四、
5.构造函数
class 类名 {
...
类名 (形参表) {
构造函数体;
}
};
当一个对象被创建时,构造函数会自动被执行,其参数来自构造实参。
int i = 10;
int i (10);
6.构造函数可以通过构造参数实现重载
7.如果一个类没有定义任何构造函数,那么系统就会缺省地为其提供一个无参构造函数,该构造函数对于基本类型的成员变量不做初始化,对于类类型的成员变量,调用其相应类型的无参构造函数初始化。
8.对象的创建过程
分配内存->调用构造函数
->调用类类型成员的构造函数->构造函数的代码
9.初始化表
class 类名 {
类名(...) : 初始化表 {
构造函数体;
}
};
const int x = 100;
x = 100;
int& a = b;
a = b;
1)如果类中含有常量或引用型的成员变量,必须通过初始化表对其初始化。
2)成员变量的初始化顺序仅于其被声明的顺序有关,而与初始化表的顺序无关。
class A {
public:
A (char* psz) : m_str (psz),
m_len (strlen (psz)) private:
size_t m_len;
string m_str;
};
练习:实现一个Clock类支持两种工作模式,计时器和电子钟。
00:01:00
14:05:37
#include <iomanip>
cout << setw (10) << setfill ('0') << 12;
0000000012
Clock
时、分、秒
走 - 显示、滴答
五、this指针
1.一般而言,在类的构造函数或成员函数中,关键字this表示一个指针,对于构造函数而言,this指向正在被构造的对象,对于成员函数而言,this指向调用该函数的对象。
2.this指针的用途
1)在类的内部区分成员变量。
2)在成员函数中返回调用对象自身。
3)在成员函数内部通过参数向外界传递调用对象自身,以实现对象间交互。
老 -问题-> 学
师 <-答案- 生
class A {
B& m_b;
};
class B {
A& m_a;
};
sizeof (A) ?
class C {
C m_c;
};
六、常函数与常对象
1.如果在一个类的成员函数的参数表后面加上const关键字,那么这个成员函数就被称为常函数,常函数的this指针是一个常指针。在常函数内部无法修改成员变量,除非该变量具有mutable属性。而且在常函数内部也无法调用非常函数。
2.常对象:拥有const属性的对象,对象引用或指针。
常对象只能调用常函数。
同型的常函数和非常函数可以构成重载关系。常对象调用常版本,非常对象调用非常版本。如果没有非常版本,非常对象也可以调用常版本。
const XXX 函数名 (const YYY yyy) const {
...
}
七、析构函数
class 类名 {
~类名 (void) {
析构函数体;
}
};
当一个对象被销毁时自动执行析构函数。
局部对象离开作用域时被销毁,堆对象被delete时被销毁。
如果一个类没有定义任何析构函数,那么系统会提供一个缺省析构函数。缺省析构函数对基本类型的成员变量什么也不干,对类类型的成员变量,调用相应类型的析构函数。
一般情况下,在析构函数中释放各种动态分配的资源。
构造:基类->成员->子类
析构:子类->成员->基类
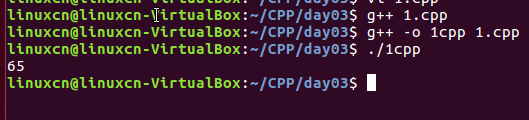
1.cpp
#include <iostream>using namespace std;void foo (const int& a) { cout << a << endl;}int main (void) { char c = 'A'; foo (static_cast<int> (c)); return 0;}
静态类型转换:
static_cast <目标类型>(源类型变量)
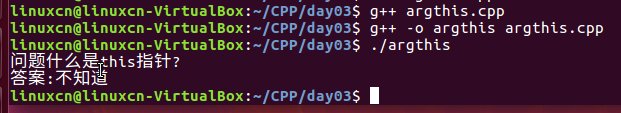
argthis.cpp
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Student;class Teacher {public: void educate (Student* s); void reply (const string& answer) { m_answer = answer; }private: string m_answer;};class Student {public: void ask (const string& question, Teacher* t) { cout << "问题:" << question << endl; t->reply ("不知道。"); }};void Teacher::educate (Student* s) { s->ask ("什么是this指针?", this); cout << "答案:" << m_answer << endl;}int main (void) { Teacher t; Student s; t.educate (&s); return 0;}
void Teacher::educate (Student* s) {
s->ask ("什么是this指针?", this);
cout << "答案:" << m_answer << endl;
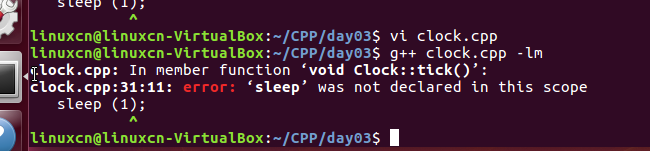
clock.cpp
