文章目录
11.二进制中1的个数
题目:输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。(链接)
解析:
按位与运算符“&”是双目运算符: 其功能是参与运算的两数各对应的二进位相与。(1&1=1; 1&0=0; 0&0=0)
n&(n-1)作用:将n的二进制表示中的最低位为1的改为0, 如: n = 10100(二进制);则(n-1) =10011
n&(n-1) = 10000 可以看到原本最低位为1的那位变为0。
n & (n-1)的其它应用
每次n和n-1按位与,二进制原本最低位为1的那位变为0。二进制1的个数减一,最终值为0时,没有1存在,count值就为1的个数。
public class Solution {
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count=0;
while(n!=0){
n &= (n-1);
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
12.数值的整数次方
题目:给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent。求base的exponent次方。(链接)
解析:求 baseexponent:指数函数
快速幂:
快速幂的目的就是做到快速求幂,假设我们要求a^b,按照朴素算法就是把a连乘b次,这样一来时间复杂度是O(b)也即是O(n)级别,快速幂能做到O(logn),快了好多好多。它的原理如下:
假设我们要求ab,那么其实b是可以拆成二进制的,该二进制数第i位的权为2(i-1),例如当b==11时,a11 = a^ (2 ^ 0+2^ 1+2^ 3)
11的二进制是1011,11 = 2³×1 + 2²×0 + 2¹×1 + 2º×1,因此,我们将a¹¹转化为算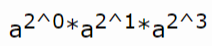 也就是a1 * a2 * a8 。
也就是a1 * a2 * a8 。
public class Solution {
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
if(exponent==0)
return 1.0;
int e = exponent > 0 ? exponent :-exponent;
double res=1;
while(e!=0){
if((e & 1) != 0)
res *=base;
base *= base;
e>>=1;
}
return exponent > 0 ? res : 1/res;
}
}
13.调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
题目:输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。(链接)
解析类似冒泡算法,前偶后奇数就交换。
public class Solution {
public void reOrderArray(int [] array) {
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
for(int j=array.length-1;j>i;j--){
if(array[j]%2==1 && array[j-1]%2 ==0)
{
int x = array[j-1];
array[j-1]=array[j];
array[j]=x;
}
}
}
}
}
14.链表中倒数第k个节点
题目:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。(链接)
解析:前后指针法,让第一个指针先向前走k-1步,然后第二个指针和第一个指针同时向后走,直到第二个指针后面没有结点,第二个指针指向的就是第k个结点。
注意:如果链表的结点个数少于k,就要返回空指针。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
ListNode pre=head,last=head;
int i=0;
for(;pre!=null;i++){
pre=pre.next;
if(i>=k){
last=last.next;
}
}
return i<k ? null : last;
}
}
15.反转链表
题目:输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。(链接)
解析:有2种方法:①递归②非递归。
代码是非递归方法,利用链表的头插法会得到反序的链表这一性质来做。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
//如果链表为空或者链表中只有一个元素
if(head==null||head.next==null)
return head;
ListNode pre=null,next=null;
while(head!=null){
next=head.next;
head.next=pre;
pre=head;
head=next;
}
return pre;
}
}
16.合并两个排序的链表
题目:输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。(链接)
解析:有2种法:①递归②非递归。
代码是递归方法:两个链表中,哪个头结点的值小就返回哪个头结点,然后合并剩下的链表,最后令头结点的值较小的那个头结点的next指向合并后的剩余链表。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null)
return list2;
if(list2==null)
return list1;
if(list1.val<=list2.val){
list1.next = Merge(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}
else{
list2.next = Merge(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}
17.树的子结构
题目:输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)(链接)
解析:首先,判断B是不是A的子结构,然后再判断B是不是A的左子树的子结构,B是不是A的右子树的子结构;
利用好 || 和 && 的短路特性。
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
if(root1==null || root2==null)
return false;
//判断根节点,其左子树,其右子树是否为tree2;
return isSubtree(root1,root2) || HasSubtree(root1.left,root2) ||HasSubtree(root1.right,root2);
}
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode node1,TreeNode node2){
if(node2 == null)
return true;
if(node1 == null)
return false;
if(node1.val == node2.val)
return isSubtree(node1.left,node2.left) && isSubtree(node1.right,node2.right);
return false;
}
}
18.二叉树的镜像
题目:操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。(链接)
解析:递归求解,把根节点的左右子树都转化成镜像二叉树,然后再交换左右指针就行了。
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return;
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = temp;
Mirror(root.left);
Mirror(root.right);
}
}
19.顺时针打印矩阵
题目:输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10.(链接)
解析:本来想做个简洁的,然鹅并没有做到- -
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int [][] matrix) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int left=0, right=matrix[0].length-1, top=0, bottom=matrix.length-1;
while(left<=right && top <=bottom){
for(int i=left;i<=right;i++)
res.add(matrix[top][i]);
for(int i=top+1;i<=bottom;i++)
res.add(matrix[i][right]);
if(top!= bottom)
for(int i=right-1;i>=left;i--)
res.add(matrix[bottom][i]);
if(left!=right)
for(int i=bottom-1;i>top;i--)
res.add(matrix[i][left]);
left++;right--;bottom--;top++;
}
return res;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int [][] matrix) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int left=0, right=matrix[0].length-1, top=0, bottom=matrix.length-1;
int x=0,y=0;
while(left<=right && top<=bottom){
for(;y<=right && left<=right && top<=bottom;y++)
res.add(matrix[x][y]);
for(top++,y--,x++; x<=bottom && left<=right && top<=bottom;x++)
res.add(matrix[x][y]);
for(right--,x--,y--; y>=left && left<=right && top<=bottom;y--)
res.add(matrix[x][y]);
for(bottom--,y++,x--; x>=top && left<=right && top<=bottom;x--)
res.add(matrix[x][y]);
left++;x++;y++;
}
return res;
}
}
20.包含min函数的栈
题目:定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))。(链接)
解析:题目要求O(1)的时间复杂度内得到最小值。那么只能空间换时间了;
每次压栈操作时,如果压栈元素比当前最小元素更小,就把这个元素压入最小元素栈,原本的最小元素就成了次小元素。同理,弹栈时,如果弹出的元素和最小元素栈的栈顶元素相等,就把最小元素的栈顶弹出。
如data依次入栈,5, 4, 3,8,10,11,12,1
则min 依次入栈,5, 4, 3,x, x , x , x , 1
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> dataStack = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
dataStack.push(node);
if( minStack.empty() || node <= min())
minStack.push(node);
}
public void pop() {
if(dataStack.peek() == min())
minStack.pop();
dataStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return dataStack.peek();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}