由于现代软件的复杂性,一个大型软件系统往往会被人为地拆分称为多个模块,另外随着移动互联网的兴起,网站的规模越来越大,为了能够支撑业务的发展,需要集群和分布式部署。模块之间的通信就需要进行跨节点通信。
在传统的Java应用中,通常使用4中方式进行跨节点通信:
- 通过RMI进行远程服务调用
- 通过Java Socket + Java序列化
- RPC框架 Thrift、Apache的Avro等
- 利用标准的公有协议进行跨节点调用,例如HTTP+XML,Restful+JSON或WebService
跨节点的远程服务调用,除了链路层的物理连接外,还需要对请求和响应消息进行编解码。 在请求和应答之外,还需要控制和管理类指令,例如链路建立的握手信息,链路检测的心跳信息。这些功能组合到一起后,就会形成私有协议 。事实上只要能够用于跨进程,跨主机数据交换的非标准协议都可以称为私有协议。
Netty协议栈功能设计
在分布式组网环境下,每个Netty节点(Netty进程)之间建立长连接,使用Netty协议进行通信。Netty节点没有服务端和客户端的区分,谁先发起连接,谁就是客户端,另一方则是服务端。一个Netty节点既能作为客户端连接另外也能做服务端被其他节点连接。

协议栈功能描述
- 基于Netty的NIO通信框架,提供高性能的异步通信能力;
- 提供消息的编解码框架,实现POJO的序列化和反序列化
- 提供基于IP地址的白名单接入认证机制;
- 链路的有效性校验机制;
- 链路的断线重连机制;
通信模型
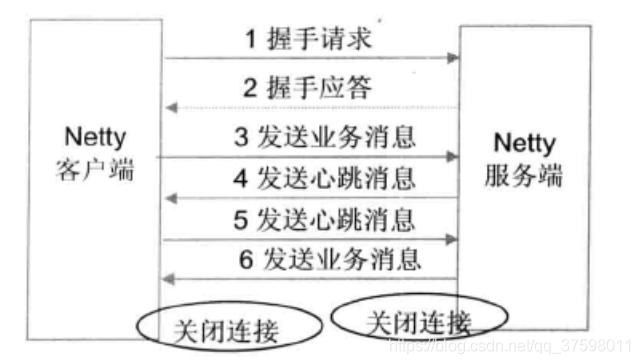
具体步骤:
- Netty协议栈客户端发送握手请求信息,携带节点ID等有效身份认证信息;
- Netty协议服务端对握手请求消息进行合法性校验,包括节点ID有效性校验、节点重复登录校验和IP地址合法性校验,校验通过后,返回登录成功的握手应答消息;
- 链路建立成功之后,客户端发送业务消息;
- 链路成功之后,服务端发送心跳消息;(采用Ping-Pong机制)
- 链路建立成功之后,客户端发送心跳消息;
- 链路建立成功之后,服务端发送业务消息;
- 服务端退出时,服务端关闭连接,客户端感知对方关闭连接后,被动关闭客户端连接。
消息定义
Netty协议栈消息定义包含两部分:
Netty消息定义表(NettyMessage)
- 消息头
- 消息体
| 名称 | 类型 | 长度 | 描述 |
| header | Header | 变长 | 消息头定义 |
| body | Object | 变长 | 对于请求消息,它是方法参数;对于响应消息,它是返回值 |
Netty协议消息头定义(Header)
| 名称 | 类型 | 长度 | 描述 |
| crcCode | 整型int | 32 | Netty消息的校验码,由三部分组成: 1.0xABEF:固定值,表明该消息时Netty协议消息,2个字节 2.主版本号:1~255,1个字节 3.次版本号:1~255,1个字节 crcCode=0xABEF+主版本号+次版本号 |
| sessionID | 整型long | 64 |
集群节点被全局唯一,由会话ID生成器生成 |
| type | Byte | 8 | 0: 表示请求消息 1: 业务响应消息 2: 业务ONE WAY消息(即是请求又是响应消息) 3: 握手请求消息 4: 握手应答消息 5: 心跳请求消息 6: 心跳应答消息 |
| priority | Byte | 8 | 消息优先级: 0-255 |
| length | 整型int | 32 | 消息长度,整个消息,包括消息头和消息体 |
| attachment | Map<String,Object> | 变长 | 可选字段,用于扩展消息头 |
Netty协议支持的消息字段类型

Netty协议的编解码规范
Netty协议NettyMessage的编码规范如下:
- crcCode: java.nio.ByteBuffer.putInt(int value),如果采用其它缓存区实现,必须与其等价
- length: java.nio.ByteBuffer.putInt(int value),如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
- sessionID: java.nio.ByteBuffer.putLong(long value),如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
- type: java.nio.ByteBuffer.put(byte b),如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
- priority: java.nio.ByteBuffer.put(byte b),如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
- attachment: 如果长度为0,表示没有可选附件,则将长度编码为0,即java.nio.ByteBuffer.putInt(0),如果大于0,表示有附件需要编码,具体规则如下:
- 首先对附件的个数进行编码,java.nio.ByteBuffer.putInt(attachment.size());
- 然后对Key进行编码,先编码长度,再将它转换成byte数组之后编码内容。具体代码如:
String key = null;
byte[] value = null;
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> param: attachment:entrySet()) {
key = param.getKey();
buffer.writeString(key);
value = marshaller.writeObject(param.getValue());
buffer.writeBinary(value);
}
key = null;
value = null;7.body的编码: 通过JBoss Marshalling将其序列化为byte数组,然后调用java.nio.ByteBuffer.put(byte[] src);将其写入ByteBuffer缓冲区中。
由于整个消息的长度必须等全部字段都编码完成后才能确认,所以死最后需要更新消息头的length字段,将其重写入ByteBuffer中。
Netty协议的解码:
- crcCode: java.nio.ByteBuffer.getInt()获取校验码字段,如果采用其它缓存区实现,必须与其等价
- length: java.nio.ByteBuffer.getInt()获取Netty消息的长度,如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
- sessionID: java.nio.ByteBuffer.getLong()获取会话ID,如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
- type: java.nio.ByteBuffer.get()获取消息类型,如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
- priority: java.nio.ByteBuffer.get()获取消息优先级,如果采用其它缓冲区实现,必须与其等价
