转自 http://xw-z1985.iteye.com/blog/1972779
当selector检测到OP_READ事件时,触发read操作:
//NioEventLoop
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
if (!ch.isOpen()) {
// Connection already closed - no need to handle write.
return;
}
}
Read方法由NioByteUnsafe实现:
public void read() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
final SelectionKey key = selectionKey();
final ChannelConfig config = config();
if (!config.isAutoRead()) {
int interestOps = key.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) != 0) {
// only remove readInterestOp if needed
key.interestOps(interestOps & ~readInterestOp);
}
}
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = this.allocHandle;
if (allocHandle == null) {
this.allocHandle = allocHandle = config.getRecvByteBufAllocator().newHandle();
}
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
final int maxMessagesPerRead = config.getMaxMessagesPerRead();
boolean closed = false;
Throwable exception = null;
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
int messages = 0;
try {
for (;;) {
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
int localReadAmount = doReadBytes(byteBuf);
if (localReadAmount == 0) {
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
break;
}
if (localReadAmount < 0) {
closed = true;
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
break;
}
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
allocHandle.record(localReadAmount);
byteBuf = null;
if (++ messages == maxMessagesPerRead) {
break;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
} finally {
if (byteBuf != null) {
if (byteBuf.isReadable()) {
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
} else {
byteBuf.release();
}
}
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof IOException) {
closed = true;
}
pipeline().fireExceptionCaught(exception);
}
if (closed) {
setInputShutdown();
if (isOpen()) {
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config().getOption(ChannelOption.ALLOW_HALF_CLOSURE))) {
key.interestOps(key.interestOps() & ~readInterestOp);
pipeline.fireUserEventTriggered(ChannelInputShutdownEvent.INSTANCE);
} else {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
}
}
}
}
一、首先分析this.allocHandle = allocHandle = config.getRecvByteBufAllocator().newHandle()
config.getRecvByteBufAllocator()返回RecvByteBufAllocator,可以取名为接受缓存分配器。该分配器用于为channel分配receive buffers以存储随后读取的字节。默认返回的分配器类型是自适应缓存分配器AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator,它能根据前一次实际读取的字节数量,自适应调整当前缓存分配的大小,以防止缓存分配过多或过少。其结构如下:
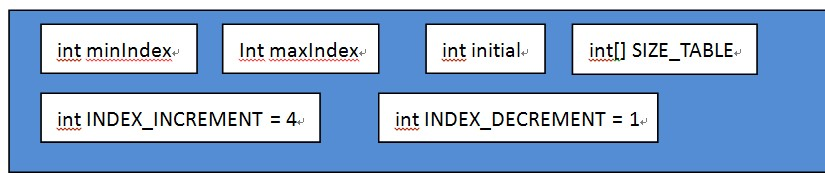
其中:
- SIZE_TABLE:为固定的静态数组,按照从小到大的顺序预先存储可以分配的缓存大小。最小的为16,然后每次累加16,直到496。然后从512开始,每次向走位移1(即放大两倍),直到int发生溢出。本机的最大值为1073741824,所以数组的size为52。
- MinIndex和maxIndex为最小缓存(64)和最大缓存(65536)在SIZE_TABLE中对应的下标。分别为3和38
- 第一次分配缓存时,由于没有上一次的实际接收到的字节数做参考,因此需要给出初始值,由Initial指定,默认值为1024
- INDEX_INCREMENT:上次预估缓存偏小时,下次Index的递增值。默认为4
- INDEX_DECREMENT:上次预估缓存偏大时,下次Index的递减值。默认为1
缓存的分配以及大小的自适应调整实际上都是由自适应缓存分配器里面的一个内部类HandleImpl代劳的,由缓存分配器的newHandle()方法返回。以下是HandleImpl的实现:
//AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator
private static final class HandleImpl implements Handle {
private final int minIndex;
private final int maxIndex;
private int index;
private int nextReceiveBufferSize;
private boolean decreaseNow;
HandleImpl(int minIndex, int maxIndex, int initial) {
this.minIndex = minIndex;
this.maxIndex = maxIndex;
index = getSizeTableIndex(initial);
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
}
@Override
public ByteBuf allocate(ByteBufAllocator alloc) {
return alloc.ioBuffer(nextReceiveBufferSize);
}
@Override
public int guess() {
return nextReceiveBufferSize;
}
@Override
public void record(int actualReadBytes) {
if (actualReadBytes <= SIZE_TABLE[Math.max(0, index - INDEX_DECREMENT - 1)]) {
if (decreaseNow) {
index = Math.max(index - INDEX_DECREMENT, minIndex);
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
decreaseNow = false;
} else {
decreaseNow = true;
}
} else if (actualReadBytes >= nextReceiveBufferSize) {
index = Math.min(index + INDEX_INCREMENT, maxIndex);
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
decreaseNow = false;
}
}
}
private static int getSizeTableIndex(final int size) {
for (int low = 0, high = SIZE_TABLE.length - 1;;) {
if (high < low) {
return low;
}
if (high == low) {
return high;
}
int mid = low + high >>> 1;
int a = SIZE_TABLE[mid];
int b = SIZE_TABLE[mid + 1];
if (size > b) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (size < a) {
high = mid - 1;
} else if (size == a) {
return mid;
} else {
return mid + 1;
}
}
}
- nextReceiveBufferSize记录下次分配缓存时应该分配的大小,即index下标在数组SIZE_TABLE中的值。
- ByteBuf allocate(ByteBufAllocator alloc)方法则根据上次预估的字节大小nextReceiveBufferSize分配缓存。
- Index记录nextReceiveBufferSize在数组SIZE_TABLE中的索引值:
a)如果是第一次分配,则该值由getSizeTableIndex方法根据initial的值(默认为1024)计算而来。 getSizeTableIndex采用二分查找算法计算SIZE_TABLE数组中值最接近initial的下标。
b)如果非第一次分配,则由record 方法根据上一次实际读取到的字节数actualReadBytes自适应的调整nextReceiveBufferSize的大小:
b.1 如果actualReadBytes连续两次都小于SIZE_TABLE[Math.max(0, index - INDEX_DECREMENT - 1)](为啥在INDEX_DECREMENT的基础上再减1?),即连续两次预估的缓存大小都偏大导致浪费了,则更新index为Math.max(index - INDEX_DECREMENT, minIndex)
b.2 如果actualReadBytes大于nextReceiveBufferSize,即上次预估的缓存大小偏小,则更新index为Math.min(index + INDEX_INCREMENT, maxIndex)
b.3 否则,保持index不变。
二、接下来分析for循环中的逻辑首 - 先调用自适应接受缓存分配器中的handleImpl的allocate方法,分配大小为nextReceiveBufferSize的缓存
- 然后通过read系统调用,将数据从channel中读取到上一步分配的接受缓存中。
a)如果返回0,则表示没有读取到数据,则退出循环
b)如果返回-1,表示对端已经关闭连接,则退出循环
c)否则,表示读到了数据,则触发ChannelRead事件(inbound处理器可以通过实现channelRead方法对本次读取到的消息进行处理)。接着调用handleImpl的record方法,根据本次读取的字节数,自适应调整下次待分配的缓存大小。然后退出循环 - 最后触发ChannelReadComplete事件(inbound处理器可以通过实现channelReadComplete方法对该事件进行响应)。
- 关于close、shutdown以及半关闭等,留待以后搞清楚后再进行分析。
总结可以借鉴的点:缓存分配大小的自适应调整策略