接着上篇的博客,我们获取imdb和roidb的数据后,就可以搭建网络进行训练了。
我们回到trian_rpn()函数里面,此时运行完了roidb, imdb = get_roidb(imdb_name),取得了imdb和roidb数据。
先进入第一阶段的训练:
print '~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~' print 'Stage 1 RPN, init from ImageNet model' print '~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~' cfg.TRAIN.SNAPSHOT_INFIX = 'stage1' mp_kwargs = dict( queue=mp_queue, imdb_name=args.imdb_name, init_model=args.pretrained_model, solver=solvers[0], max_iters=max_iters[0], cfg=cfg) p = mp.Process(target=train_rpn, kwargs=mp_kwargs) ##创建线程对象 p.start() ##开始进程 rpn_stage1_out = mp_queue.get() ##从进程里面获取运行结果 p.join() ##等待子进程结束
进入子进程train_rpn:
def train_rpn(queue=None, imdb_name=None, init_model=None, solver=None, max_iters=None, cfg=None): """Train a Region Proposal Network in a separate training process. """ # Not using any proposals, just ground-truth boxes cfg.TRAIN.HAS_RPN = True cfg.TRAIN.BBOX_REG = False # applies only to Fast R-CNN bbox regression cfg.TRAIN.PROPOSAL_METHOD = 'gt' cfg.TRAIN.IMS_PER_BATCH = 1 print 'Init model: {}'.format(init_model) print('Using config:') pprint.pprint(cfg) import caffe _init_caffe(cfg) roidb, imdb = get_roidb(imdb_name) ##获取roidb和imdb格式的数据集 print 'roidb len: {}'.format(len(roidb)) output_dir = get_output_dir(imdb) ##训练的输出路径:'py-faster-rcnn/output/faster_rcnn_alt_opt/voc_2007_trainval' print 'Output will be saved to `{:s}`'.format(output_dir) model_paths = train_net(solver, roidb, output_dir, ##进入训练网络,其实里面还包裹了一层solver,定义该对象之后才进行训练。 pretrained_model=init_model, max_iters=max_iters) # Cleanup all but the final model for i in model_paths[:-1]: ##除了最后一个快照,把所有其他的快照都清除掉 os.remove(i) rpn_model_path = model_paths[-1] # Send final model path through the multiprocessing queue queue.put({'model_path': rpn_model_path}) ##将最后的快照保存到线程里面,进行线程通信。
接着我们运行到了model_paths = train_net(solver, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model=init_model, max_iters=max_iters)函数,我们进入该函数里面看看:
def train_net(solver_prototxt, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model=None, max_iters=40000): """Train a Fast R-CNN network.""" roidb = filter_roidb(roidb) ##过滤部分roidb,具体判断一个图片的roidb是否合格:前景大于某个值,背景在某个范围内,不符合则过滤掉 sw = SolverWrapper(solver_prototxt, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model=pretrained_model) print 'Solving...' model_paths = sw.train_model(max_iters) ##开始训练函数 print 'done solving' return model_paths
接着我们进入sw = SolverWrapper(solver_prototxt, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model=pretrained_model) 函数:
class SolverWrapper(object): """A simple wrapper around Caffe's solver. This wrapper gives us control over he snapshotting process, which we use to unnormalize the learned bounding-box regression weights. """ def __init__(self, solver_prototxt, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model=None): """Initialize the SolverWrapper.""" self.output_dir = output_dir if (cfg.TRAIN.HAS_RPN and cfg.TRAIN.BBOX_REG and cfg.TRAIN.BBOX_NORMALIZE_TARGETS): # RPN can only use precomputed normalization because there are no # fixed statistics to compute a priori assert cfg.TRAIN.BBOX_NORMALIZE_TARGETS_PRECOMPUTED if cfg.TRAIN.BBOX_REG: print 'Computing bounding-box regression targets...' self.bbox_means, self.bbox_stds = \ rdl_roidb.add_bbox_regression_targets(roidb) print 'done' self.solver = caffe.SGDSolver(solver_prototxt) ##该函数主要是用来建造层的,这里建立ROI层和anchors层 if pretrained_model is not None: ##如果存在'data/imagenet_models/ZF.v2.caffemodel'则加载进来 print ('Loading pretrained model ' 'weights from {:s}').format(pretrained_model) self.solver.net.copy_from(pretrained_model) self.solver_param = caffe_pb2.SolverParameter() with open(solver_prototxt, 'rt') as f: ##加载py-faster-rcnn/models/pascal_voc/ZF/faster_rcnn_alt_opt/stage1_rpn_solver60k80k.pt文件参数 pb2.text_format.Merge(f.read(), self.solver_param) self.solver.net.layers[0].set_roidb(roidb) ##创建该包裹对象的时候把外部的roidb设置进包裹函数的self.solver.net.layers[0]里面,用以训练 def snapshot(self): """Take a snapshot of the network after unnormalizing the learned bounding-box regression weights. This enables easy use at test-time. """ net = self.solver.net scale_bbox_params = (cfg.TRAIN.BBOX_REG and cfg.TRAIN.BBOX_NORMALIZE_TARGETS and net.params.has_key('bbox_pred')) if scale_bbox_params: # save original values orig_0 = net.params['bbox_pred'][0].data.copy() orig_1 = net.params['bbox_pred'][1].data.copy() # scale and shift with bbox reg unnormalization; then save snapshot net.params['bbox_pred'][0].data[...] = \ (net.params['bbox_pred'][0].data * self.bbox_stds[:, np.newaxis]) net.params['bbox_pred'][1].data[...] = \ (net.params['bbox_pred'][1].data * self.bbox_stds + self.bbox_means) infix = ('_' + cfg.TRAIN.SNAPSHOT_INFIX if cfg.TRAIN.SNAPSHOT_INFIX != '' else '') filename = (self.solver_param.snapshot_prefix + infix + '_iter_{:d}'.format(self.solver.iter) + '.caffemodel') filename = os.path.join(self.output_dir, filename) net.save(str(filename)) print 'Wrote snapshot to: {:s}'.format(filename) if scale_bbox_params: # restore net to original state net.params['bbox_pred'][0].data[...] = orig_0 net.params['bbox_pred'][1].data[...] = orig_1 return filename def train_model(self, max_iters):...
def get_training_roidb(imdb):...
def filter_roidb(roidb): ...
def train_net(solver_prototxt, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model=None, max_iters=40000):...
这里我们可以发现SolverWrapper是一个类,作者这里使用新的solverwrapper来包裹原来的solver,这样就能在原来的基础上添加部分功能。以便于控制了网络的快照过程,以用来对bounding-box 回归的权重进行非归一化。
该类的核心语句其实就是self.solver = caffe.SGDSolver(solver_prototxt),这里的solver_prototxt=py-faster-rcnn/tools/../lib/roi_data_layer;
上面的SGDSolver函数里面创建类class RoIDataLayer(caffe.Layer),该类是caffe layer的一个扩展实现,用于fast rcnn训练。