- attachment: 它的解码规则为-首先创建一个新的attachment对象,调用java.nio.ByteBuffer.getInt()获取附件的长度,如果为0,说明附件为空,解码结束,解析解消息体,否则,根据长度通过for循环进行解码。
- body: 使用JBoss marshaller对其进行解码
String key = null;
Object value = null;
for (int i =0; i < size;i++) {
key = buffer.readString();
value = unmarshaller.readObject(buffer.readBinary());
this.attachment.put(key, value);
}
key = null;
value = null;链路的建立
Netty协议栈支持服务端和客户端,对于使用Netty协议栈的应用程序而言,不需要刻意区分是客户端还是服务端。在分布式组网环境中,一个节点可能即是服务端也是客户端。
客户端与服务端链路建立成功后,由客户端发送握手请求消息,请求消息的定义如下:
- 消息头的type字段为3;
- 可选附件个数为0;
- 消息体为空;
- 握手消息的长度为22个字节;
服务端接受客户端的握手请求消息后,如果IP校验通过,返回握手成功应答消息给客户端,应用层链路建立成功,握手应答消息定义如下:
- 消息头type为4
- 可选附件个数为0
- 消息体为byte类型的结果,"0"表示认证成功,"-1"表示认证失败。
链路的关闭
由于采用长连接通信,正常的业务运行期间,双方通过心跳和业务消息维持链路,任何一方不需要主动关闭连接。
但是,在以下情况下,客户端和服务端需要关闭连接。
- 当对方宕机或者重启时,会主动释放链路,另一方读取到操作系统的通知信号,得到对方REST链路,需要关闭连接,释放自身的句柄等资源。由于采用TCP全双工通信,通信双方都需要关闭连接,释放资源;
- 消息在读写过程中,发生了I/O异常,需要主动关闭连接;
- 心跳消息读写过程中发生了I/O异常,需要主动关闭连接;
- 心跳超时,需要主动关闭连接;
- 发生编码异常等不可恢复的错误时,需要主动关闭连接;
可靠性设计
1.心跳机制
- 当网络处于空闲时间达到了T(连续周期T没有读写消息)时,客户端主动发送Ping心跳消息给服务端;
- 如果在下一个周期T到来时客户端没有收到对方发送的Pong心跳应答消息或者读取到服务端发送的其他业务消息,则心跳失败计数器+1
- 每当客户端接收到服务的业务消息或者Pong应答消息时,将心跳失败计数器清0;连续N次没有接收到服务端的Pong消息或者业务消息,则关闭链路,间隔INTERVAL时间后发起重连操作;
- 服务端网络空闲状态持续时间达到T后,服务器端将心跳失败计数器+1;只要接收到客户端发送的Ping消息或者其他业务消息,计数器清0
- 服务器端连续N次没有接收到客户端的Ping消息或者其他业务消息,则关闭链路,释放资源,等待客户端重连。
2.重连机制
如果链路中断,等待INTERVAL时间后,由客户端发起重连操作,如果重连失败,间隔周期INTERVAL之后再继续重连,直到重连成功。
为了保证服务端能够有充足的时间释放句柄资源,在首次断连时客户端需要等待INTERVAL时间之后再发起重连而不是失败后立即重连。
为了句柄资源能够及时释放,无论什么场景下的重连失败,客户端必须保证自身资源被成功及时释放,包括企鹅不限于SocketChannel、Socket等。
重连失败,需要记录异常堆栈信息,方便问题定位。
3.重复登录保护
客户端握手成功之后,链路处于正常状态下,不允许客户端重复登录,以防止客户端在异常状态下反复重连导致句柄资源被耗尽。
服务端在接收到握手消息后,首先进行ip合法性校验,如果成功,则在缓存的地址表中查看客户端是否已经登录,如果已经登录,则拒绝重复登录,返回错误码-1,同时关闭链路,并且在服务端日志中打印错误信息。
客户端接收到握手失败的应答消息之后,关闭客户端的TCP连接,等待INTERVAL时间之后,再次发起TCP连接,知道认证成功。
为了防止由服务端和客户端对链路状态理解不一致的问题,当服务端连续N次心跳超时之后需要主动关闭链路,同时清空该客户端的缓存信息,保证后续的客户端可以重连,防止被重复登录保护机制拒绝掉。
4.消息缓存重发
无论是客户端还是服务端,在发生链路中断之后,恢复链路之前,缓存在消息队列的待发送的消息不能丢失。等链路恢复之后,重新发送这些消息,保证链路中断期间消息不丢失。同时考虑到内存溢出风险,应该在消息缓存队列中设置上限,当达到上限之后,应该拒绝继续向该队列添加新的消息。
安全性设计
为了保证整个集群环境的安全,内部长连接采用基于IP地址的安全认证机制,服务端对握手请求的IP进行合法性校验。如果将Neety放到公网使用,需要采用更严格的安全认证机制,如基于秘钥和AES加密,也可以采用SSL/TSL安全传输。
可扩展性设计
Netty协议栈需要具备一定的扩展能力,例如统一的消息拦截、接口日志、安全、加密解密等可以被方便地添加和删除,推荐使用Servelt的FilterChain机制,考虑到性能因素,不推荐AOP。
Netty协议栈开发
需要的jar
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.30.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.marshalling</groupId>
<artifactId>jboss-marshalling</artifactId>
<version>1.4.10.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.marshalling</groupId>
<artifactId>jboss-marshalling-serial</artifactId>
<version>1.4.10.Final</version>
</dependency>数据结构定义
首先对Netty协议栈使用到的数据结构进行定义,Netty消息如下:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 消息头
*/
public final class Header {
private int crcCode = 0xabef0101;
private int length;// 消息长度
private long sessionID;// 会话ID
private byte type;// 消息类型
private byte priority;// 消息优先级
private Map<String, Object> attachment = new HashMap<String, Object>(); // 附件
/**
* @return the crcCode
*/
public final int getCrcCode() {
return crcCode;
}
/**
* @param crcCode the crcCode to set
*/
public final void setCrcCode(int crcCode) {
this.crcCode = crcCode;
}
/**
* @return the length
*/
public final int getLength() {
return length;
}
/**
* @param length the length to set
*/
public final void setLength(int length) {
this.length = length;
}
