Problem of Precision
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1957 Accepted Submission(s): 1206
Problem Description
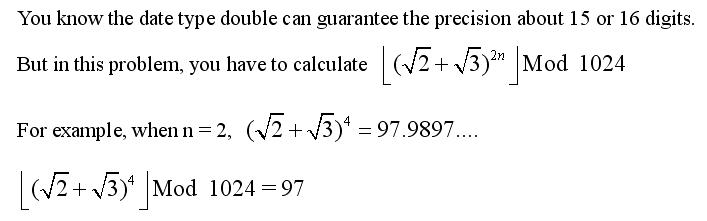
Input
The first line of input gives the number of cases, T. T test cases follow, each on a separate line. Each test case contains one positive integer n. (1 <= n <= 10^9)
Output
For each input case, you should output the answer in one line.
Sample Input
3 1 2 5
Sample Output
9 97 84
Source
HDOJ 2008 Summer Exercise(4)- Buffet Dinner
Recommend
lcy
So Easy!
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 6238 Accepted Submission(s): 2064
Problem Description
A sequence Sn is defined as:
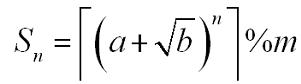
Where a, b, n, m are positive integers.┌x┐is the ceil of x. For example, ┌3.14┐=4. You are to calculate Sn.
You, a top coder, say: So easy!

Input
There are several test cases, each test case in one line contains four positive integers: a, b, n, m. Where 0< a, m < 215, (a-1)2< b < a2, 0 < b, n < 231.The input will finish with the end of file.
Output
For each the case, output an integer Sn.
Sample Input
2 3 1 2013 2 3 2 2013 2 2 1 2013
Sample Output
4 14 4
Source
Recommend
zhoujiaqi2010
题目大意:两道题目几乎一样,都是给以个带根号的式子,让你求这个式子的n次幂对一个数取模。
解题思路:
这样的式子与斐波那契的通项公式有一些相似。
对于第一题。(5+2sqrt(6))^n
考虑该式子能否化简成fn = an+bn*sqrt(6)
通项公式为 fn = an + bn*sqrt(6);
则fn-1 = an-1 + bn-1*sqrt(6);
fn=5+sqrt(6)*fn-1
得到
an = 5*an-1+12*bn-1
bn=5*an-1+2*bn-1
所以通过矩阵快速幂可以求得an,
然后再利用5-2*sqrt(6)的通项公式消掉bn即可
HDU2256
-
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define rep(i,j,k) for(int i=j;i<=k;i++) #define sca(x) scanf("%d",&x); #define LL long long using namespace std; const int mod = 1024; struct node { int a[3][3]; }; void Print(node k) { for(int i=1;i<=2;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=2;j++) { cout<<k.a[i][j]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } } node mul(node x,node y) { node tmp; memset(tmp.a,0,sizeof(tmp.a)); for(int i=1;i<=2;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=2;j++) { for(int k=1;k<=2;k++) { tmp.a[i][j]+=(x.a[i][k]*y.a[k][j])%mod; } tmp.a[i][j]%=mod; } } //Print(tmp); return tmp; } void solve(int k) { node ans,tmp; memset(ans.a,0,sizeof(ans.a)); memset(tmp.a,0,sizeof(tmp.a)); ans.a[1][1]=5;ans.a[2][1]=2; tmp.a[1][1]=5,tmp.a[1][2]=12; tmp.a[2][1]=2,tmp.a[2][2]=5; while(k) { if(k&1) ans=mul(tmp,ans); tmp=mul(tmp,tmp); k>>=1; } printf("%d\n",(2*ans.a[1][1]-1)%mod); } int main() { int t; sca(t); while(t--) { int n; sca(n); solve(n-1); } } -
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define rep(i,j,k) for(int i=j;i<=k;i++) #define sca(x) scanf("%d",&x); #define LL long long using namespace std; LL mod = 1024; struct node { LL a[3][3]; }; node mul(node x,node y) { node tmp; memset(tmp.a,0,sizeof(tmp.a)); for(int i=1;i<=2;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=2;j++) { for(int k=1;k<=2;k++) { tmp.a[i][j]+=(x.a[i][k]*y.a[k][j])%mod; } tmp.a[i][j]%=mod; } } //Print(tmp); return tmp; } LL aa,bb; void solve(int k) { node ans,tmp; memset(ans.a,0,sizeof(ans.a)); memset(tmp.a,0,sizeof(tmp.a)); ans.a[1][1]=aa;ans.a[2][1]=1; tmp.a[1][1]=aa,tmp.a[1][2]=bb; tmp.a[2][1]=1,tmp.a[2][2]=aa; while(k) { if(k&1) ans=mul(tmp,ans); tmp=mul(tmp,tmp); k>>=1; } printf("%d\n",(2*ans.a[1][1])%mod); } int main() { int n; while(~scanf("%lld%lld%d%lld",&aa,&bb,&n,&mod)) { solve(n-1); } }