参考博客:图的深度优先遍历(递归、非递归;邻接表,邻接矩阵)
本篇默认连通图,非连通情况会在邻接表处补上
1.邻接矩阵的递归解法
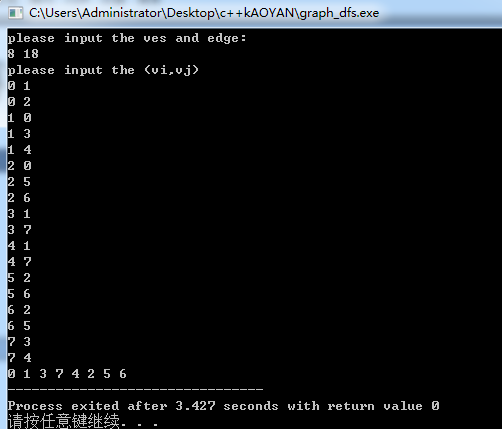
#include<stdio.h> #define MAX 100 typedef struct { int e[MAX][MAX]; int ves; int edge; int book[MAX];//标志判断是否有被访问过 }MGraph; void createMGraph(MGraph *G) { int i; int j; int start; int end; printf("please input the ves and edge:\n"); scanf("%d %d",&G->ves,&G->edge); //初始化 for(i = 0; i < G->ves; i++) { for(j = 0; j < G->ves; j++) G->e[i][j] = 0; G->book[i] = 0;//没被访问过的结点置为0 } //创建邻接矩阵 printf("please input the (vi,vj)\n"); for(i = 0; i < G->edge; i++) { scanf("%d %d",&start,&end); G->e[start][end] = 1; } } void dfs(MGraph *G,int ves) { int i; G->book[ves] = 1;//被访问过的结点置为1 printf("%d ",ves); for(i = 0; i < G->ves; i++) if(G->e[ves][i] != 0 && G->book[i] == 0) dfs(G,i); } int main() { MGraph G; createMGraph(&G); dfs(&G,0); return 0; } /* 输入样例: 8 18 0 1 0 2 1 0 1 3 1 4 2 0 2 5 2 6 3 1 3 7 4 1 4 7 5 2 5 6 6 2 6 5 7 3 7 4 */

2.邻接矩阵的非递归解法
基本思想:
- 初始化栈
- 输出起始顶点,起始顶点改为“已访问”标志,将起始顶点进栈
- 重复以下操作直至栈空:
- 去栈顶元素顶点,找到未被访问的邻接结点W
- 输出W,W改为“已访问”,将W进栈
- 否则当前顶点退栈
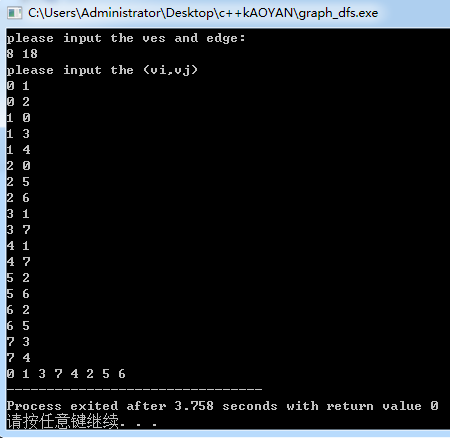
#include<stdio.h> #include<stack> #define MAX 100 using namespace std; typedef struct { int e[MAX][MAX]; int ves; int edge; int book[MAX];//标志判断是否有被访问过 }MGraph; void createMGraph(MGraph *G) { int i; int j; int start; int end; printf("please input the ves and edge:\n"); scanf("%d %d",&G->ves,&G->edge); //初始化 for(i = 0; i < G->ves; i++) { for(j = 0; j < G->ves; j++) G->e[i][j] = 0; G->book[i] = 0;//没被访问过的结点置为0 } //创建邻接矩阵 printf("please input the (vi,vj)\n"); for(i = 0; i < G->edge; i++) { scanf("%d %d",&start,&end); G->e[start][end] = 1; } } void dfs(MGraph* G,int ves) { stack<int> s;//创建一个栈 printf("%d ", ves); G->book[ves] = 1;//已经访问过结点ves了 s.push(ves);//入栈 while(!s.empty()) { int data, i; data = s.top();//取top的顶点 for(i = 0; i < G->ves; i++) { if(G->e[data][i] != 0 && G->book[i] != 1) { printf("%d ", i); G->book[i] = 1; s.push(i); break;//深度优先 } } if(i == G->ves)//data相邻的结点都访问结束了,就弹出data { s.pop(); } } } int main() { MGraph G; createMGraph(&G); dfs(&G,0); return 0; } /* 输入样例: 8 18 0 1 0 2 1 0 1 3 1 4 2 0 2 5 2 6 3 1 3 7 4 1 4 7 5 2 5 6 6 2 6 5 7 3 7 4 */