/**
* @return the sessionID
*/
public final long getSessionID() {
return sessionID;
}
/**
* @param sessionID the sessionID to set
*/
public final void setSessionID(long sessionID) {
this.sessionID = sessionID;
}
/**
* @return the type
*/
public final byte getType() {
return type;
}
/**
* @param type the type to set
*/
public final void setType(byte type) {
this.type = type;
}
/**
* @return the priority
*/
public final byte getPriority() {
return priority;
}
/**
* @param priority the priority to set
*/
public final void setPriority(byte priority) {
this.priority = priority;
}
/**
* @return the attachment
*/
public final Map<String, Object> getAttachment() {
return attachment;
}
/**
* @param attachment the attachment to set
*/
public final void setAttachment(Map<String, Object> attachment) {
this.attachment = attachment;
}
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*
* @see java.lang.Object#toString()
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "数据头:Header [crcCode=" + crcCode + ", length=" + length
+ ", sessionID=" + sessionID + ", type=" + type + ", priority="
+ priority + ", attachment=" + attachment + "]";
}
}import proprietary.protocol.dao.Header;
/**
* Netty消息
*/
public final class NettyMessage {
private Header header;
private Object body;
/**
* @return the header
*/
public final Header getHeader() {
return header;
}
/**
* @param header the header to set
*/
public final void setHeader(Header header) {
this.header = header;
}
/**
* @return the body
*/
public final Object getBody() {
return body;
}
/**
* @param body the body to set
*/
public final void setBody(Object body) {
this.body = body;
}
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*
* @see java.lang.Object#toString()
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "NettyMessage [header=" + header + "]";
}
}消息编解码
分别定义NettyMessageDecoder和NettyMessageEncoder用于NettyMessage消息的编解码:
消息编码类:
/**
* NettyMessage消息编码器
*/
public class NettyMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<NettyMessage> {
MarshallingEncoder marshallingEncoder;
public NettyMessageEncoder() throws IOException {
this.marshallingEncoder = new MarshallingEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, NettyMessage msg, ByteBuf sendBuf) throws Exception {
if (null == msg || null == msg.getHeader()) {
throw new Exception("The encode message is null");
}
//---写入crcCode---
sendBuf.writeInt((msg.getHeader().getCrcCode()));
//---写入length---
sendBuf.writeInt((msg.getHeader().getLength()));
//---写入sessionId---
sendBuf.writeLong((msg.getHeader().getSessionID()));
//---写入type---
sendBuf.writeByte((msg.getHeader().getType()));
//---写入priority---
sendBuf.writeByte((msg.getHeader().getPriority()));
//---写入附件大小---
sendBuf.writeInt((msg.getHeader().getAttachment().size()));
String key = null;
byte[] keyArray = null;
Object value = null;
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> param : msg.getHeader().getAttachment()
.entrySet()) {
key = param.getKey();
keyArray = key.getBytes("UTF-8");
sendBuf.writeInt(keyArray.length);
sendBuf.writeBytes(keyArray);
value = param.getValue();
marshallingEncoder.encode(value, sendBuf);
}
// for gc
key = null;
keyArray = null;
value = null;
if (msg.getBody() != null) {
marshallingEncoder.encode(msg.getBody(), sendBuf);
} else
