# datetime模块
import datetime now_time = datetime.datetime.now() print(now_time) # 只能调整的字段:weeks days hours minutes seconds # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(weeks=3)) # 三周后 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(weeks=-3)) # 三周前 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=-3)) # 三天前 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=3)) # 三天后 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=5)) # 5小时后 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=-5)) # 5小时前 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(minutes=-15)) # 15分钟前 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(minutes=15)) # 15分钟后 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(seconds=-70)) # 70秒前 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(seconds=70)) # 70秒后 current_time = datetime.datetime.now() # 现在时间 # 可直接调整到指定的 年 月 日 时 分 秒 等 print(current_time.replace(year=1977)) # 直接调整到1977年 print(current_time.replace(month=1)) # 直接调整到1月份 print(current_time.replace(year=1989,month=4,day=25)) # 1989-04-25 18:49:05.898601 # 将时间戳转化成时间 print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(1232132131)) # 2009-01-17
# shutil模块
import shutil shutil.copyfileobj(open('shutil1', encoding='utf-8'), open('shutil2',encoding='utf-8', mode='w')) #以写的模式复制到空的shutil2文件 shutil.copyfile('a1.log','abc.txt') # 复制一个a1.log变成abc.txt,相当于复制粘贴 copy文件 -->复制重命名一个文件 import shutil import time ret = shutil.make_archive("blog_bak%s" %(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')), 'gztar', root_dir='blog') # 打包blog文件夹变成blog_bak+日期.tar.gz import tarfile t= tarfile.open(r'D:\24期周末班\day08\blog_bak.tar.gz','r') #解包 t.extractall('blog2') #解包到当前目录下变成blog2 t.close()
# xml(了解)

<?xml version="1.0"?> <data> <country name="Liechtenstein"> <rank updated="yes">2</rank> <year>2008</year> <gdppc>141100</gdppc> <neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/> <neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/> </country> <country name="Singapore"> <rank updated="yes">5</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>59900</gdppc> <neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/> </country> <country name="Panama"> <rank updated="yes">69</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>13600</gdppc> <neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/> <neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/> </country> </data>
# import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# tree = ET.parse('二狗.xml')
# root = tree.getroot()
# print(root) # <Element 'data' at 0x000000000274D548>
# print([tag for tag in root])
# 查
# print(root.iter('year')) # 查询所有的year标签。
# for i in root.iter('year'):
# print(i)
#
# print(root.find('country')) # 找到第一个就返回
# print(root.findall('country')) # 找到子标签所有的country
# 找寻标签属性以及内容
#
# year_list = [year for year in root.iter('year')]
# print(year_list[0].attrib) #{name:'脸哥'}
# print(year_list[0].text)
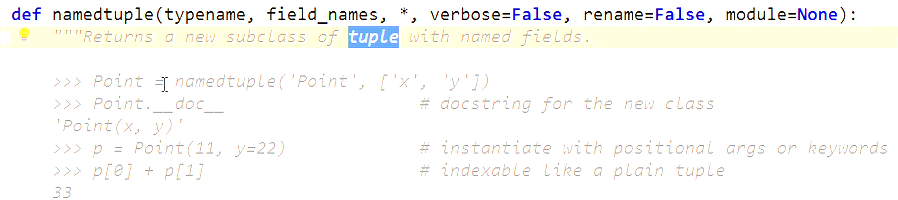
# collections 模块 #用在坐标,矢量 半径表示一个圆
from collections import namedtuple
Point = namedtuple('Point', ['x', 'y'])
p = Point(1, 2)
# print(p[0])
print(p.x)
deque
使用list存储数据时,按索引访问元素很快,但是插入和删除元素就很慢了,因为list是线性存储,数据量大的时候,插入和删除效率很低。
deque是为了高效实现插入和删除操作的双向列表,适合用于队列和栈:
>>> from collections import deque
>>> q = deque(['a', 'b', 'c'])
>>> q.append('x')
>>> q.appendleft('y')
>>> q
deque(['y', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'x'])


