try{ Thread.sleep(500); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error.");} } } } class Righthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); try{ Thread.sleep(300); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error.");} } } } public class M { public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable r=new Lefthand(); Runnable r1=new Righthand(); Thread t=new Thread(r); Thread t1=new Thread(r1); t.start(); t1.start(); } }
得出结果: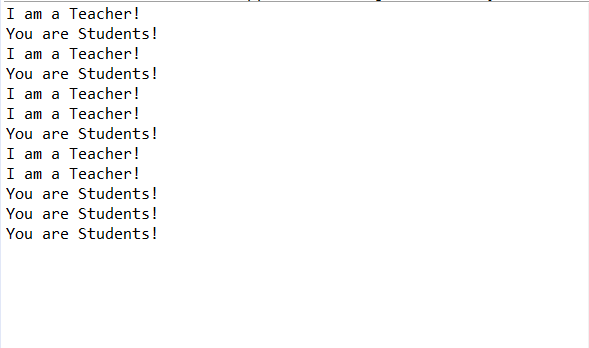
测试程序2:
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材625页程序14-1、14-2 、14-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材631页程序14-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 对比两个程序,理解线程的概念和用途;
l 掌握线程创建的两种技术。
14-1.14-2.14-3:
BallComponent:
package bounce; import java.awt.*; import java.util.*; import javax.swing.*; public class BallComponent extends JPanel { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 450; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350; private java.util.List<Ball> balls = new ArrayList<>(); /** 向组件中添加一个球。*/ public void add(Ball b) { balls.add(b); } public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { super.paintComponent(g); // 擦除背景 Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; for (Ball b : balls) { g2.fill(b.getShape()); } } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } }
BounceFrame:
package bounce; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; public class Bounce { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new BounceFrame(); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** 带有球组件和按钮的框架。*/ class BounceFrame extends JFrame { private BallComponent comp; public static final int STEPS = 1000; public static final int DELAY = 3; /** * 用显示弹跳球和的组件构造框架 *启动和关闭按钮 **/ public BounceFrame() { setTitle("Bounce"); comp = new BallComponent(); add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER); JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall()); addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0)); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } /** * 将按钮添加到容器中 *按钮标题 * 按钮的动作监听器 */ public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener) { JButton button = new JButton(title); c.add(button); button.addActionListener(listener); } /** *向面板中添加一个弹跳球,使其弹跳1000次。 */ public void addBall() { try { Ball ball = new Ball(); comp.add(ball); for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++) { ball.move(comp.getBounds()); comp.paint(comp.getGraphics()); Thread.sleep(DELAY); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } }
Ball:
package bounce; import java.awt.geom.*; /** * 从长方形边缘上移动和弹跳的球 */ public class Ball { private static final int XSIZE = 15; private static final int YSIZE = 15; private double x = 0; private double y = 0; private double dx = 1; private double dy = 1; /** * 将球移动到下一个位置,如果球碰到其中一条边,则反向移动 */ public void move(Rectangle2D bounds) { x += dx; y += dy; if (x < bounds.getMinX()) { x = bounds.getMinX(); dx = -dx; } if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX()) { x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE; dx = -dx; } if (y < bounds.getMinY()) { y = bounds.getMinY(); dy = -dy; } if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY()) { y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE; dy = -dy; } } /** * 获取球在当前位置的形状。 */ public Ellipse2D getShape() { return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE); } }
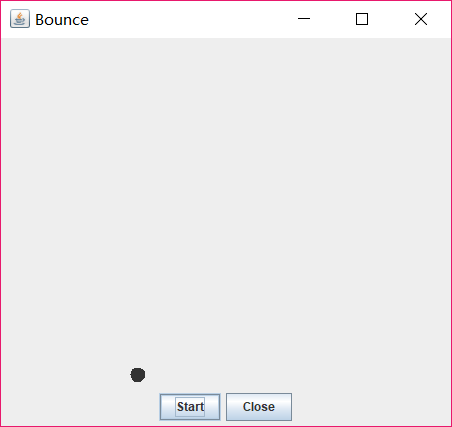
14-4:
BounceThread:
package bounceThread; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; public class BounceThread { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new BounceFrame(); frame.setTitle("BounceThread"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } class BounceFrame extends JFrame { private BallComponent comp; public static final int STEPS = 1000; public static final int DELAY = 5; public BounceFrame() { comp = new BallComponent(); add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER); JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall()); addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0)); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener) { JButton button = new JButton(title); c.add(button); button.addActionListener(listener); } public void addBall() /** 在画布上添加一个弹跳球,并启动一个线程使其运行*/ { Ball ball = new Ball(); comp.add(ball); Runnable r = () -> { try { for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++) { ball.move(comp.getBounds()); comp.repaint(); Thread.sleep(DELAY); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }; Thread t = new Thread(r); t.start(); } }
得出结果:
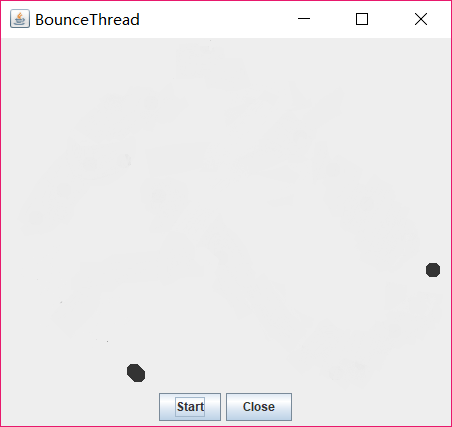
测试程序3:分析以下程序运行结果并理解程序。
class Race extends Thread { public static void main(String args[]) { Race[] runner=new Race[4]; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i]=new Race( ); for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i].start( ); runner[1].setPriority(MIN_PRIORITY); runner[3].setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);} public void run( ) { for(int i=0; i<1000000; i++); System.out.println(getName()+"线程的优先级是"+getPriority()+"已计算完毕!"); } }

测试程序4
l 教材642页程序模拟一个有若干账户的银行,随机地生成在这些账户之间转移钱款的交易。每一个账户有一个线程。在每一笔交易中,会从线程所服务的账户中随机转移一定数目的钱款到另一个随机账户。
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材642页程序14-5、14-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
UnsynchBankTest:
package unsynch; /** * 当多个线程访问一个数据结构时,这个程序显示数据损坏。 */ public class UnsynchBankTest { public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100; public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000; public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000; public static final int DELAY = 10; public static void main(String[] args) { Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE); for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++) { int fromAccount = i; Runnable r = () -> { try { while (true) { int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random()); double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random(); bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount); Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random())); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }; Thread t = new Thread(r); t.start(); } } }
Bank:
package unsynch; import java.util.*; public class Bank { private final double[] accounts; /** * @参数n表示账户数量 * @每个帐户的初始余额 */ public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) { accounts = new double[n]; Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); } /** * 把钱从一个账户转到另一个账户。 * @从帐户中调出参数 * @向要转账的账户输入参数 * @要转帐的金额 */ public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) { if (accounts[from] < amount) return; System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()); accounts[from] -= amount; System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); accounts[to] += amount; System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); } /** * 获取所有帐户余额的总和。 * 返回总余额 */ public double getTotalBalance() { double sum = 0; for (double a : accounts) sum += a; return sum; } /** *获取银行中的帐户编号. * 返回账号 */ public int size() { return accounts.length; } }