sendBuf.writeInt(0);
// 之前写了crcCode 4bytes,除去crcCode和length 8bytes即为更新之后的字节
sendBuf.setInt(4, sendBuf.readableBytes() - 8);
}
}Netty消息编码工具类:MarshallingEncoder
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler.Sharable;
import org.jboss.marshalling.Marshaller;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消息编码工具类
*/
@Sharable
public class MarshallingEncoder {
private static final byte[] LENGTH_PLACEHOLDER = new byte[4];
Marshaller marshaller;
public MarshallingEncoder() throws IOException {
marshaller = MarshallingCodecFactory.buildMarshalling();
}
// 使用marshall对Object进行编码,并且写入bytebuf...
protected void encode(Object msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
try {
//1. 获取写入位置
int lengthPos = out.writerIndex();
//2. 先写入4个bytes,用于记录Object对象编码后长度
out.writeBytes(LENGTH_PLACEHOLDER);
//3. 使用代理对象,防止marshaller写完之后关闭byte buf
ChannelBufferByteOutput output = new ChannelBufferByteOutput(out);
//4. 开始使用marshaller往bytebuf中编码
marshaller.start(output);
marshaller.writeObject(msg);
//5. 结束编码
marshaller.finish();
//6. 设置对象长度
out.setInt(lengthPos, out.writerIndex() - lengthPos - 4);
} finally {
marshaller.close();
}
}
}
Netty消息解码类:NettyMessageDecoder:
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import proprietary.protocol.dao.Header;
import proprietary.protocol.dao.NettyMessage;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Netty消息解码类
*/
public class NettyMessageDecoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder {
MarshallingDecoder marshallingDecoder;
public NettyMessageDecoder(int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset,
int lengthFieldLength) throws IOException {
super(maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength);
marshallingDecoder = new MarshallingDecoder();
}
@Override
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in)
throws Exception {
ByteBuf frame = (ByteBuf) super.decode(ctx, in);
if (frame == null) {
return null;
}
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setCrcCode(frame.readInt());
header.setLength(frame.readInt());
header.setSessionID(frame.readLong());
header.setType(frame.readByte());
header.setPriority(frame.readByte());
int size = frame.readInt();
if (size > 0) {
Map<String, Object> attch = new HashMap<String, Object>(size);
int keySize = 0;
byte[] keyArray = null;
String key = null;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
keySize = frame.readInt();
keyArray = new byte[keySize];
frame.readBytes(keyArray);
key = new String(keyArray, "UTF-8");
attch.put(key, marshallingDecoder.decode(frame));
}
keyArray = null;
key = null;
header.setAttachment(attch);
}
if (frame.readableBytes() > 4) {
message.setBody(marshallingDecoder.decode(frame));
}
message.setHeader(header);
return message;
}
}这里用Netty的LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder解码器,它支持自动的TCP粘包和半包处理,只需要给出标识消息长度的字段偏移量和消息长度自身所占的字节数,Netty就能自动实现对半包的处理。
Netty消息解码工具类:MarshallingDecoder:
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import org.jboss.marshalling.ByteInput;
import org.jboss.marshalling.Unmarshaller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StreamCorruptedException;
/**
* Netty消息解码工具类
*/
public class MarshallingDecoder {
private final Unmarshaller unmarshaller;
/**
* Creates a new decoder whose maximum object size is {@code 1048576} bytes.
* If the size of the received object is greater than {@code 1048576} bytes,
* a {@link StreamCorruptedException} will be raised.
*
* @throws IOException
*/
public MarshallingDecoder() throws IOException {
unmarshaller = MarshallingCodecFactory.buildUnMarshalling();
}
protected Object decode(ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
//1. 读取第一个4bytes,里面放置的是object对象的byte长度
int objectSize = in.readInt();
ByteBuf buf = in.slice(in.readerIndex(), objectSize);
//2 . 使用bytebuf的代理类
ByteInput input = new ChannelBufferByteInput(buf);
try {
//3. 开始解码
unmarshaller.start(input);
Object obj = unmarshaller.readObject();
unmarshaller.finish();
//4. 读完之后设置读取的位置
in.readerIndex(in.readerIndex() + objectSize);
return obj;
} finally {
unmarshaller.close();
}
}
}import org.jboss.marshalling.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 解码器工厂类
*/
public final class MarshallingCodecFactory {
/**
* 创建Jboss Marshaller
*
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
protected static Marshaller buildMarshalling() throws IOException {
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling
.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
Marshaller marshaller = marshallerFactory
.createMarshaller(configuration);
return marshaller;
}
/**
* 创建Jboss Unmarshaller
*
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
protected static Unmarshaller buildUnMarshalling() throws IOException {
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling
.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
final Unmarshaller unmarshaller = marshallerFactory
.createUnmarshaller(configuration);
return unmarshaller;
}
}import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import org.jboss.marshalling.ByteInput;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link ByteInput} implementation which reads its data from a {@link ByteBuf}
*/
public class ChannelBufferByteInput implements ByteInput {
private final ByteBuf buffer;
public ChannelBufferByteInput(ByteBuf buffer) {
this.buffer = buffer;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
// nothing to do
}
@Override
public int available() throws IOException {
return buffer.readableBytes();
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
if (buffer.isReadable()) {
return buffer.readByte() & 0xff;
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public int read(byte[] array) throws IOException {
return read(array, 0, array.length);
}
@Override
public int read(byte[] dst, int dstIndex, int length) throws IOException {
int available = available();
if (available == 0) {
return -1;
}
length = Math.min(available, length);
buffer.readBytes(dst, dstIndex, length);
return length;
}
@Override
public long skip(long bytes) throws IOException {
int readable = buffer.readableBytes();
if (readable < bytes) {
bytes = readable;
}
buffer.readerIndex((int) (buffer.readerIndex() + bytes));
return bytes;
}
}import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import org.jboss.marshalling.ByteOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link ByteOutput} implementation which writes the data to a {@link ByteBuf}
*
*
*/
public class ChannelBufferByteOutput implements ByteOutput {
private final ByteBuf buffer;
/**
* Create a new instance which use the given {@link ByteBuf}
*/
public ChannelBufferByteOutput(ByteBuf buffer) {
this.buffer = buffer;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
// Nothing to do
}
@Override
public void flush() throws IOException {
// nothing to do
}
@Override
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
buffer.writeByte(b);
}
@Override
public void write(byte[] bytes) throws IOException {
buffer.writeBytes(bytes);
}
@Override
public void write(byte[] bytes, int srcIndex, int length) throws IOException {
buffer.writeBytes(bytes, srcIndex, length);
}
/**
* Return the {@link ByteBuf} which contains the written content
*
*/
ByteBuf getBuffer() {
return buffer;
}
}握手和安全认证
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import proprietary.protocol.dao.Header;
import proprietary.protocol.dao.NettyMessage;
/**
* 握手认证的客户端
*/
public class LoginAuthReqHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
// private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(LoginAuthReqHandler.class);
/**
* Calls {@link ChannelHandlerContext#fireChannelActive()} to forward to the
* next {@link ChannelHandler} in the {@link ChannelPipeline}.
* <p/>
* Sub-classes may override this method to change behavior.
