本文将介绍系统接收到来电之后,如何在电话薄中进行匹配联系人的流程。分析将从另外一篇文章(基于Android6.0的RIL框架层模块分析)中提到的与本文内容相关的代码开始。
//packages/service/***/Call.java
public void handleCreateConnectionSuccess(
CallIdMapper idMapper,
ParcelableConnection connection) {
setHandle(connection.getHandle(), connection.getHandlePresentation());//这个函数很重要,会启动一个查询
setCallerDisplayName(connection.getCallerDisplayName(), connection.getCallerDisplayNamePresentation());
setExtras(connection.getExtras());
if (mIsIncoming) {
// We do not handle incoming calls immediately when they are verified by the connection
// service. We allow the caller-info-query code to execute first so that we can read the
// direct-to-voicemail property before deciding if we want to show the incoming call to
// the user or if we want to reject the call.
mDirectToVoicemailQueryPending = true;
// Timeout the direct-to-voicemail lookup execution so that we dont wait too long before
// showing the user the incoming call screen.
mHandler.postDelayed(mDirectToVoicemailRunnable, Timeouts.getDirectToVoicemailMillis(
mContext.getContentResolver()));
}
}
这个setHandle函数如下:
//Call.java
public void setHandle(Uri handle, int presentation) {
startCallerInfoLookup();
}
private void startCallerInfoLookup() {
final String number = mHandle == null ? null : mHandle.getSchemeSpecificPart();
mQueryToken++; // Updated so that previous queries can no longer set the information.
mCallerInfo = null;
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(number)) {
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mCallerInfoAsyncQueryFactory.startQuery(mQueryToken,
mContext,number,mCallerInfoQueryListener,Call.this);
}});
}
}
注意后面post的那个Runnable。这个就是启动查询号码的逻辑了。这个mCallerInfoAsyncQueryFactory的赋值的流程比较曲折。在TelecomService被连接上调用onBind的时候,会调用initializeTelecomSystem函数。那这个TelecomService是在哪里被启动的呢?在TelecomLoaderService.java里面定义了:
private static final ComponentName SERVICE_COMPONENT = new ComponentName(
"com.android.server.telecom",
"com.android.server.telecom.components.TelecomService");
private void connectToTelecom() {
synchronized (mLock) {
TelecomServiceConnection serviceConnection = new TelecomServiceConnection();
Intent intent = new Intent(SERVICE_ACTION);
intent.setComponent(SERVICE_COMPONENT);
// Bind to Telecom and register the service
if (mContext.bindServiceAsUser(intent, serviceConnection, flags, UserHandle.OWNER)) {
mServiceConnection = serviceConnection;
} }}
public void onBootPhase(int phase) {//这个在系统启动阶段就会触发
if (phase == PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY) {
connectToTelecom();
}}
所以从这里看,在系统启动阶段就会触发TelecomService这个service,且在成功连接到服务之后,将调用ServiceManager.addService(Context.TELECOM_SERVICE, service),将这个服务添加到系统服务中了。这个类的构造函数中,在调用函数initializeTelecomSystem初始化TelecomSystem时,就实例化了一个内部匿名对象,并且在TelecomSystem的构造函数中初始化一个mCallsManager时将该匿名对象传入,而在CallsManager的processIncomingCallIntent中会用这个函数初始化一个Call对象。所以这个mCallerInfoAsyncQueryFactory的实际内容见TelecomService中的initializeTelecomSystem:
//TelecomService.java
TelecomSystem.setInstance(
new TelecomSystem(
context,
new MissedCallNotifierImpl(context.getApplicationContext()),
new CallerInfoAsyncQueryFactory() {
@Override
public CallerInfoAsyncQuery startQuery(int token, Context context,
String number,CallerInfoAsyncQuery.OnQueryCompleteListener listener,
Object cookie) {
return CallerInfoAsyncQuery.startQuery(token, context, number, listener, cookie);
}},
new HeadsetMediaButtonFactory() {},
new ProximitySensorManagerFactory() {},
new InCallWakeLockControllerFactory() {},
new ViceNotifier() {}));
可以看到,通过startQuery来查询传入的number的动作。我们来看看CallerInfoAsyncQuery的startQuery函数。
//frameworks/base/telephony/java/com/android/internal/CallerInfoAsyncQuery.java
/**
* Factory method to start the query based on a number.
