版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/www851903307/article/details/82430559
一、基本概念:
1、栈是什么?
是一个只能在某一端进行插入、删除操作的线性表。
* 从栈顶插入一个元素称之为入栈(push)
* 从栈顶删除一个元素称之为出栈(pop)
2、图解:
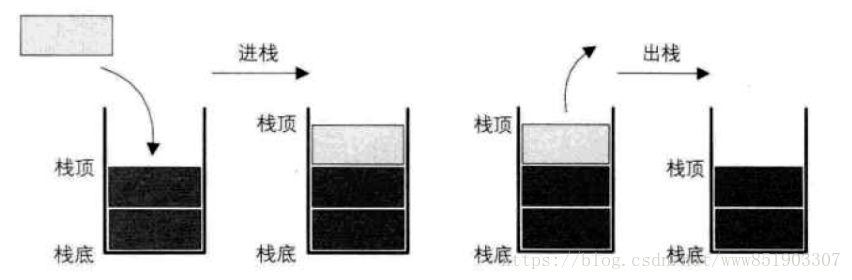
3、栈的实现:
- 链式存储(链表)
- 顺序存储(数组)
4、继承关系:
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
...
}二、常用方法:
1、入栈
public E push(E item) {
//调用Vector方法
addElement(item);
return item;
}2、出栈(返回栈顶元素,并删除)
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
//通过调用peek获取栈顶元素
obj = peek();
//调用Vector的removeElementAt方法
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}3、获取栈顶元素(不删除)
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
//Vector方法
return elementAt(len - 1);
}4、查找某元素位置
public synchronized int search(Object o) {
//Vector方法
int i = lastIndexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) {
return size() - i;
}
return -1;
}三、Vector源码分析
1、变量
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{
//内部实现为数组
protected Object[] elementData;
...
}2、添加元素
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
//扩容
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
//在数组最后赋值
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}Stack入栈的操作就是在数组的尾部插入元素
3、删除数组尾部元素:
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
4174445 查看本文章


public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
//index = elementCount-1,此时为出栈(移除数组尾部元素)
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
//尾部赋值为null
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}Stack出栈的操作就是将数组尾部的元素移除
4、获取某位置元素:
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
//获取数组某索引元素
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}5、获取某元素所在的位置:
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
}
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
//遍历数组获取到元素的位置
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}6、结论:
Vector特点:
- 内部实现为数组
- 方法通过synchronized修饰,线程安全
Stack特点:
- 入栈出栈的操作,本质就是对数组尾部添加、删除元素。