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(buildLoginReq());
}
/**
* Calls {@link ChannelHandlerContext#fireChannelRead(Object)} to forward to
* the next {@link ChannelHandler} in the {@link ChannelPipeline}.
* <p/>
* Sub-classes may override this method to change behavior.
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg;
// 如果是握手应答消息,需要判断是否认证成功
if (message.getHeader() != null
&& message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.LOGIN_RESP
.value()) {
byte loginResult = (Byte) message.getBody();
if (loginResult != (byte) 0) {
// 握手失败,关闭连接
ctx.close();
} else {
// LOG.info("Login is ok : " + message);
System.out.println("登录成功:"+message);
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
} else
//调用下一个channel链..
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
/**
* 构建登录请求
*/
private NettyMessage buildLoginReq() {
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(MessageType.LOGIN_REQ.value());
message.setHeader(header);
return message;
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
}
当客户端和服务端TCP三次握手后,由客户端构造握手请求消息发送给服务端,由于采用IP白名单认证机制,因此不需要携带消息体,消息体为空,消息类型为“3:握手请求消息”。握手请求发送后,按照协议规范,服务端需要返回握手应答消息。

这里首先对握手应答消息进行处理,判断消息是否是握手应答消息,如果不是直接透传给后面的ChannelHandler进行处理;如果是握手应答消息则对应答结果进行判断,如果非0说明认证失败关闭链路,重新发起连接。
服务端的握手接入和安全认证代码:
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import proprietary.protocol.dao.Header;
import proprietary.protocol.dao.NettyMessage;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* 服务端的握手和安全认证
*/
public class LoginAuthRespHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
// private final static Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(LoginAuthRespHandler.class);
/**
* 本地缓存
*/
private Map<String, Boolean> nodeCheck = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Boolean>();
private String[] whitekList = {"127.0.0.1", "192.168.1.104"};
/**
* Calls {@link ChannelHandlerContext#fireChannelRead(Object)} to forward to
* the next {@link ChannelHandler} in the {@link ChannelPipeline}.
* <p>
* Sub-classes may override this method to change behavior.
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg;
// 如果是握手请求消息,处理,其它消息透传
if (message.getHeader() != null
&& message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.LOGIN_REQ
.value()) {
String nodeIndex = ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString();
NettyMessage loginResp = null;
// 重复登陆,拒绝
if (nodeCheck.containsKey(nodeIndex)) {
loginResp = buildResponse((byte) -1);
} else {
InetSocketAddress address = (InetSocketAddress) ctx.channel()
.remoteAddress();
String ip = address.getAddress().getHostAddress();
boolean isOK = false;
for (String WIP : whitekList) {
if (WIP.equals(ip)) {
isOK = true;
break;
}
}
loginResp = isOK ? buildResponse((byte) 0)
: buildResponse((byte) -1);
if (isOK)
nodeCheck.put(nodeIndex, true);
}
System.out.println("登录响应是:"+loginResp+" body :"+loginResp.getBody());
ctx.writeAndFlush(loginResp);
} else {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}
private NettyMessage buildResponse(byte result) {
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(MessageType.LOGIN_RESP.value());
message.setHeader(header);
message.setBody(result);
return message;
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
nodeCheck.remove(ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString());// 删除缓存
ctx.close();
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
}
这里首先定义了重复登录保护和IP认证白名单列表,主要用于提升握手的可靠性。在channelRead方法中用于接入认证,首先根据客户端的源地址进行重复登录判断,如果已经成功登录,拒绝重复登录,以防止由于客户端重复登录导致句柄泄露。然后通过ChannelHandlerContext的Channel接口获取客户端的InetSocketAddress地址,从中取得发送方的源地址信息,通过源地址进行白名单校验,最后通过buildResponse方法构造握手应答消息返回给客户端。当发生异常时,需要将客户端信息从登录注册表中去注册,以保证后续客户端可以重连成功。
心跳检测机制
握手成功后由客户端主动发送心跳消息,服务端接收到心跳消息后,返回心跳应答消息。由于心跳消息的目的是为了检测链路的可用性,因此不需要携带消息体。
客户端发送心跳消息请求代码如下:
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import proprietary.protocol.dao.Header;
import proprietary.protocol.dao.NettyMessage;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 客户端心跳消息
*/
public class HeartBeatReqHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
// private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(HeartBeatReqHandler.class);
//使用定时任务发送
private volatile ScheduledFuture<?> heartBeat;
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg;
// 当握手成功后,Login响应向下透传,主动发送心跳消息
if (message.getHeader() != null
&& message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.LOGIN_RESP
.value()) {