#include <iostream>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;class Clock {public: Clock (bool timer = true) : m_hour (0), m_min (0), m_sec (0) { if (! timer) { time_t t = time (NULL); tm* local = localtime (&t); m_hour = local->tm_hour; m_min = local->tm_min; m_sec = local->tm_sec; } } void run (void) { for (;;) { show (); tick (); } }private: void show (void) { cout << '\r' << setfill ('0') << setw (2) << m_hour << ':' << setw (2) << m_min << ':' << setw (2) << m_sec << flush;// printf ("\r%02d:%02d:%02d", m_hour,// m_min, m_sec); } void tick (void) { sleep (1); if (++m_sec == 60) { m_sec = 0; if (++m_min == 60) { m_min = 0; if (++m_hour == 24) m_hour = 0; } } } int m_hour; int m_min; int m};int main (void) { Clock clock (false); clock.run (); return 0;}
<< setw (2) << m_hour << ':'<< setw (2) << m_min << ':'<< setw (2) << m_sec << flush;
setw 设置预宽;
m_hour 指定填充字符;
cout << ......<< endl; ‘\n’
cout << ......<< flush; "把缓冲区里的东西冲刷到屏幕上"
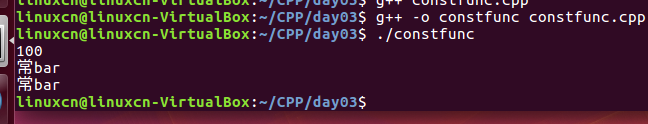
constfunc.cpp
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class A {public:// void bar (void) {// cout << "非常bar" << endl;// } void bar (void) const { cout << "常bar" << endl; }// void XXXbarYYY (A* this) {} void foo (void) const {// m_i = 100; const_cast<A*>(this)->m_i = 100; } void print (void) const { cout << m_i << endl; }// _ZNK1A3fooEv (const A* this) {// const_cast<A*>(this)->m_i = 100;// } int m_i;};void func (void) /*const*/ {}int main (void) { A a; a.foo (); a.print (); const A& r = a; r.bar ();// XXXbarYYY (&r); // const A* a.bar ();// XXXbarYYY (&a); // A* return 0;}
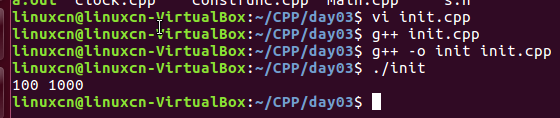
init.cpp
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int g_data = 1000;class A {public: A (void) : m_c (100), m_r (g_data) {// m_c = 100;/// m_r = g_data; } void print (void) { cout <initc << ' ' << m_r << endl; }private: const int m_c; int& m_r;};int main (void) { A a; a.print (); return 0;}
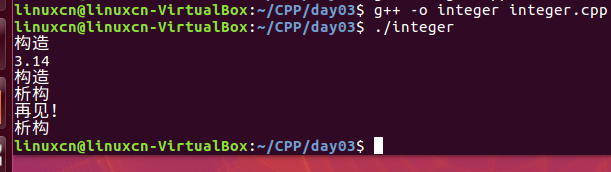
integer.cpp
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Double {public: Double (double data) : m_data (new double (data)) { cout << "构造" << endl; } ~Double (void) { cout << "析构" << endl; delete m_data; } void print (void) const { cout << *m_data << endl; }private: double* m_data; string m_lable;};int main (void) {// { Double d1 (3.14); d1.print ();// } Double* d2 = new Double (1.23); delete d2; cout << "再见!" << endl; return 0;}
main.cpp
#include "s.h"// 使用Student类int main (void) { Student s ("张飞", 25); s.eat ("包子"); return 0;}
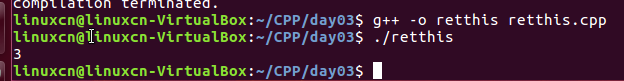
retthis.cpp
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Counter {public: Counter (void) : m_data (0) {} Counter& inc (void) { ++m_data; return *this; } void print (void) { cout << m_data << endl; }private: int m_data;};int main (void) { Counter c;// c.inc ();// c.inc ();// c.inc (); c.inc ().inc ().inc (); c.print (); // 3 return 0;}
s.h