*
* Note: if the number contains an "@" character we treat it
* as a SIP address, and look it up directly in the Data table
* rather than using the PhoneLookup table.
* TODO: But eventually we should expose two separate methods, one for
* numbers and one for SIP addresses, and then have
* PhoneUtils.startGetCallerInfo() decide which one to call based on
* the phone type of the incoming connection.
*/
public static CallerInfoAsyncQuery startQuery(int token, Context context, String number,
OnQueryCompleteListener listener, Object cookie) {
int subId = SubscriptionManager.getDefaultSubId();
return startQuery(token, context, number, listener, cookie, subId);
}
/**
* Factory method to start the query with a Uri query spec.
*/
public static CallerInfoAsyncQuery startQuery(int token, Context context, Uri contactRef,
OnQueryCompleteListener listener, Object cookie) {
c.mHandler.startQuery(token,
cw, // cookie
contactRef, // uri,注意这里的查询地址
null, // projection
null, // selection
null, // selectionArgs
null); // orderBy
return c;
}
注意看注释,该函数还会对SIP号码(包含@的号码)进行处理,还有紧急号码和语音邮箱号码进行区分。实际上,当对一个号码进行查询的时候,这三个startQuery都用到了。注意,上面的startQuery会根据结果对connection的值进行修改。
其中将号码转换成uri格式的数据,后续会对这个数据进行查询:
//frameworks/base/***/CallerInfoAsyncQuery.java
public static CallerInfoAsyncQuery startQuery(int token, Context context, String number, OnQueryCompleteListener listener, Object cookie, int subId) {
// Construct the URI object and query params, and start the query.
final Uri contactRef = PhoneLookup.ENTERPRISE_CONTENT_FILTER_URI.buildUpon().appendPath(number)
.appendQueryParameter(PhoneLookup.QUERY_PARAMETER_SIP_ADDRESS, String.valueOf(PhoneNumberUtils.isUriNumber(number)))
.build();
CallerInfoAsyncQuery c = new CallerInfoAsyncQuery();
c.allocate(context, contactRef);
//create cookieWrapper, start query
CookieWrapper cw = new CookieWrapper();
cw.listener = listener; cw.cookie = cookie;
cw.number = number; cw.subId = subId;
// check to see if these are recognized numbers, and use shortcuts if we can.
if (PhoneNumberUtils.isLocalEmergencyNumber(context, number)) {
cw.event = EVENT_EMERGENCY_NUMBER;
} else if (PhoneNumberUtils.isVoiceMailNumber(subId, number)) {
cw.event = EVENT_VOICEMAIL_NUMBER;
} else {
cw.event = EVENT_NEW_QUERY;
}
c.mHandler.startQuery(token,
cw, // cookie
contactRef, // uri
null, // projection
null, // selection
null, // selectionArgs
null); // orderBy
return c;
}
这个函数里面的contactRef的值应该是“content://com.android.contacts/phone_lookup_enterprise/13678909678/sip?”类似的。
实际上这个query是调用CallerInfoAsyncQueryHandler的startQuery函数,而这个函数是直接调用它的父类AsyncQueryHandler的同名函数。
//AsyncQueryHandler.java
public void startQuery(int token, Object cookie, Uri uri,
String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs,
String orderBy) {
// Use the token as what so cancelOperations works properly
Message msg = mWorkerThreadHandler.obtainMessage(token);
msg.arg1 = EVENT_ARG_QUERY;
WorkerArgs args = new WorkerArgs();
args.handler = this;
args.uri = uri;
msg.obj = args;
mWorkerThreadHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
这个mWorkerThreadHandler是在CallerInfoAsyncQueryHandler函数覆写父类的createHandler函数中赋值,是CallerInfoWorkerHandler类型。所以后续的处理函数是该类的handleMessage函数。
//AsyncQueryHandler.java
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
WorkerArgs args = (WorkerArgs) msg.obj;
CookieWrapper cw = (CookieWrapper) args.cookie;
if (cw == null) {
// Normally, this should never be the case for calls originating
// from within this code.
// However, if there is any code that this Handler calls (such as in
// super.handleMessage) that DOES place unexpected messages on the
// queue, then we need pass these messages on.