//NioEventLoop是一个Schedule,因此支持定时器的执行,创建心跳计时器
heartBeat = ctx.executor().scheduleAtFixedRate(
new HeartBeatReqHandler.HeartBeatTask(ctx), 0, 5000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else if (message.getHeader() != null
&& message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.HEARTBEAT_RESP
.value()) {
System.out.println("客户端接收服务器心跳消息--------->"+message);
// LOG.info("Client receive server heart beat message : ---> "
// + message);
} else
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
//Ping消息任务类
private class HeartBeatTask implements Runnable {
private final ChannelHandlerContext ctx;
public HeartBeatTask(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
this.ctx = ctx;
}
@Override
public void run() {
NettyMessage heatBeat = buildHeatBeat();
// LOG.info("Client send heart beat messsage to server : ---> "
// + heatBeat);
System.out.println("客户端将心跳信息发送到服务器------>"+heatBeat);
ctx.writeAndFlush(heatBeat);
}
private NettyMessage buildHeatBeat() {
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(MessageType.HEARTBEAT_REQ.value());
message.setHeader(header);
return message;
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
if (heartBeat != null) {
heartBeat.cancel(true);
heartBeat = null;
}
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
}
当握手成功后,握手请求Handler会继续将握手成功消息进行向下传递,HeartBeatReqHandler接收到之后对消息进行判断,如果是握手成功消息,则启动无限循环定时器用于定期发送心跳消息。

为了统一在一个Handler中处理所有心跳消息,因此下面用于接收服务端发送心跳应答消息,并打印客户端接收和发送的心跳消息。

服务端的心跳应答Handler:
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import proprietary.protocol.dao.Header;
import proprietary.protocol.dao.NettyMessage;
/**
* 服务端的心跳应答Handler:
*/
public class HeartBeatRespHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
// private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(HeartBeatRespHandler.class);
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
NettyMessage message = (NettyMessage) msg;
// 返回心跳应答消息
if (message.getHeader() != null
&& message.getHeader().getType() == MessageType.HEARTBEAT_REQ
.value()) {
// LOG.info("Receive client heart beat message : ---> "
// + message);
System.out.println("接收客户心跳信息:--->"+message);
NettyMessage heartBeat = buildHeatBeat();
// LOG.info("Send heart beat response message to client : ---> "
// + heartBeat);
System.out.println("向客户发送心跳响应信息:--->"+heartBeat);
ctx.writeAndFlush(heartBeat);
} else
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
private NettyMessage buildHeatBeat() {
NettyMessage message = new NettyMessage();
Header header = new Header();
header.setType(MessageType.HEARTBEAT_RESP.value());
message.setHeader(header);
return message;
}
}
服务端的心跳Handler在接收到心跳请求消息之后,构造心跳应答消息返回,并打印接收和发送的心跳消息。
public enum MessageType {
LOGIN_REQ((byte)3),
LOGIN_RESP((byte)4),
HEARTBEAT_REQ((byte)5),
HEARTBEAT_RESP((byte)6),
;
public byte value;
MessageType(byte v){
this.value = v;
}
public byte value(){
return value;
}
}public final class NettyConstant {
public static final String REMOTEIP = "127.0.0.1";
public static final int PORT = 8080;
public static final int LOCAL_PORT = 12088;
public static final String LOCALIP = "127.0.0.1";
}
客户端代码
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.ReadTimeoutHandler;
import proprietary.protocol.*;
import proprietary.protocol.NettyMessageDecoder;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 客户端
*/
public class NettyClient {
// private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(NettyClient.class);
private ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors
.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
public void connect(int port, String host) throws Exception {
// 配置客户端NIO线程组
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new NettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4));
ch.pipeline().addLast("MessageEncoder",
new NettyMessageEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("readTimeoutHandler",
new ReadTimeoutHandler(50));
ch.pipeline().addLast("LoginAuthHandler",
new LoginAuthReqHandler());
ch.pipeline().addLast("HeartBeatHandler",
new HeartBeatReqHandler());
}
});
// 发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture future = b.connect(
new InetSocketAddress(host, port),
new InetSocketAddress(NettyConstant.LOCALIP,
NettyConstant.LOCAL_PORT)).sync();
// 当对应的channel关闭的时候,就会返回对应的channel。
// Returns the ChannelFuture which will be notified when this channel is closed. This method always returns the same future instance.
