考试排名
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 19617 Accepted Submission(s): 6788
Problem Description
C++编程考试使用的实时提交系统,具有即时获得成绩排名的特点。它的功能是怎么实现的呢?
我们做好了题目的解答,提交之后,要么“AC”,要么错误,不管怎样错法,总是给你记上一笔,表明你曾经有过一次错误提交,因而当你一旦提交该题“AC”后,就要与你算一算帐了,总共该题错误提交了几回。虽然你在题数上,大步地跃上了一个台阶,但是在耗时上要摊上你共花去的时间。特别是,曾经有过的错误提交,每次都要摊上一定的单位时间分。这样一来,你在做出的题数上,可能领先别人很多,但是,在做出同样题数的人群中,你可能会在耗时上处于排名的劣势。
例如:某次考试一共8题(A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H),每个人做的题都在对应的题号下有个数量标记,负数表示该学生在该题上有过的错误提交次数,但到现在还没有AC,正数表示AC所耗的时间,如果正数a跟上一对括号,里面有个整数b,那就表示该学生提交该题AC了,耗去了时间a,同时,曾经错误提交了b次,因此对于下述输入数据: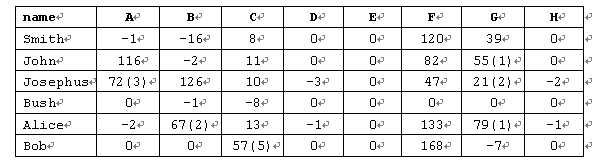
若每次错误提交的罚分为20分,则其排名从高到低应该是这样的:
Josephus 5 376
John 4 284
Alice 4 352
Smith 3 167
Bob 2 325
Bush 0 0
Input
输入数据的第一行是考试题数n(1≤n≤12)以及单位罚分数m(10≤m≤20),每行数据描述一个学生的用户名(不多于10个字符的字串)以及对所有n道题的答题现状,其描述采用问题描述中的数量标记的格式,见上面的表格,提交次数总是小于100,AC所耗时间总是小于1000。
Output
将这些学生的考试现状,输出一个实时排名。实时排名显然先按AC题数的多少排,多的在前,再按时间分的多少排,少的在前,如果凑巧前两者都相等,则按名字的字典序排,小的在前。每个学生占一行,输出名字(10个字符宽),做出的题数(2个字符宽,右对齐)和时间分(4个字符宽,右对齐)。名字、题数和时间分相互之间有一个空格。

题意:模拟ACM比赛实时排名,优先级为:解题数 > 所耗时间 > 字典序
虽然是水题,但还是考验了一下字符处理能力和优先级定义能力的,最终结果需要重定向文件读入才能看。
AC Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<cctype>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<list>
#define mod 998244353
#define Max 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Min 0xc0c0c0c0
#define mst(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define f(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 5;
int indegree[1005];
struct Node{
char name[15];
int solve, times;
}G[1005];
bool cmp(Node a, Node b){
if(a.solve == b.solve){
if(a.times == b.times){
return strcmp(a.name, b.name) < 0;
}
return a.times < b.times;
}
return a.solve > b.solve;
}
int main(){
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n, m;
int index = 0;
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
while(scanf("%s", G[index].name) != EOF){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int v;
scanf("%d", &v);
if(v > 0){
G[index].times += v;
G[index].solve++;
char ch = getchar();
if(ch == '('){
scanf("%d", &v);
G[index].times += v * m;
getchar();
}
}
}
index++;
}
sort(G, G + index, cmp);
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++){
printf("%-10s %2d %4d\n", G[i].name, G[i].solve, G[i].times);
}
//system("pause");
return 0;
}