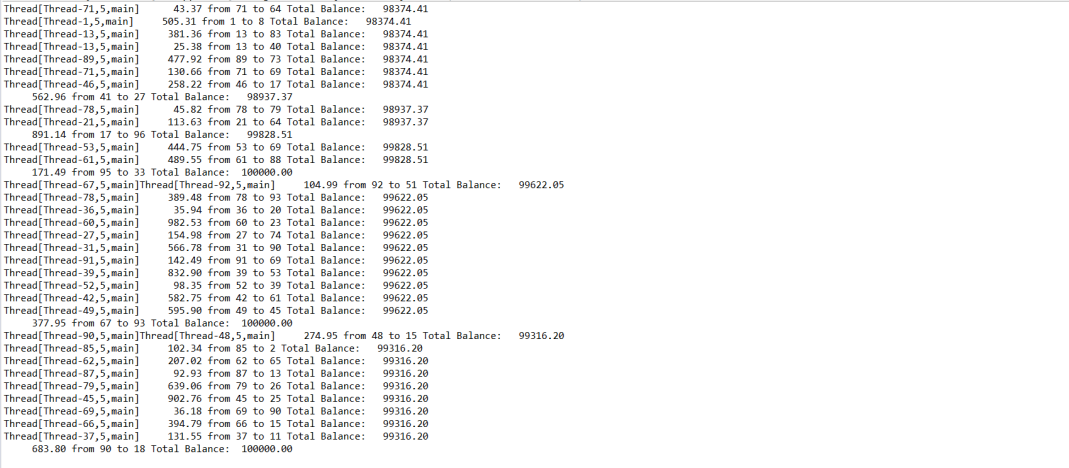
得出结果:
综合编程练习
编程练习1
- 设计一个用户信息采集程序,要求如下:
(1) 用户信息输入界面如下图所示:
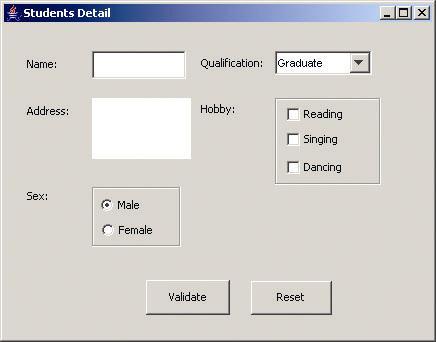
(2) 用户点击提交按钮时,用户输入信息显示控制台界面;
(3) 用户点击重置按钮后,清空用户已输入信息;
(4) 点击窗口关闭,程序退出。
Main:
import java.awt.EventQueue; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class Mian { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { demo page = new demo(); }); } }
WinCenter:
import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.Toolkit; import java.awt.Window; public class WinCenter { public static void center(Window win){ Toolkit tkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); Dimension sSize = tkit.getScreenSize(); Dimension wSize = win.getSize(); if(wSize.height > sSize.height){ wSize.height = sSize.height; } if(wSize.width > sSize.width) { wSize.width = sSize.width; } win.setLocation((sSize.width - wSize.width)/ 2, (sSize.height - wSize.height)/ 2); } }
Demo:
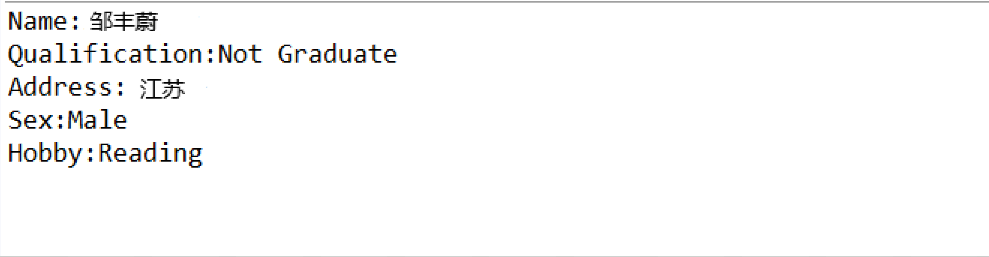
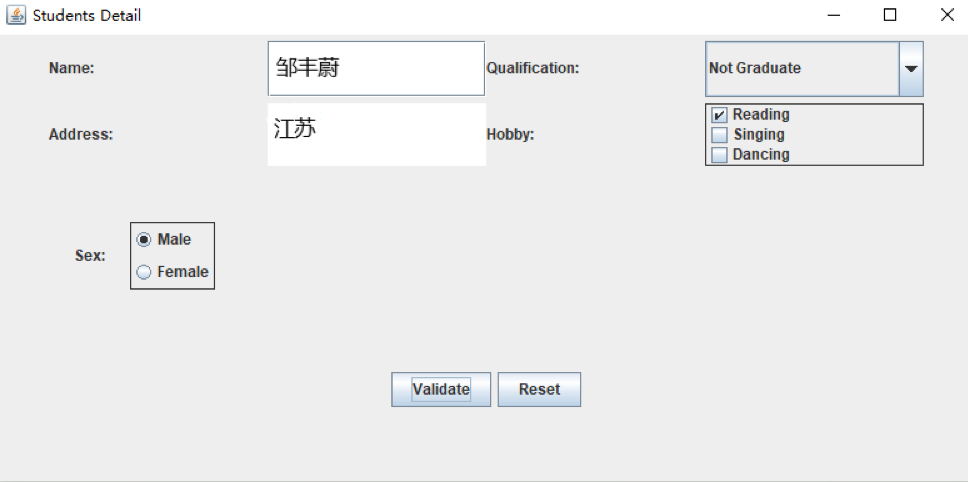
import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.border.*; public class demo extends JFrame { public demo() { JPanel panel1 = new JPanel(); panel1.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 45)); panel1.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4)); JLabel label1 = new JLabel("Name:"); JTextField j1 = new JTextField(""); JLabel label2 = new JLabel("Qualification:"); JComboBox<Object> j2 = new JComboBox<>(); j2.addItem("Graduate"); j2.addItem("Not Graduate"); panel1.add(label1); panel1.add(j1); panel1.add(label2); panel1.add(j2); JPanel panel2 = new JPanel(); panel2.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 50)); panel2.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4)); JLabel label3 = new JLabel("Address:"); JTextArea j3 = new JTextArea(); JLabel label4 = new JLabel("Hobby:"); JPanel p = new JPanel(); p.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 1)); p.setBorder(BorderFactory.createLineBorder(null)); JCheckBox c1 = new JCheckBox("Reading"); JCheckBox c2 = new JCheckBox("Singing"); JCheckBox c3 = new JCheckBox("Dancing"); p.add(c1); p.add(c2); p.add(c3); panel2.add(label3); panel2.add(j3); panel2.add(label4); panel2.add(p); JPanel panel3 = new JPanel(); panel3.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150)); FlowLayout flowLayout1 = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT, 20, 40); panel3.setLayout(flowLayout1); JLabel label5 = new JLabel("Sex:"); JPanel p1 = new JPanel(); p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1)); p1.setBorder(BorderFactory.createLineBorder(null)); ButtonGroup bu = new ButtonGroup(); JRadioButton jr1 = new JRadioButton("Male"); JRadioButton jr2 = new JRadioButton("Female"); bu.add(jr1); bu.add(jr2); p1.add(jr1); p1.add(jr2); panel3.add(label5); panel3.add(p1); add(panel1); add(panel2); add(panel3); JPanel panel4 = new JPanel(); panel4.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150)); JButton b1 = new JButton("Validate"); panel4.add(b1); JButton b2 = new JButton("Reset"); panel4.add(b2); add(panel4); FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(); this.setLayout(flowLayout); this.setTitle("Students Detail"); this.setBounds(200, 200, 800, 400); this.setVisible(true); this.setDefaultCloseOperation(DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE); b1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 String xueli = j2.getSelectedItem().toString(); System.out.println("Name:" + j1.getText()); System.out.println("Qualification:" + xueli); String hobbystring = "Hobby:"; if (c1.isSelected()) { hobbystring += "Reading"; } if (c2.isSelected()) { hobbystring += "Singing"; } if (c3.isSelected()) { hobbystring += "Dancing"; } System.out.println("Address:" + j3.getText()); if (jr1.isSelected()) { System.out.println("Sex:Male"); } if (jr2.isSelected()) { System.out.println("Sex:Female"); } System.out.println(hobbystring); } }); b2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 j1.setText(null); j3.setText(null); j2.setSelectedIndex(0); c1.setSelected(false); c2.setSelected(false); c3.setSelected(false); bu.clearSelection(); } }); } public static void main(String args[]) { new demo(); } }
得出结果:
2.创建两个线程,每个线程按顺序输出5次“你好”,每个“你好”要标明来自哪个线程及其顺序号。
package demo; class Lefthand extends Thread { public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("左:"+i+" 你好!"); try { sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error."); } } } } class Righthand extends Thread{ public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("右:"+i+" 你好!"); try { sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error."); } } } } public class ThreadTest { static Lefthand left; static Righthand right; public static void main(String[] args) { left = new Lefthand(); right = new Righthand(); left.start(); right.start(); } }
得出结果:

完善实验十五 GUI综合编程练习程序。
身份证:
package demo1; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class ButtonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new Main(); frame.setTitle("身份证"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
package demo1; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Scanner; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.event.*; public class Main extends JFrame { private static ArrayList<Student> studentlist; private static ArrayList<Student> list; private JPanel panel; private JPanel buttonPanel; private static final int DEFAULT_WITH = 600; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 300; public Main() { studentlist = new ArrayList<>(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); File file = new File("C:\\Users\\ASUS\\Desktop\\身份证号.txt"); try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); String temp = null; while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" "); String name = linescanner.next(); String number = linescanner.next(); String sex = linescanner.next(); String age = linescanner.next(); String province = linescanner.nextLine(); Student student = new Student(); student.setName(name); student.setnumber(number); student.setsex(sex); int a = Integer.parseInt(age); student.setage(a); student.setprovince(province); studentlist.add(student); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("学生信息文件找不到"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误"); e.printStackTrace(); } panel = new JPanel(); panel.setLayout(new BorderLayout()); JTextArea jt = new JTextArea(); panel.add(jt); add(panel, BorderLayout.NORTH); buttonPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 7)); JButton jButton = new JButton("名单"); JButton jButton1 = new JButton("年龄"); JLabel lab = new JLabel("省份"); JTextField jt1 = new JTextField(); JLabel lab1 = new JLabel("年龄:"); JTextField jt2 = new JTextField(); JLabel lab2 = new JLabel("输入你的身份证号码:"); JTextField jt3 = new JTextField(); JButton jButton2 = new JButton("退出"); jButton.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30); jButton1.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30); jt1.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30); jt2.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30); jt3.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30); jButton2.