} else {
switch (cw.event) {
case EVENT_NEW_QUERY://它的值跟AsyncQueryHandler的EVENT_ARG_QUERY一样,都是1
//start the sql command.
super.handleMessage(msg);
break;
case EVENT_END_OF_QUEUE:
// query was already completed, so just send the reply.
// passing the original token value back to the caller
// on top of the event values in arg1.
Message reply = args.handler.obtainMessage(msg.what);
reply.obj = args;
reply.arg1 = msg.arg1;
reply.sendToTarget();
break;
default:
}}}}
这个super就是AsyncQueryHandler的内部类WorkerHandler了。
//AsyncQueryHandler.java
protected class WorkerHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
final ContentResolver resolver = mResolver.get();
WorkerArgs args = (WorkerArgs) msg.obj;
int token = msg.what;
int event = msg.arg1;
switch (event) {
case EVENT_ARG_QUERY:
Cursor cursor;
try {
cursor = resolver.query(args.uri, args.projection,
args.selection, args.selectionArgs,
args.orderBy);
// Calling getCount() causes the cursor window to be filled,
// which will make the first access on the main thread a lot faster.
if (cursor != null) {
cursor.getCount();
}}
args.result = cursor;
break;
}
// passing the original token value back to the caller
// on top of the event values in arg1.
Message reply = args.handler.obtainMessage(token);
reply.obj = args;
reply.arg1 = msg.arg1;
reply.sendToTarget();
}}
可以看到流程就是简单的用resolver.query来查询指定的query URI,然后将返回值通过消息机制发送到AsyncQueryHandler的handleMessage里面处理,而在这里会调用CallerInfoAsyncQuery的onQueryComplete函数。注意这个ContentResolver是在uri上查询结果,而这个uri是由某个ContentProvider来提供的。注意这个地址里面的authorities里面的值为”com.android.contacts”,同样看看ContactsProvider的androidmanifest.xml文件:
<provider android:name="ContactsProvider2"
android:authorities="contacts;com.android.contacts"
android:readPermission="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS"
android:writePermission="android.permission.WRITE_CONTACTS">
<path-permission android:pathPrefix="/search_suggest_query"
