下面使用简单的例子说下在PHP中操作MySql数据库,内容包括连接数据库、查询操作、事务及存储过程。
1、访问MySql一般步骤
1)连接MySql服务器
使用mysql_connect()函数建立与MySql服务器的连接。
2)选择MySql数据库
使用mysql_select_db()函数选择MySql服务器上的数据库,并与数据库建立连接。
3)执行SQL语句
使用mysql_query()函数执行SQL语句。(包括增加、删除、修改、查询、显示)
4)关闭结果集
使用mysql_free_result($result)关闭结果集,以释放资源。
5)关闭MySql服务器连接
每一次调用mysql_connect()或mysql_query()函数都会消耗系统资源,使用mysql_close($link)关闭与服务器的连接。
说明:PHP中与数据库中的连接是非持久型连接,系统会自动回收。如果对数据库的访问频繁可以建立持续连接,调用函数mysql_pconnect(0代替mysql_connect(),建立持续连接在本程序结束时不需要调用mysql_close()来关闭与数据库服务器的连接,下次执行mysql_pconnect()时,系统直接返回已经建立的持续连接ID号,而不是直接去连接数据库。
2、操作MySql数据库的方法
- 基本连接查询函数
1)mysql_connect(‘hostname’,’username’,’password’);
注:hostname为服务器的主机名或IP,缺省端口号为3306.
2)mysql_select_db(‘databasename’,[,resource link_identifier]);
注:如果没有指定resource link_identifier则使用上一个打开的连接。如果没有打开的连接,则调用mysql_connect()函数来尝试打开一个数据库并使用。
4)mysql_query(<SQL语句>,[,resource link_identifier]);
注:在mysql_query()函数中执行的SQL语句不应以分号”;”结尾。mysql_unbuffered_query()函数发送一条SQL查询语句,但是不获取和缓存结果集。
使用示例:(root用户登录没有设置密码,数据库名为students,数据库表为score)
<?php
$link=mysql_connect("localhost","root") or die("Error,Can't connect mySql");
$db_selected=mysql_select_db("students",$link);
$result=mysql_query("insert into score values('kit',78)",$link);//执行插入操作
$result=mysql_query("delete from score where name ='zhangsan'",$link); //执行删除操作
$result=mysql_query("update score set english=77 where name='zhangsan'");//执行更新操作
$result=mysql_query("select * from score",$link);//执行查询操作
mysql_free_result($result);
mysql_close($link);
?>
- mysql_fetch_array()函数
mysql_fetch_array()函数从数组结果集中获取信息
使用示例:
数据库表score内容如下:
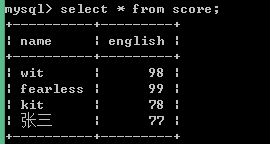
<?php
$link=mysql_connect("localhost","root") or die("Error,Can't connect mySql");
$db_selected=mysql_select_db("students",$link);
mysql_query("set names gb2312");//设置编码格式为GB2312,防止乱码
$result=mysql_query("select * from score where name like '%i%'",$link);//执行查询操作
$info=mysql_fetch_array($result);
?>
<table>
<tr>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>英语分数</td>
</tr>
<?php
do{
?>
<tr>
<th><?php echo $info[name];?></th>
<th><?php echo $info[english];?></th>
</tr>
<?php
}while ($info = mysql_fetch_array($result));
?>
</table>
注意:设置编码格式为GB2312,防止乱码。通配符”%”可以匹配零个或任意多个字符。
- mysql_fetch_object()函数
使用mysql_fetch_object()函数从结果集中获取一行作为对象
示例:
<?php
$link=mysql_connect("localhost","root") or die("Error,Can't connect mySql".mysql_errno());
$db_selected=mysql_select_db("students",$link);
mysql_query("set names gb2312");//设置编码格式为GB2312,防止乱码
$result=mysql_query("select * from score",$link);//执行查询操作
$info=mysql_fetch_object($result);
?>
<table>
<tr>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>英语分数</td>
</tr>
<?php
do{
?>
<tr>
<th><?php echo $info->name;?></th>
<th><?php echo $info->english;?></th>
</tr>
<?php
}while ($info = mysql_fetch_object($result));
