Spring 的配置
一、Spring的发展
Spring1.x
全部通过xml文件配置bean,随着项目的不断扩大,需要将xml配置分放到不同的配置文件中,需要频繁的在java类和xml配置文件中切换。
Spring2.x
随着JDK 1.5带来的注解支持,Spring2.x可以使用注解对Bean进行声名和注入,大大的减少了xml配置文件,同时也大大简化了项目的开发。
最佳实践:
1、 应用的基本配置用xml,比如:数据源、资源文件等;
2、 业务开发用注解,比如:Service中注入bean等;
Spring3.x
从Spring3.x开始提供了Java配置方式,使用Java配置方式可以更好的理解你配置的Bean。
Spring4.x +
Spring4.x和Spring boot都推荐使用java配置的方式,可以完全替代xml配置。
二、Spring的Java配置方式
@Configuration 和 @Bean
Spring的Java配置方式是通过 @Configuration 和 @Bean 这两个注解实现的:
1、@Configuration 作用于类上,相当于一个xml配置文件;
2、@Bean 作用于方法上,相当于xml配置中的;
示例
该示例演示了通过Java配置的方式进行配置Spring,并且实现了Spring IOC功能。
1. 创建Maven工程以及导入依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>cn.itcast.springboot</groupId>
<artifactId>itcast-springboot</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jolbox</groupId>
<artifactId>bonecp-spring</artifactId>
<version>0.8.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName>
<plugins>
<!-- 资源文件拷贝插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<!-- java编译插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.7</source>
<target>1.7</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<!-- 配置Tomcat插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
2.编写User对象
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
3.编写UserDAO,模拟操作数据库
public class UserDAO {
public List<User> queryUserList(){
List<User> result = new ArrayList<User>();
// 模拟数据库的查询
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("username_" + i);
user.setPassword("password_" + i);
user.setAge(i + 1);
result.add(user);
}
return result;
}
}
4.编写UserService
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired // 注入Spring容器中的bean对象
private UserDAO userDAO;
public List<User> queryUserList() {
// 调用userDAO中的方法进行查询
return this.userDAO.queryUserList();
}
}
5.编写SpringConfig 用于实例化Spring容器
@Configuration //通过该注解来表明该类是一个Spring的配置,相当于一个xml文件
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "cn.itcast.springboot.javaconfig") //配置扫描包
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean // 通过该注解来表明是一个Bean对象,相当于xml中的<bean>
public UserDAO getUserDAO(){
return new UserDAO(); // 直接new对象做演示
}
}
6.编写测试方法 用于启动Spring容器
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过Java配置来实例化Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
// 在Spring容器中获取Bean对象
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
// 调用对象中的方法
List<User> list = userService.queryUserList();
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println(user.getUsername() + ", " + user.getPassword() + ", " + user.getPassword());
}
// 销毁该容器
context.destroy();
}
}
7.测试效果

8.小结
从以上的示例中可以看出,使用Java代码就完美的替代xml配置文件,并且结构更加的清晰。
实战
读取外部的资源配置文件
通过@PropertySource可以指定读取的配置文件,通过@Value注解获取值,具体用法:
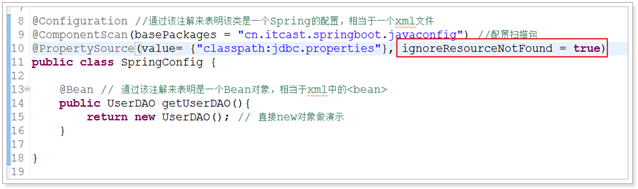
@Configuration //通过该注解来表明该类是一个Spring的配置,相当于一个xml文件
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "cn.itcast.springboot.javaconfig") //配置扫描包
@PropertySource(value= {"classpath:jdbc.properties"})
public class SpringConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String jdbcUrl;
@Bean // 通过该注解来表明是一个Bean对象,相当于xml中的<bean>
public UserDAO getUserDAO(){
return new UserDAO(); // 直接new对象做演示
}
}
思考:
1、 如何配置多个配置文件?
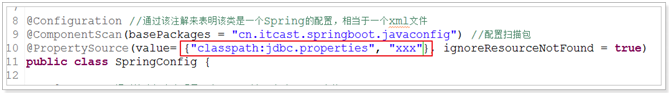
2、 如果配置的配置文件不存在会怎么样?
配置数据库连接池
导入依赖:
<!-- 连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jolbox</groupId>
<artifactId>bonecp-spring</artifactId>
<version>0.8.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
之前的Spring xml配置:
<!-- 定义数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.jolbox.bonecp.BoneCPDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<!-- 数据库驱动 -->
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<!-- 相应驱动的jdbcUrl -->
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<!-- 数据库的用户名 -->
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<!-- 数据库的密码 -->
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<!-- 检查数据库连接池中空闲连接的间隔时间,单位是分,默认值:240,如果要取消则设置为0 -->
<property name="idleConnectionTestPeriod" value="60" />
<!-- 连接池中未使用的链接最大存活时间,单位是分,默认值:60,如果要永远存活设置为0 -->
<property name="idleMaxAge" value="30" />
<!-- 每个分区最大的连接数 -->
<!--
判断依据:请求并发数
-->
<property name="maxConnectionsPerPartition" value="100" />
<!-- 每个分区最小的连接数 -->
<property name="minConnectionsPerPartition" value="5" />
</bean>
参考xml配置改造成java配置方式:
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String jdbcUrl;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
private String jdbcDriverClassName;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String jdbcUsername;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String jdbcPassword;
@Bean(destroyMethod = "close")
public DataSource dataSource() {
BoneCPDataSource boneCPDataSource = new BoneCPDataSource();
// 数据库驱动
boneCPDataSource.setDriverClass(jdbcDriverClassName);
// 相应驱动的jdbcUrl
boneCPDataSource.setJdbcUrl(jdbcUrl);
// 数据库的用户名
boneCPDataSource.setUsername(jdbcUsername);
// 数据库的密码
boneCPDataSource.setPassword(jdbcUsername);
// 检查数据库连接池中空闲连接的间隔时间,单位是分,默认值:240,如果要取消则设置为0
boneCPDataSource.setIdleConnectionTestPeriodInMinutes(60);
// 连接池中未使用的链接最大存活时间,单位是分,默认值:60,如果要永远存活设置为0
boneCPDataSource.setIdleMaxAgeInMinutes(30);
// 每个分区最大的连接数
boneCPDataSource.setMaxConnectionsPerPartition(100);
// 每个分区最小的连接数
boneCPDataSource.setMinConnectionsPerPartition(5);
return boneCPDataSource;
}
思考: 如何使用该DataSource对象?