android:readPermission="android.permission.GLOBAL_SEARCH" />
<path-permission android:pathPattern="/contacts/.*/photo" android:readPermission="android.permission.GLOBAL_SEARCH" />
<grant-uri-permission android:pathPattern=".*" />
</provider>
所以最后这个查询是由ContactsProvider来执行的。
我们来看看查询完成之后,调用CallerInfoAsyncQuery的onQueryComplete函数的具体流程:
protected void onQueryComplete(int token, Object cookie, Cursor cursor) {
// check the token and if needed, create the callerinfo object.
if (mCallerInfo == null) {
if (cw.event == EVENT_EMERGENCY_NUMBER) {
} else if (cw.event == EVENT_VOICEMAIL_NUMBER) {
} else {
mCallerInfo = CallerInfo.getCallerInfo(mContext, mQueryUri, cursor);
}
}
}
//notify the listener that the query is complete.
if (cw.listener != null) {
cw.listener.onQueryComplete(token, cw.cookie, mCallerInfo);
}
}
}
注意,上面代码里面的CallerInfo.getCallerInfo非常重要。在这里面会使用查询处理的cursor结果,并将合适的结果填充到mCallerInfo,将其传递到cw.listener.onQueryComplete函数中,作为最终结果进行进一步处理。
//CallerInfo.java
public static CallerInfo getCallerInfo(Context context, Uri contactRef, Cursor cursor) {
CallerInfo info = new CallerInfo();
if (cursor != null) {
if (cursor.moveToFirst()) {
columnIndex = cursor.getColumnIndex(PhoneLookup.LOOKUP_KEY);
if (columnIndex != -1) {
info.lookupKey = cursor.getString(columnIndex);
}
info.contactExists = true;
}
cursor.close();
cursor = null;
}
info.needUpdate = false;
info.name = normalize(info.name);
info.contactRefUri = contactRef;
return info;
}
系统原生的逻辑是取搜索结果的第一个记录,并用来实例化。当客户需求改变,需要匹配不同号码的时候,就需要修改这个地方的了。最优先是遍历整个cursor集合,并且根据客户需求选出适合的结果,赋值给CallerInfo实例。
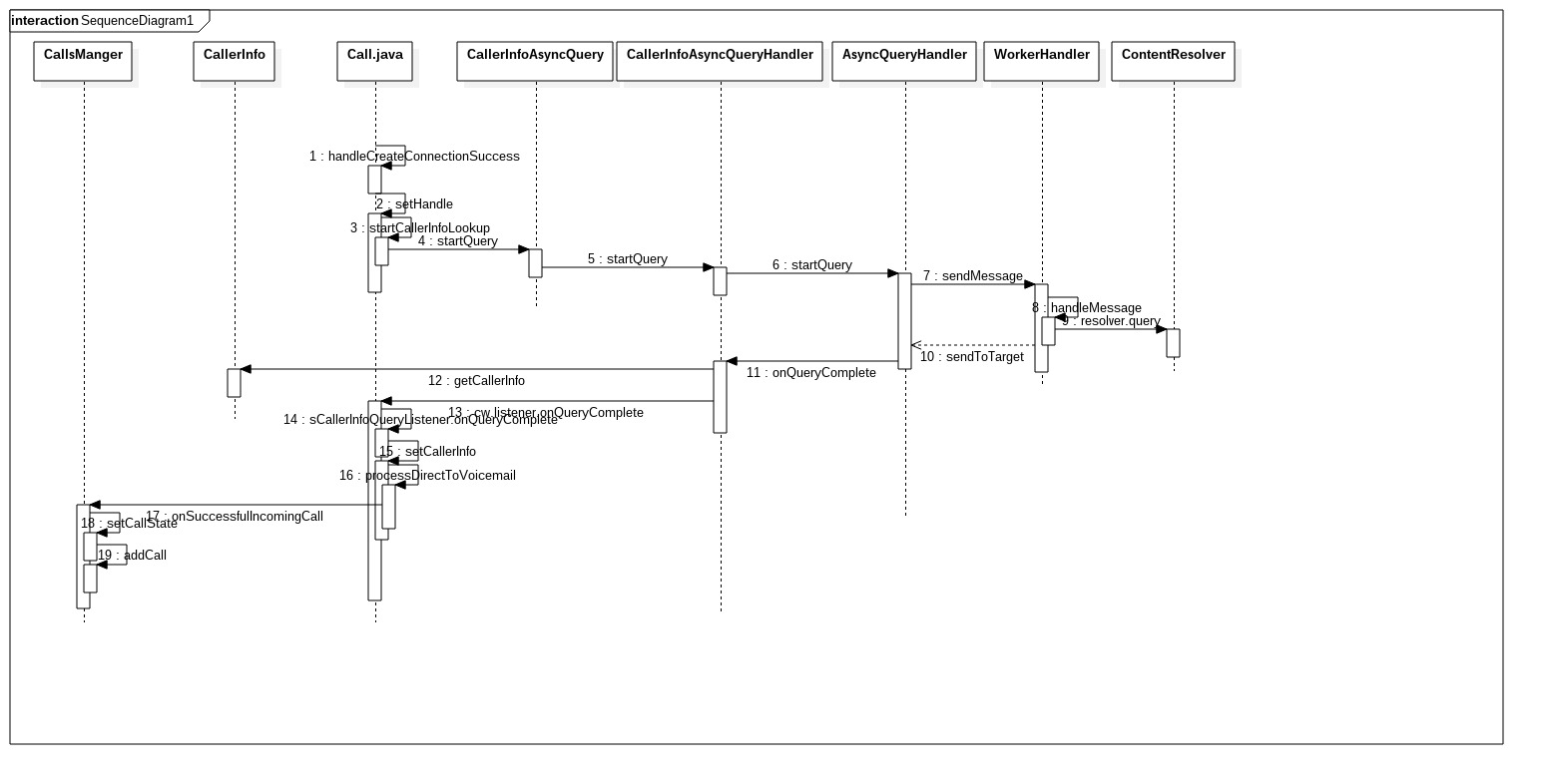
下面是整个号码匹配的流程图:
Call.java会将查询后的结果设置到Call实例里面,并将其传送到CallsManager里面进行后续处理。而这个CallsManager会将这个Call显示给客户。
当网络端来电时,frame层会接收到,并且连接成功之后会触发Call.java里面的handleCreateConnectionSuccess。这个函数逻辑是从数据库中查询复合要求的联系人,并且只取结果集的第一条记录,用来初始化这个Call里面的变量。而后将这个Call传到CallsManager进行处理,显示给用户。