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30); jButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { Collections.sort(studentlist); jt.setText(studentlist.toString()); } }); jButton1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { int max = 0, min = 100; int j, k1 = 0, k2 = 0; for (int i = 1; i < studentlist.size(); i++) { j = studentlist.get(i).getage(); if (j > max) { max = j; k1 = i; } if (j < min) { min = j; k2 = i; } } jt.setText("年龄最大:" + studentlist.get(k1) + "年龄最小:" + studentlist.get(k2)); } }); jButton2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { dispose(); System.exit(0); } }); jt1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String find = jt1.getText(); String text = ""; String place = find.substring(0, 3); for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++) { if (studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1, 4).equals(place)) { text += "\n" + studentlist.get(i); jt.setText("老乡:" + text); } } } }); jt2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String yourage = jt2.getText(); int a = Integer.parseInt(yourage); int near = agenear(a); int value = a - studentlist.get(near).getage(); jt.setText("年龄相近:" + studentlist.get(near)); } }); jt3.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() { public void keyTyped(KeyEvent e) { list = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.sort(studentlist); String key = jt3.getText(); for (int i = 1; i < studentlist.size(); i++) { if (studentlist.get(i).getnumber().contains(key)) { list.add(studentlist.get(i)); jt.setText(“\n" + list); } } } }); buttonPanel.add(jButton); buttonPanel.add(jButton1); buttonPanel.add(lab); buttonPanel.add(jt1); buttonPanel.add(lab1); buttonPanel.add(jt2); buttonPanel.add(lab2); buttonPanel.add(jt3); buttonPanel.add(jButton2); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); setSize(DEFAULT_WITH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } public static int agenear(int age) { int min = 53, value = 0, k = 0; for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++) { value = studentlist.get(i).getage() - age; if (value < 0) value = -value; if (value < min) { min = value; k = i; } } return k; } }
package demo1; public class Student implements Comparable<Student> { private String name; private String number ; private String sex ; private int age; private String province; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getnumber() { return number; } public void setnumber(String number) { this.number = number; } public String getsex() { return sex ; } public void setsex(String sex ) { this.sex =sex ; } public int getage() { return age; } public void setage(int age) { // int a = Integer.parseInt(age); this.age= age; } public String getprovince() { return province; } public void setprovince(String province) { this.province=province ; } public int compareTo(Student o) { return this.name.compareTo(o.getName()); } public String toString() { return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n"; } }
计算器:
package T; import java.awt.Font; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Scanner; import javax.swing.*; import java.math.*; public class D extends JFrame { private String[] c=new String[10]; private String[] c1=new String[11]; private int[] list=new int[10]; int i=0,i1=0,sum = 0; private PrintWriter out = null; private JTextArea text,text1; private int counter; public D() { JPanel Panel = new JPanel();Panel.setLayout(null); JLabel JLabel1=new JLabel("...");JLabel1.setBounds(500, 800, 400, 30);JLabel1.