?>
</table>
- mysql_fetch_row()函数
该函数逐行获取结果集中的每条记录。
示例:
<?php
$link=mysql_connect("localhost","root") or die("Error,Can't connect mySql".mysql_errno());
$db_selected=mysql_select_db("students",$link);
mysql_query("set names gb2312");//设置编码格式为GB2312,防止乱码
$result=mysql_query("select * from score",$link);//执行查询操作
$info=mysql_fetch_row($result);
?>
<table>
<tr>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>英语分数</td>
</tr>
<?php
do{
?>
<tr>
<th><?php echo $info[0];?></th>
<th><?php echo $info[1];?></th>
</tr>
<?php
}while ($info = mysql_fetch_row($result));
?>
</table>
- mysql_num_rows()函数
使用mysql_num_rows()函数可以获取由select语句查询到的结果集中行的数目。
示例:
<?php
$link=mysql_connect("localhost","root") or die("Error,Can't connect mySql".mysql_errno());
$db_selected=mysql_select_db("students",$link);
mysql_query("set names gb2312");//设置编码格式为GB2312,防止乱码
$result=mysql_query("select * from score",$link);//执行查询操作
$count=mysql_num_rows($result);
echo "查询结果总数为:".$count;
mysql_free_result($result);
mysql_close($link);
?>
注:要获取有Insert、update、delete语句所影响的数据行数,则必须使用mysql_affected_rows()函数来实现。
3、PDO操作数据库
要使用PDO需要在zend Studios安装目录下的php.ini文件中加上extession=php_pdo_mysql.dll
及extestion=php.pdo.dll,入下图:

- 连接数据库
PDO构造函数如下:
_construct(string $dsn[,string $username[,string $password[,array $driver_options]]]);
参数说明:dsn为数据源名称,包括主机端口号和数据库名称。
【例1】连接mySql数据库
<?php
//header(“Content-Type:text/html;charset=uft-8”);
$dsn="mysql:host=localhost;dbname=students";
try {
$pdo=new PDO($dsn, "root");
echo "PDO连接成功!";
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "连接失败!".$e->getMessage();
}
【例2】使用ODBC连接MS Sql Server数据库
<?php
$dsn="odbc:Driver={SQL Server};server=localhost;database=tmp";
try {
$pdo=new PDO($dsn, "root");
echo "PDO连接成功!";
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "连接失败!".$e->getMessage();
}
- 执行sql语句
exec()方法返回sql语句收影响的行数,语法为:
int PDO::exec(string statement)
参数statement是要执行的SQL语句,通常用于INSERT,DELETE和UPDATE语句中。
query()方法通常用于返回执行查询后的结果集,语法如下:
PDOStatement PDO::query(string statement)
参数statement为要执行的SQL语句。
Prepare()和execute()方法
prepaer()方法做查询的准备工作,然后通过execte()方法执行查询,还可以通过bindParam()方法来绑定参数提供 给execute()方法。语法如下:
PDOStatement PDO::prepare(string statement[,array driver_options])
bool PDOStatement::execute([array input_parameters])
示例:
<?php
$dsn="odbc:Driver={SQL Server};server=localhost;database=tmp";
$pdo=new PDO($dsn, "sa","123456");
$query="select * from Student";
$result=$pdo->prepare($query);
$result->execute();
?>
注:绿色背景部分可以用$result=$pdo->query($query);代替。
- PDO中获取结果集—fetch()
fetch()方法获取结果集中的下一行数据,语法格式:
mixed PDOStatement::fetch([int_fetch_style[,int cursor_orientation[,int cursor_offset]]])
参数说名:
参数fect_style可取值如下:
| 值 |
说明 |
| PDO::FETCH_ASOC |
关联数组形式 |
| PDO::FETCH_NUM |
关联索引数组形式 |
| PDO::FETCH_BOTH |
