// for循环
#include "iostream"
const int arSize = 16;
int main() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
long long factorials[arSize];
factorials[0] = factorials[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < arSize; i++)
factorials[i] = i * factorials[i - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arSize; i++)
cout << "factorials[" << i << "] = " << factorials[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果

// for循环
// for循环
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
const int arSize = 16;
int main() {
string str;
cout << "enter a string : " << endl;
cin >> str;
for (int i = str.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
cout << str[i];
cout << "\n end " << endl;
int guests = 0;
while (guests++ < 10)
cout << guests << endl;
return 0;
}
由于guest++ < 10, 是先拿guest和10比较后, 再对guest+1, 然后才运行输出语句, 所以运行结果如上
基于范围的for循环
注意其中一个能改变prices数组里的值, 另一个却不能
double prices[5] = {1.11, 1.22, 1.33, 1.44, 1.55};
for (double x : prices)
cout << x << endl;
// 这种写法能够改变prices里的数值, 上面的写法不行
// 符号&表明x是一个引用变量
for (double &x : prices)
x = x * 0.8;再看一下下面这个输出设计到++运算符
int x = 1;
int y = (4 + x++) + (6 * x++);
cout << x << endl;
cout << y << endl;运行结果为
3

17
++运算符和指针混合一起使用:
++和指针运算
// for循环
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
const int arSize = 16;
int main() {
double arr[5] = {1.11, 1.22, 1.33, 1.44, 1.55};
// 指针pt指向了数组的首地址
double* pt = arr;
// 相当于pt向后移动了一个double的长度, 也就是指向了数组的第二个元素
++pt;
cout << *pt << endl;
double x = *++pt;
// 1.33
cout << x << endl;
// 先是取出pt指针指向的地址里的数值, 然后+1, 赋值给y
double y = ++*pt;
// 2.33
cout << y << endl;
cout << "arr[2] = " << arr[2] << endl;
cout << "before (*pt)++ , *pt = " << *pt << endl;
double z = *pt++;
cout << z << endl;
cout << *pt << endl;
return 0;
}程序运行结果为:
1.22
1.33
2.33
arr[2] = 2.33
before (*pt)++ , *pt = 2.33
2.33
1.44在看一个利用for循环做字符串反转
字符串翻转
#include "iostream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Enter a wrod : ";
string word;
cin >> word;
for (int j = 0, i = word.size() - 1; j < i; j++, i--)
{
// temp 在使用完就会回收
char temp;
temp = word[i];
word[i] = word[j];
word[j] = temp;
}
cout << word << endl;
cout << "Enter second wrod : ";
char word2[5];
cin >> word2;
// 这里之所以写-2 是因为数组最后一位应该留给\0, 如果写-1会直接打印空字符串, 因为上来就是\0导致直接结束
for (int j = 0, i = sizeof(word2) - 2; j < i; j++, i--)
{
char temp;
temp = word2[i];
word2[i] = word2[j];
word2[j] = temp;
}
cout << word2 << endl;
return 0;
}程序运行结果为:

逗号运算符花絮:
#include "iostream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
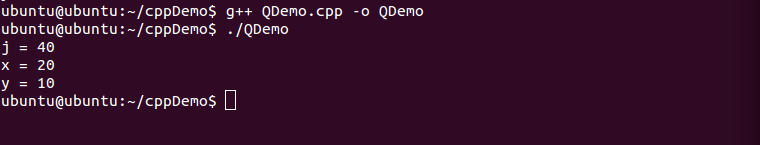
int i = 20, j = 2 * i;
cout << "j = " << j << endl;
// c++规定 逗号运算符的值是第二部分的值
int x = (10, 20);
cout << "x = " << x << endl;
int y = 1;
// 注意这种写法是不对的 int y = 10, 20;
// 逗号运算符的优先级是最低的, 因此下面这句话被解释为 (y = 10), 20; 所以20没有起作用
y = 10, 20;
cout << "y = " << y << endl;
return 0;
}程序输出结果:
程序需要注意的都写在注释中
字符串比较
先看c语言的字符串比较
// c风格字符串比较
#include "iostream"
#include "cstring"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char word[5] = "?ate";
for (char c = 'a'; strcmp(word, "mate"); c++)
{
cout << word << endl;
word[0] = c;
}
cout << "finish word is : " << word << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果为:

c++中使用c语言风格比较两个字符串是否相同要用strcmp函数, 记得需要导入cstring头文件
strcmp(s1, s2); s1, s2可是是数组名也可以是指针,
如果s1和s2相同返回0,
如果s1在s2的前面返回-1,
如果s1在s2的后面返回1
c++里0在bool类型里是false, 非0是true, 因此在上面的demo中可以使用strcmp(word, "mate");做for循环是否结束的判断
再看使用string类进行字符串比较
// string风格字符串比较
#include "iostream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string word = "?ate";
for (char c = 'a'; word != "mate"; c++)
{
cout << word << endl;
word[0] = c;
}
cout << "finish word is : " << word << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:

c++中的string类重载了运算符!=, 使得能够在至少有一个操作数是string对象, 而另一个操作数可以使string对象, 也可是是c风格字符串的时候进行比较两个字符串是否相等.
while循环
// while循环
#include "iostream"
#include "cstring"
using namespace std;
const int ArrSize = 20;
int main()
{
char name[ArrSize];
cout << "please input your name : ";
cin >> name;
cout << "Here is your name : " << endl;
int i = 0;
while (name[i] != '\0')
{
cout << name[i] << " : " << int(name[i]) << endl;
i++;
}
string name2;
cout << "please input your name2 : ";
cin >> name2;
cout << "Here is your name : " << endl;
i = 0;
while (name2[i] != '\0')
{
cout << name2[i] << " : " << int(name2[i]) << endl;
i++;
}
return 0;
}运行结果:

利用while循环做一个延迟
#include "iostream"
#include "ctime"
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Enter the delay time in secod : " << endl;
float secs;
cin >> secs;
// clock_t 是clock()返回类型的别名
// CLOCKS_PER_SEC是一个常量表示每秒钟包含的系统时间单位数
// 都包含在ctime头文件中
clock_t delay = secs * CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
cout << "starting\a\n";
clock_t start = clock();
// 利用while做了一个延迟
while (clock() - start < delay);
cout << "done\a\n";
return 0;
}
类型别名
c++为类型建立别名的方式有两种:
1.使用预处理器
#define BYTE char
这样预处理器将在编译程序时使用char代替所有的BYTE, 从而使BYTE称为char的别名.
2.第二种方法是使用c++的关键词typedef来创建别名
typedef char byte;
typedef char * byte_pointer; // 将byte_pointer声明为char指针