#ifndef _S_H#define _S_H#include <string>using namespace std;// 声明Student类class Student {public: Student (const string& name = "", int age = 0); void eat (const string& food);private: string m_name; int m_age;};#endif // _S_H
s.cpp
#include <iostream>using namespace std;#include "s.h"// 实现Student类Student::Student (const string& name /* = "" */, int age /* = 0 */) : m_name (name), m_age (age) {}void Student::eat (const string& food) { cout << m_name << "," << m_age << "," << food << endl;}
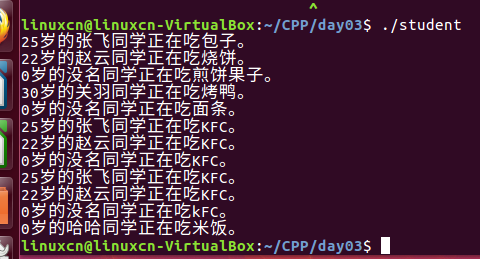
student.cpp
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class A {public: A (int a) {}g++ g};class Student {private: string m_name; int m_age; A m_a;public: void eat (const string& food) { cout << m_age << "岁的" << m_name << "同学正在吃" << food << "。" << endl; }// void _ZN7Student3eatERKSs (Student* this,// const string& food) int{// cout << this->m_age << "岁的"<<this->m_name// << "同学正在吃" << food << "。" << endl;// } void setName (const string& name) { if (name == "2") cout << "你才" << name << "!" << endl; else m_name = name; } void setAge (int age) { if (age < 0) cout << "无效的年龄!" << endl; else m_age = age; } // 构造函数 Student (const string& name, int age) : m_a (100) { m_name = name; m_age = age; } // 无参构造 Student (void) : m_a (100) { m_name = "没名"; m_age = 0; } // 单参构造 Student (const string& name) : m_a (100), m_name (name), m_age (0) { m_name = "哈哈"; }};int main (void) { Student s1 ("张飞", 25); s1.eat ("包子");// _ZN7Student3eatERKSs (&s1, "包子"); Student s2 = Student ("赵云", 22); s2.eat ("烧饼");// _ZN7Student3eatERKSs (&s2, "烧饼"); Student s3; s3.eat ("煎饼果子"); Student* s4 = new Student ("关羽", 30); s4->eat ("烤鸭"); delete s4; Student& s5 = *new Student (); s5.eat ("面条"); delete &s5; Student sa1[3] = {s1, s2}; sa1[0].eat ("KFC"); sa1[1].eat ("KFC"); sa1[2].eat ("KFC"); Student* sa2 = new Student[3] {s1, s2}; // 2011 sa2[0].eat ("KFC"); sa2[1].eat ("KFC"); sa2[2].eat ("KFC"); delete[] sa2; Student s6 ("刘备"); s6.eat ("米饭"); return 0;}
this.cpp
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class A {public: A (int data) : data (data) { cout << "构造: " << this << endl;:set cursorline
// this->data = data; } void foo (void) { cout << "foo: " << this << endl; cout << this->data << endl; } int data;};int main (void) { A a (1000); cout << "main: " << &a << endl; a.foo (); A* pa = new A (1000); cout << "main: " << pa << endl; pa->foo (); delete pa;}
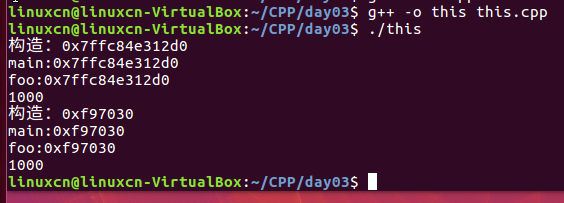
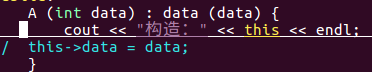
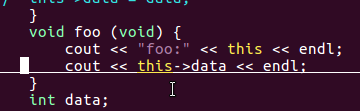
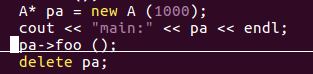
this指针:
一般而言,在类的构造函数或成员函数中,关键字this表示一个指针,
对于构造函数而言,this 指向正在被构造的对象,对于成员函数而言,
this指向调用该函数的对象。