两者数组形式都有,这是缺省值 |
| PDO::FETCH_OBJ |
按照对象的形式,类似于以前的mysql_fetch_object() |
| PDO::FETCH_BOUND |
以布尔值的形式返回结果,同时将获取的列值赋给bindParam()方法中指定的变量 |
| PDO::FECTH_LAZY |
以关联数组、索引数组和对象3种形式返回结果 |
参数cursor_orientation可用于获取指定的一行;
参数cursor_offset表示游标的偏移量。
示例:
数据库表student内容如下:
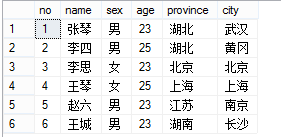
<?php
$dsn="odbc:Driver={SQL Server};server=localhost;database=tmp";
try {
$pdo=new PDO($dsn, "sa","123456");
$query="select * from Student";
$result=$pdo->prepare($query);
$result->execute();
?>
<table>
<tr>
<th>学号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>性别</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>所在省份</th>
<th>居住城市</th>
</tr>
<?php
while ($res=$result->fetch(pdo::FETCH_ASSOC)){
?>
<tr>
<td><?php echo $res['no']?></td>
<td><?php echo $res['name']?></td>
<td><?php echo $res['sex']?></td>
<td><?php echo $res['age']?></td>
<td><?php echo $res['province']?></td>
<td><?php echo $res['city']?></td>
</tr>
<?php
}
?>
</table>
<?php
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "连接失败!".$e->getMessage();
}
- PDO中获取结果集—fetchAll()
fetchAll()方法获取结果集中的所有航,语法如下:
array PDOStatement::fetchAll([int fetch_style[,int column_index]]);
参数column_index为字段的索引值。
示例:
<?php
$dsn="odbc:Driver={SQL Server};server=localhost;database=tmp";
try {
$pdo=new PDO($dsn, "sa","123456");
$query="select * from Student";
$result=$pdo->prepare($query);
$result->execute();
?>
<table>
<tr>
<th>学号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>性别</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>所在省份</th>
<th>居住城市</th>
</tr>
<?php
$res=$result->fetchAll(pdo::FETCH_ASSOC);
for($index=0;$index<count($res);$index++){
?>
<tr>
<td><?php echo $res[$index]['no']?></td>
<td><?php echo $res[$index]['name']?></td>
<td><?php echo $res[$index]['sex']?></td>
<td><?php echo $res[$index]['age']?></td>
<td><?php echo $res[$index]['province']?></td>
<td><?php echo $res[$index]['city']?></td>
</tr>
<?php
}
?>
</table>
<?php
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "连接失败!".$e->getMessage();
}
- PDO中获取结果集—fetchColumn()
fetchColumn()方法获取结果集中下一行指定列的值,语法格式为:
string PDOStatement::fetchColumn([int column_number]);
参数column_number从0开始,如果省略该参数则从第1列开始取值。
示例:
<?php
$dsn="odbc:Driver={SQL Server};server=localhost;database=tmp";
try {
$pdo=new PDO($dsn, "sa","123456");
$query="select * from Student";
$result=$pdo->prepare($query);
$result->execute();
?>
<table>
<tr>
<th>姓名</th>
</tr>
<?php
while($res=$result->fetchColumn(1)){
?>
<tr>
<td><?php echo $res?></td>
</tr>
<?php
}
?>
</table>
<?php
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "连接失败!".$e->getMessage();
}
4、PDO中错误处理
PDO中捕获SQL语句中的错误有以下三种模式:
PDO::ERRORMODE_SILIENT:设置PDStatement对象的errorCode属性,但是不进行任何其它操作;
PDO::ERRORMODE_WARNING:会产生一个PHP警告,并设置errorCode属性;