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); JButton Button = new JButton("生成题目");Button.setBounds(50,150,150,50);Button.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20)); Button.addActionListener(new Action()); JButton Button2 = new JButton("确定答案");Button2.setBounds(300,150,150,50);Button2.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20));Button2.addActionListener(new Action1()); JButton Button3 = new JButton("读出文件");Button3.setBounds(500,150,150,50);Button3.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20));Button3.addActionListener(new Action2()); text=new JTextArea(30,80);text.setBounds(30, 50, 200, 50);text.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); text1=new JTextArea(30,80);text1.setBounds(270, 50, 200, 50);text1.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); Panel.add(text); Panel.add(text1); Panel.add(Button); Panel.add(Button2); Panel.add(Button3); Panel.add(JLabel1); add(Panel); } private class Action implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { text1.setText("0"); if(i<11) { int a = 1+(int)(Math.random() * 99); int b = 1+(int)(Math.random() * 99); int m= (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3); switch(m) { case 1: while(a<b){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } c[i]=((i+1)+":"+a+"/"+b+"="); list[(i+1)]=Math.floorDiv(a, b); text.setText((i+1)+":"+a+"/"+b+"="); i++; break; case 2: c[i]=((i+1)+":"+a+"*"+b+"="); list[(i+1)]=Math.multiplyExact(a, b); text.setText((i+1)+":"+a+"*"+b+"="); i++; break; case 3: c[i]=((i+1)+":"+a+"+"+b+"="); list[(i+1)]=Math.addExact(a, b); text.setText((i+1)+":"+a+"+"+b+"="); i++; break ; case 4: while(a<=b){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } c[i]=((i+1)+":"+a+"-"+b+"="); text.setText((i+1)+":"+a+"-"+b+"="); list[(i+1)]=Math.subtractExact(a, b); i++; break ; } } } } private class Action1 implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { if(i<10) { String daan=text1.getText().toString().trim(); int a = Integer.parseInt(daan); if(text1.getText()!=" ") { if(list[i1]==a) sum+=10; } c1[i1]=daan; i1++; } } } private class Action2 implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { try { out = new PrintWriter("text.txt"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for(int counter=0;counter<10;counter++) { out.println(c[counter]+c1[counter]); } out.println("成绩"+sum); out.close(); } } }
package T; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.EventQueue; import java.awt.Toolkit; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class N { public static void main (String args[]) { Toolkit t=Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); Dimension s=t.getScreenSize(); EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new D(); frame.setBounds(0, 0,(int)s.getWidth()/2,(int)s.getHeight()/2); frame.setTitle(" "); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
实验总结:
多线程的概念:
多线程是进程执行过程中产生的多条执行线索。
‐线程是比进程执行更小的单位。
线程不能独立存在,必须存在于进程中,同一进
程的各线程间共享进程空间的数据。
‐每个线程有它自身的产生、存在和消亡的过程,
是一个动态的概念。
多线程意味着一个程序的多行语句可以看上去几
乎在同一时间内同时运行。
‐线程创建、销毁和切换的负荷远小于进程,又称
为轻量级进程(lightweight process)。
用Thread类的子类创建线程:
⚫首先需从Thread类派生出一个子类,在该子类中
重写run()方法。
⚫ 然后用创建该子类的对象
⚫ 最后用start()方法启动线程
用Thread类的子类创建多线程的关键性操作:
–定义Thread类的子类并实现用户线程操作,即
run()方法的实现。
–在适当的时候启动线程。
由于Java只支持单重继承,用这种方法定义的类不
可再继承其他父类。
用Runnable()接口实现线程:
⚫ 首先设计一个实现Runnable接口的类;
⚫ 然后在类中根据需要重写run方法;
⚫ 再创建该类对象,以此对象为参数建立Thread
类的对象;
⚫ 调用Thread类对象的start方法启动线程,将
CPU执行权转交到run方法。
线程两种创建方法比较:
实现Runnable接口的优势:
•符合OO设计的思想
•便于用extends继承其它类
✓ 采用继承Thread类方法的优点:代码简单
✓ 提倡采用第一种方式
通过本周理论知识的学习以及在实验课上所做的实验,我掌握了线程的概念,也懂得了如何去理论线程的知识点在页面布局管理器上编辑一些东西。