1.AboutException.java
源代码:
package 动手动脑; import javax.swing.*; publicclass AboutException { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { inti=1, j=0, k; k=i/j; try { k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception //throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!"); } catch ( ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { if (einstanceof ArithmeticException) System.out.println("被0除"); else { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } finally { JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK"); } } }
运行截图:
Try中监测“k=i/j;”这一语句,当j等于0时给出错误。
2
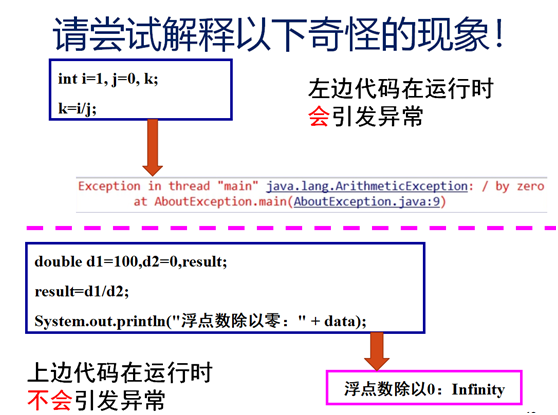
这是因为两段程序在编译之后生成的是不同的字节码指令,JVM在具体实现这两个指令时采用的是不同的方法,所以会出现不同的结果。
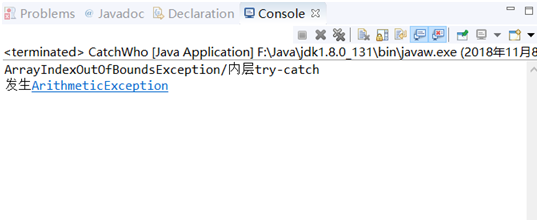
3.CatchWho.java
package 动手动脑; publicclass CatchWho { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { try { try { thrownew ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } thrownew ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
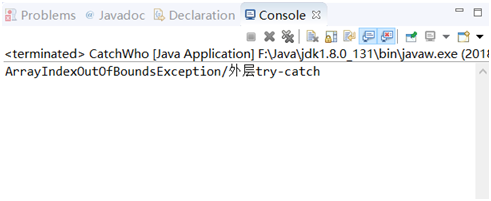
4CatchWho2.java
public class CatchWho2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
5 EmbededFinally.Java
public class EmbededFinally { public static void main(String args[]) { int result; try { System.out.println("in Level 1"); try { System.out.println("in Level 2"); // result=100/0; //Level 2 try { System.out.println("in Level 3"); result=100/0; //Level 3 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 3 finally"); } // result=100/0; //Level 2 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 2 finally"); } // result = 100 / 0; //level 1 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { . System.out.println("In Level 1 finally"); } } }

6SystemExitAndFinally.java
public class SystemExitAndFinally { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ System.out.println("in main"); throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main"); //System.exit(0); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); System.exit(0); } finally { System.out.println("in finally"); } } }
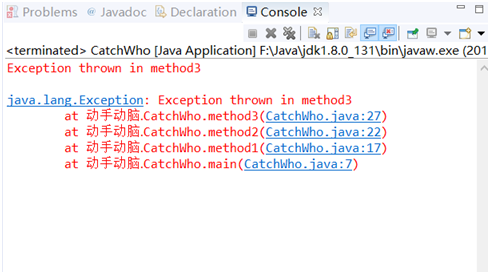
7PrintExceptionStack.java
// UsingExceptions.java // Demonstrating the getMessage and printStackTrace // methods inherited into all exception classes. public class PrintExceptionStack { public static void main( String args[] ) { try { method1(); } catch ( Exception e ) { System.err.println( e.getMessage() + "\n" ); e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void method1() throws Exception { method2(); } public static void method2() throws Exception { method3(); } public static void method3() throws Exception { throw new Exception( "Exception thrown in method3" ); } }