转载注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lucasysfeng/p/4847662.html
上一讲地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lucasysfeng/p/5036562.html
项目地址:https://github.com/lucasysfeng/lucasOS
我们知道,内存管理是操作系统的重要组成部分,在学习内存管理之前,首先要解决一个问题:如何获取物理内存?在前几讲我们谈到,内核是由GRUB启动的,因此要在内核中获取物理内存时,我们可以通过GRUB获取。
multiboot_t结构体
GRUB将内存的分布放到了multiboot_t结构体里,关于该结构体的相关信息和字段介绍可以看这里http://www.uruk.org/orig-grub/boot-proposal.html,该结构体如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
typedef
struct
multiboot_t
{
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t mem_lower;
uint32_t mem_upper;
uint32_t boot_device;
uint32_t cmdline;
uint32_t mods_count;
uint32_t mods_addr;
uint32_t num;
uint32_t size;
uint32_t addr;
uint32_t shndx;
uint32_t mmap_length;
uint32_t mmap_addr;
uint32_t drives_length;
uint32_t drives_addr;
uint32_t config_table;
uint32_t boot_loader_name;
uint32_t apm_table;
uint32_t vbe_control_info;
uint32_t vbe_mode_info;
uint32_t vbe_mode;
uint32_t vbe_interface_seg;
uint32_t vbe_interface_off;
uint32_t vbe_interface_len;
}__attribute__((packed)) multiboot_t;
|
我们没有必要了解每个字段,重点来关注下mmap_addr和mmap_length, mmap_addr是缓冲区的地址,mmap_length是缓冲区的总大小。缓冲区由一个或者多个下面的结构对组成:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
typedef
struct
mmap_entry_t
{
uint32_t size;
uint32_t base_addr_low;
uint32_t base_addr_high;
uint32_t length_low;
uint32_t length_high;
uint32_t type;
}__attribute__((packed)) mmap_entry_t;
|
size是相关结构的大小,单位是字节,它可能大于最小值20. base_addr_low是启动地址的低32位,base_addr_high是高32位,启动地址总共有64位。length_low是内存区域大小的低32位,length_high是内存区域大小的高32位,总共是64位。type是相应地址区间的类型,1代表可用RAM,所有其它的值代表保留区域。
获取物理内存
我们在内核代码里打印出地址,如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
void
show_memory_map()
{
uint32_t mmap_addr = glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_addr;
uint32_t mmap_length = glb_mboot_ptr->mmap_length;
mmap_entry_t *mmap = (mmap_entry_t *) mmap_addr;
for
(mmap = (mmap_entry_t *) mmap_addr;
(uint32_t) mmap < mmap_addr + mmap_length; mmap++)
{
print_hex((uint32_t) mmap->base_addr_low);
print_char(
'\n'
);
}
}
|
编译和运行
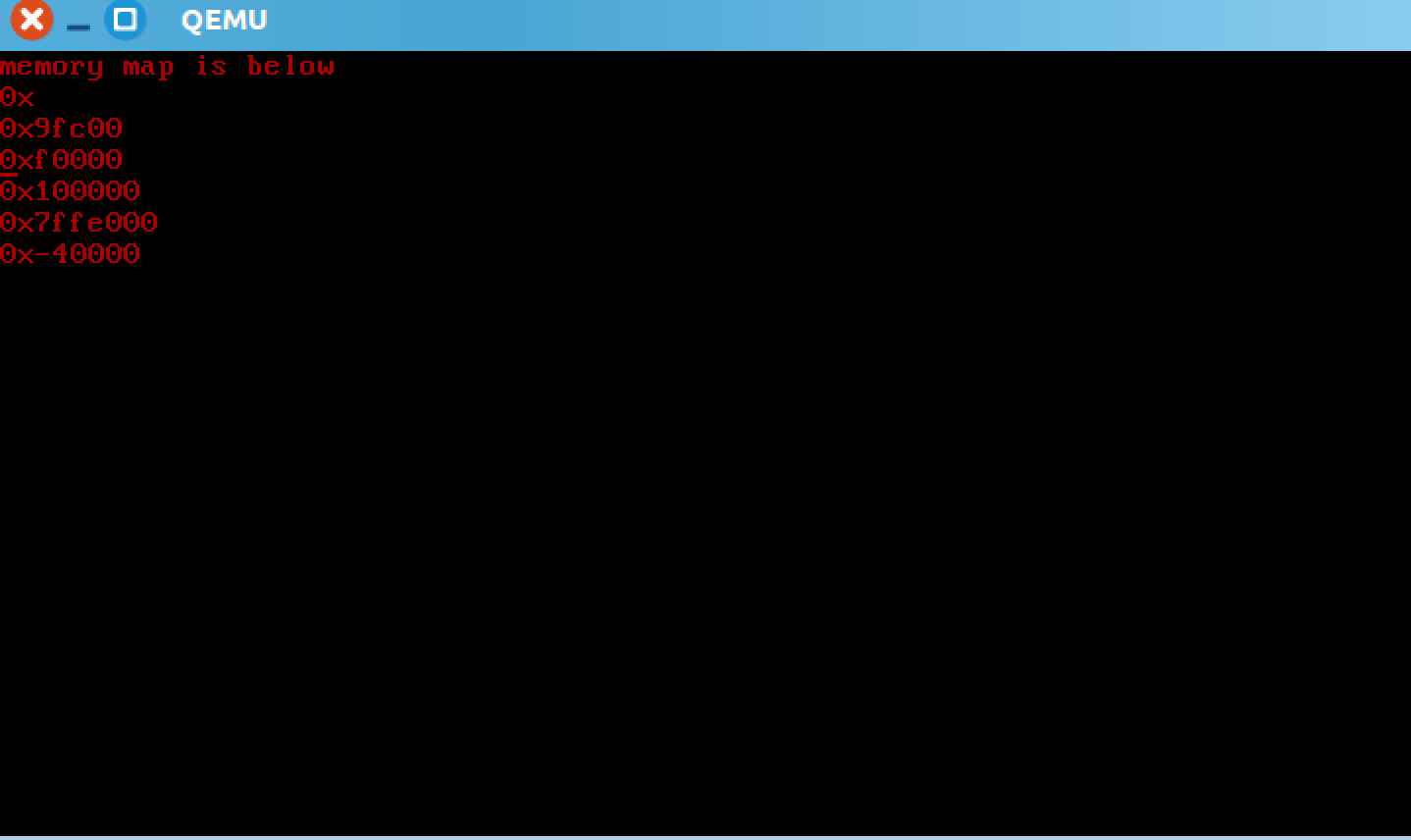
我们使用qemu启动虚拟机。
$ make
$ make qemu
make后会生成kernel内核,并将内核拷贝到lucasOS.img中,运行make qemu就会加载lucasOS.img,并出现下面窗口,表示成功了:
代码获取
本系列GitHub地址 https://github.com/lucasysfeng/lucasOS,本讲的代码是code/chapter4.