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 所有资源释放完成之后,清空资源,再次发起重连操作
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
try {
connect(NettyConstant.PORT, NettyConstant.REMOTEIP);// 发起重连操作
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
/**
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new NettyClient().connect(NettyConstant.PORT, NettyConstant.REMOTEIP);
}
}
此处用于Netty消息解码,为了防止由于单条消息国道导致内存溢出或者畸形码流导致解码错位引起内存分配失败,这里对单条消息做了最大长度进行上限限制。
![]()
这是新增了Netty消息解码器,用于协议消息的自动编码。随后依次增加了读超时Handler,握手请求Handler和心跳Handler。
利用Netty的ChannelPipeline和ChannelHandler机制,可以非常方便地实现功能解耦和业务产品的定制。通过Handler Chain的机制可以方便地实现切面拦截和定制,相比于AOP它的性能更高。
服务端代码
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.ReadTimeoutHandler;
import proprietary.protocol.*;
import proprietary.protocol.NettyMessageDecoder;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 服务端
*/
public class NettyServer {
// private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(NettyServer.class);
public void bind() throws Exception {
// 配置服务端的NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws IOException {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new NettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyMessageEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("readTimeoutHandler",
new ReadTimeoutHandler(50));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoginAuthRespHandler());
ch.pipeline().addLast("HeartBeatHandler",
new HeartBeatRespHandler());
}
});
// 绑定端口,同步等待成功
b.bind(NettyConstant.REMOTEIP, NettyConstant.PORT).sync();
System.out.println("Netty服务启动正常:"+(NettyConstant.REMOTEIP + " : " + NettyConstant.PORT));
// LOG.info("Netty server start ok : "
// + (NettyConstant.REMOTEIP + " : " + NettyConstant.PORT));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new NettyServer().bind();
}
}

将服务端关闭后:
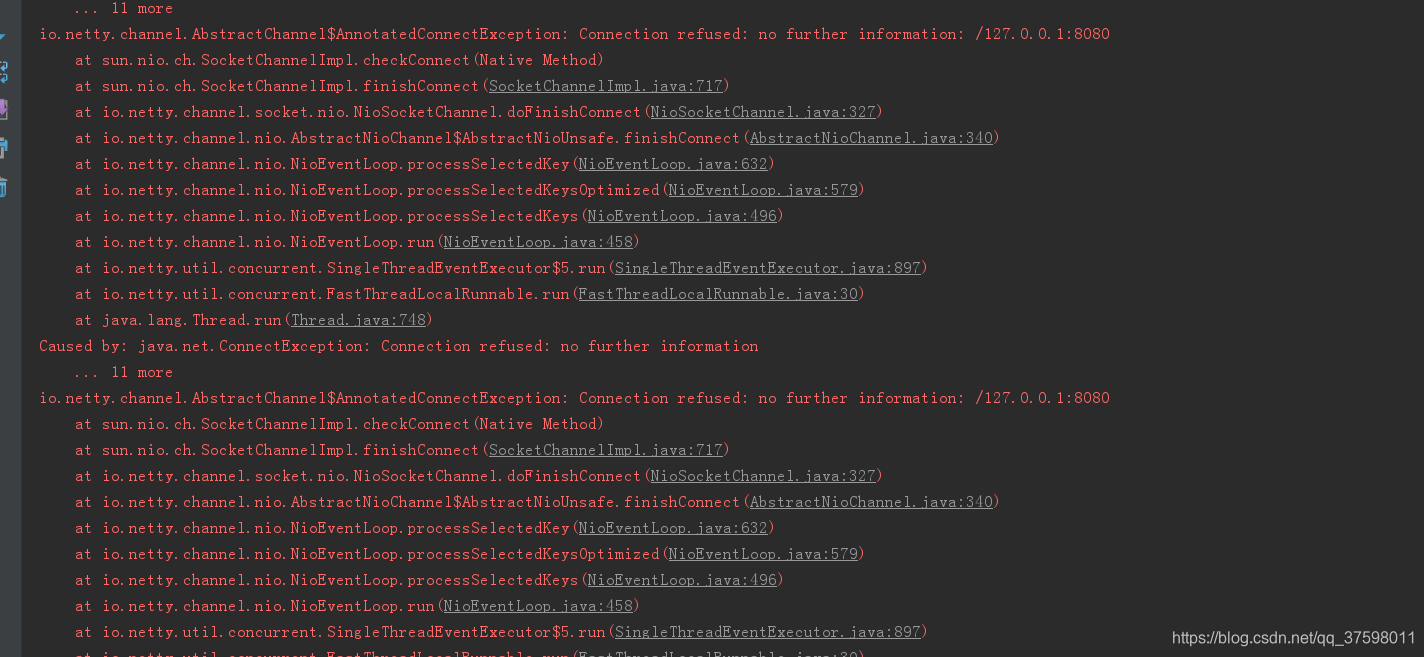
重试机制!!!!!!!
参考《Netty权威指南》