PDO::ERRORMODE_EXCEPTION:会创建一个PDOException,并设置errorCode属性。
示例:当查询一个不存在的数据库表时,
如果为PDO::ERRORMODE_SILIENT模式则伍任何错误输出;若为PDO::ERRORMODE_WARNING模式输出错误如下:

若为PDO::ERRORMODE_EXCEPTION模式输出错误如下:
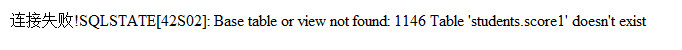
errorCode()方法用于获取在操作数据库句柄时所发生的错误代码;
errorInfo()方法用于获取操作数据库句柄时所发生的错误信息;
【示例1】
<?php
$dsn='mysql:host=localhost;dbname=students';
try {
$pdo=new PDO($dsn,"root","");
$pdo->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$query="select * from score1";
$result=$pdo->prepare($query);
$result->execute();
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "连接失败!".$e->getMessage();
echo "错误代码:".$pdo->errorCode();
print_r($pdo->errorInfo());
}
【示例2】数据库表score1不存在
<?php
$dsn='mysql:host=localhost;dbname=students';
try {
$pdo=new PDO($dsn,"root","");
$pdo->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$query="select * from score1";
$result=$pdo->prepare($query);
$result->execute();
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "<pre>";
echo "ErrorInfo:".$e->getMessage()."<br/>";
echo "ErrorCode:".$e->getCode()."<br/>";
echo "File:".$e->getFile()."<br/>";
echo "Line:".$e->getLine()."<br/>";
echo "Trace:".$e->getTraceAsString()."<br/>";
echo "</pre>";
}
输出错误信息如下:
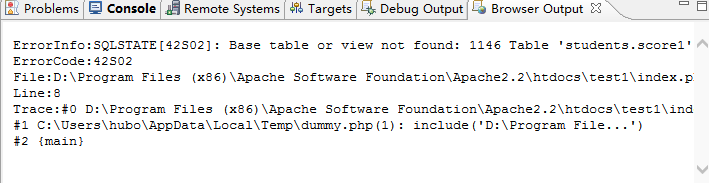
5、PDO中事物处理
beginTransaction()开启事务,commit()提交事务;rollBack()回滚事务。
示例:
数据库表score有name和english两个字段,下面插入两条记录,第一条记录是合法的,第二条记录是不法的,会导致操作失败。使用了事务后,两条记录都不会插入到数据库,如果不使用事务,则第1条记录会插入到数据库。
<?php
$dsn='mysql:host=localhost;dbname=students;charset=gbk';//设置编码格式
try {
$pdo=new PDO($dsn,"root","");
$pdo->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$pdo->beginTransaction();//开启事务
$result=$pdo->query("insert into score values('张琴',88)");
$result=$pdo->query("insert into score values('郑三',88,'asd’)");
$pdo->commit();//提交事务
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "ErrorInfo:".$e->getMessage()."<br/>";
$pdo->rollBack();//事务回滚
}
?>
6、PDO中存储过程
在mySql中创建存储过程pro_reg,
mysql> drop procedure if exists pro_reg;
mysql> delimiter //
mysql> create procedure pro_reg(in name nvarchar(80),in age int,in address nvarc
har(200))
-> begin
-> insert into tb_reg(name,age,address) values(name,age,address);
-> end;
-> //
注:delimiter //作用是将结束符更改为//。数据库tb_reg有三个字段:name,age,address.
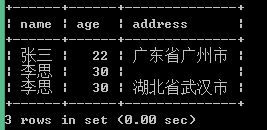
示例:
<?php
$dsn='mysql:host=localhost;dbname=students';
try {
$pdo=new PDO($dsn,"root","");
$pdo->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$pdo->query("set names gbk");
//$query="call pro_reg('张三',22,'广东省广州市')";
$name='李思';
$age=30;
$address='湖北省武汉市';
$query="call pro_reg('$name','$age','$address')";
$result=$pdo->prepare($query);
if($result->execute()){
echo "数据库添加成功!";
}
else {
echo "数据库添加失败!";
}
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "ErrorInfo:".$e->getMessage()."<br/>";
}
?>
执行后结果为: