Yarn之ResourceManager详细分析笔记(一)
http://zengzhaozheng.blog.51cto.com/8219051/1438204/
2014-07-15 08:58:18
http://zengzhaozheng.blog.51cto.com/8219051/1438204
一、概述
本文将介绍ResourceManager在Yarn中的功能作用,从更细的粒度分析RM内部组成的各个组件功能和他们相互的交互方式。
二、ResourceManager的交互协议与基本职能
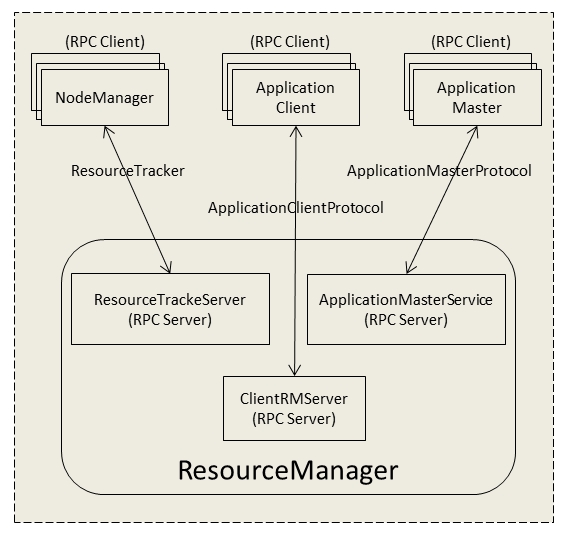
1、ResourceManager交互协议
在整个Yarn框架中主要涉及到7个协议,分别是ApplicationClientProtocol、MRClientProtocol、ContainerManagementProtocol、ApplicationMasterProtocol、ResourceTracker、LocalizationProtocol、TaskUmbilicalProtocol,这些协议封装了各个组件交互的信息。ResourceManager现实功能需要和NodeManager以及ApplicationMaster进行信息交互,其中涉及到的RPC协议有ResourceTrackerProtocol、ApplicationMasterProtocol和ResourceTrackerProtocol。
-
ResourceTracker
NodeManager通过该协议向ResourceManager中注册、汇报节点健康情况以及Container的运行状态,并且领取ResourceManager下达的重新初始化、清理Container等命令。NodeManager和ResourceManager这种RPC通信采用了和MRv1类似的“pull模型”(ResourceManager充当RPC server角色,NodeManager充当RPC client角色),NodeManager周期性主动地向ResourceManager发起请求,并且领取下达给自己的命令。
-
ApplicationMasterProtocol
应用程序的ApplicationMaster同过该协议向ResourceManager注册、申请和释放资源。该协议和上面协议同样也是采用了“pull模型”,其中在RPC机制中,ApplicationMaster充当RPC client角色,ResourceManager充当RPC server角色。
-
ApplicationClientProtocol
-
客户端通过该协议向ResourceManager提交应用程序、控制应用程序(如杀死job)以及查询应用程序的运行状态等。在该RPC 协议中应用程序客户端充当RPC client角色,ResourceManager充当RPC server角色。
整理一下ResourceManager与NodeManager、ApplicationMaster和客户端RPC协议交互的信息:
上图中的ResourceTrackeServer、ApplicationMasterService 、ClientRMServer是ResourceManager中处理上述功能的组件。
1、ResourceManager基本职能
ResourceManager基本职能概括起来就以下几方面:
-
与客户端进行交互,处理来自于客户端的请求,如查询应用的运行情况等。
-
启动和管理各个应用的ApplicationMaster,并且为ApplicationMaster申请第一个Container用于启动和在它运行失败时将它重新启动。
-
管理NodeManager,接收来自NodeManager的资源和节点健康情况汇报,并向NodeManager下达管理资源命令,例如kill掉某个container。
-
资源管理和调度,接收来自ApplicationMaster的资源申请,并且为其进行分配。这个是它的最重要的职能。
三、ResourceManager内部组成架构分析
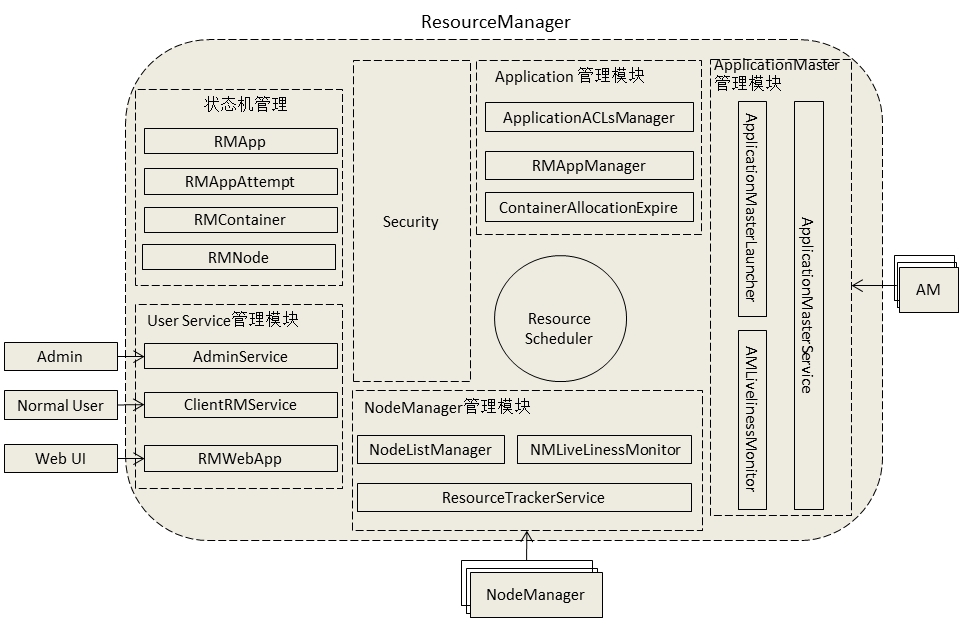
ResourceManager在底层代码实现上将各个功能模块分的比较细,各个模块功能具有很强的独立性。下图所示的是ResourceManager中的大概的功能模块组成:
1、用户交互模块
用户交互模块即上图显示的User Service管理模块。在这里边还可以看到根据不同的用户类型启用了不同的服务进行处理,AdminService处理管理员相关请求,ClientRMService处理普通客户相关请求,这样使得管理员不会因为普通客户请求太多而造成堵塞。下面看看这2个服务的具体实现代码:
-
ClientRMService
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
|
从上面ClientRMService的基本代码架构我们可以看出:
(1)ClientRMService是一个RPC Server,主要为来自于普通客户端的各种RPC请求。从代码实现的角度看,它是ApplicationClientProtocol协议的一个实现。
(2)之前我们已经说了,普通用户可以通过该服务来获得正在运行应用程序的相关信息,如进度情况、应用程序列表等。上面代码中都将ResourceManager运行信息封装在RMContxt接口中了,下面来看看这个接口的一个实现对象RMContextImpl:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
|
-
AdminService
AdminService和ClientRMService一样都是作为RPC的服务端,它针对的处理管理员RPC请求,负责访问权限的控制,中Yarn中管理员权限的设定可以在yarn-site.xml中yarn.admi.acl项进行设置,该项的默认值是*,也就是说如果不进行设置的话就当所有的用户都是管理员。从代码上看,它是ResourceManagerAdministrationProtocol协议的一个实现:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
|
AdminService代码和ClientRMService比较相似,它各类功能对象也差不多。
2、NodeManager管理
NodeManager主要是通过NMLivelinessMonitor、ResourceTrackerService和NodeListManager这3大组件来对NodeManager的生命周期、心跳处理以及黑名单处理。
(1)ResourceTrackerService
ResourceTrackerService是RPC协议ResourceTracker的一个实现,它作为一个RPC Server端接收NodeManager的RPC请求,请求主要包含2种信息,注册NodeManager和处理心跳信息。NodeManger启动时第一件事就是像ResourceManager注册,注册时NodeManager发给ResourceTrackerService的RPC包主要包含NodeManager所在节点的可用资源总量、对外开放的htpp端口、节点的host和port等信息,具体代码看ResourceTrackerService#registerNodeManager方法:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
ResourceTrackerService另外一种功能就是处理心跳信息了,当NodeManager启动后,它会周期性地调用RPC函数ResourceTracker#nodeHeartbeat汇报心跳,心跳信息主要包含该节点的各个Container的运行状态、正在运行的Application列表、节点的健康状况等,随后ResourceManager为该NodeManager返回需要释放的Container列表、Application列表等信息。其中心跳信息处理的流程:首先,从NodeManager发来的心跳包中获得节点的状态状态信息,然后检测该节点是否已经注册过,然后检测该节点的host名称是否合法,例如是否在excluded列表中,然后再检测该次心跳是不是第一次心跳信息,这点非常重要,因为关系到心跳的重复发送与应答的相关问题。其实ResourceTrackerService和NodeManager的心跳处理机制和之前Hadoop1.x中的JobTracker与TaskTacker之间的心跳处理很想象,具体请看我之前写的一篇blog:http://zengzhaozheng.blog.51cto.com/8219051/1359887 ,再然后,为NodeManager返回心跳应答信息,最后,想RMNode发送该NodeManager的状态信息并且保存最近一次心跳应答信息。再具体看看ResourceTracker#nodeHeart方法:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 |
|
(2)NodeListManager
NodeListManager主要分管黑名单(include列表)和白名单(exlude列表)管理功能,分别有yarnresouecemanager.nodes.include-path和yarnresourcemanager.nodes.exclude-path指定。黑名单列表中的nodes不能够和RM直接通信(直接抛出RPC异常),管理员可以对这两个列表进行编辑,然后使用$HADOOP_HOME/bin/yarn rmadmin-refreshNodes动态加载修改后的列表,使之生效。
(3)NMLivelinessMonitor
NMLivelinessMonitor主要是分管心跳异常请求。该服务会周期性地遍历集群中的所有NodeManager,如果某个NodeManager在一定时间内(默认10min,可以有参数yarn.nm.liveness-monitor.expiry-interval-ms配置)没有进行心跳汇报,那么则认为它已经死掉,同时在该节点上运行的Container也会被置为运行失败释放资源。那么这些被置为失败的Container是不会直接被RM分配执行的,RM只是负责将这些被置为失败的Container信息告诉它们所对应的ApplicationMaster,需不需要重新运行它说的算,如果需要从新运行的话,该ApplicationMaster要从新向RM申请资源,然后由ApplicationMaster与对应的NodeManager通信以从新运行之前失败的Container。
2、ApplicationMaster管理模块
后面部分请看:http://zengzhaozheng.blog.51cto.com/8219051/1542067
本文出自 “蚂蚁” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://zengzhaozheng.blog.51cto.com/8219051/1438204