进入该层class RoIDataLayer(caffe.Layer)看看:
class RoIDataLayer(caffe.Layer): """Fast R-CNN data layer used for training.""" def _shuffle_roidb_inds(self):...def _get_next_minibatch_inds(self):... def _get_next_minibatch(self):...def set_roidb(self, roidb):... def setup(self, bottom, top): """Setup the RoIDataLayer.""" # parse the layer parameter string, which must be valid YAML layer_params = yaml.load(self.param_str_) ##获取该层的参数 layer_params={'num_classes': 21} self._num_classes = layer_params['num_classes'] self._name_to_top_map = {} # data blob: holds a batch of N images, each with 3 channels idx = 0 top[idx].reshape(cfg.TRAIN.IMS_PER_BATCH, 3, max(cfg.TRAIN.SCALES), cfg.TRAIN.MAX_SIZE) self._name_to_top_map['data'] = idx idx += 1 if cfg.TRAIN.HAS_RPN: top[idx].reshape(1, 3) self._name_to_top_map['im_info'] = idx idx += 1 top[idx].reshape(1, 4) self._name_to_top_map['gt_boxes'] = idx idx += 1 else: # not using RPN # rois blob: holds R regions of interest, each is a 5-tuple # (n, x1, y1, x2, y2) specifying an image batch index n and a # rectangle (x1, y1, x2, y2) top[idx].reshape(1, 5) self._name_to_top_map['rois'] = idx idx += 1 # labels blob: R categorical labels in [0, ..., K] for K foreground # classes plus background top[idx].reshape(1) self._name_to_top_map['labels'] = idx idx += 1 if cfg.TRAIN.BBOX_REG: # bbox_targets blob: R bounding-box regression targets with 4 # targets per class top[idx].reshape(1, self._num_classes * 4) self._name_to_top_map['bbox_targets'] = idx idx += 1 # bbox_inside_weights blob: At most 4 targets per roi are active; # thisbinary vector sepcifies the subset of active targets top[idx].reshape(1, self._num_classes * 4) self._name_to_top_map['bbox_inside_weights'] = idx idx += 1 top[idx].reshape(1, self._num_classes * 4) self._name_to_top_map['bbox_outside_weights'] = idx idx += 1 print 'RoiDataLayer: name_to_top:', self._name_to_top_map assert len(top) == len(self._name_to_top_map) def forward(self, bottom, top):...
def backward(self, top, propagate_down, bottom):... def reshape(self, bottom, top):...
对于上面我们主要分析下setup函数,我们这里设置了RPN层,所以结构上有三个输入:data(1 3 600 1000)、im_info(1 3)、gt_boxes(1 4)
RoiDataLayer: name_to_top: {'gt_boxes': 2, 'data': 0, 'im_info': 1}
rpn_cls_score_rpn_cls_score_0_split:1 18 39 64 ##9个anchors × 2个前后景
rpn_cls_score_reshape:1 2 351 64 ##reshape成前后景两类的概率
rpn_bbox_pred:1 36 39 64 ##9个anchors × 4个坐标值
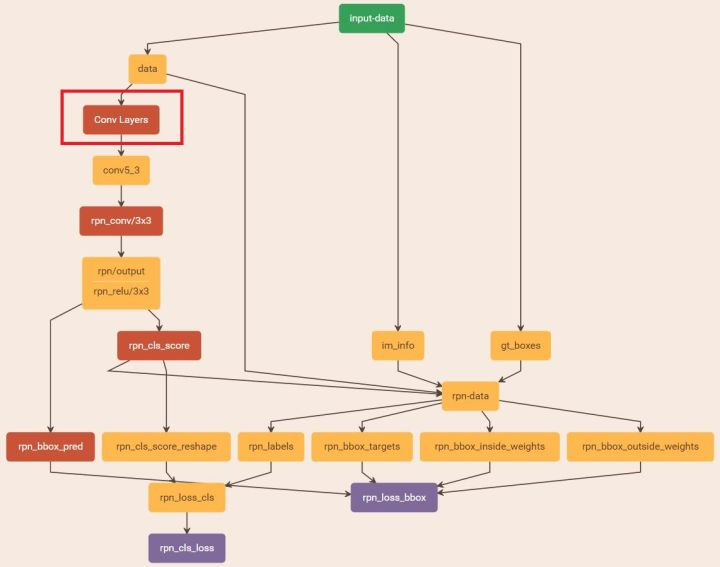
此时系统开始构造该roi网络结构,然后进入类class AnchorTargetLayer(caffe.Layer):
class AnchorTargetLayer(caffe.Layer):
"""
Assign anchors to ground-truth targets. Produces anchor classification
labels and bounding-box regression targets.
"""
def setup(self, bottom, top):
layer_params = yaml.load(self.param_str_) ##获取该层参数layers_params={'feat_stride': 16},这里是anchors的其中一个比例(8,16,32)
anchor_scales = layer_params.get('scales', (8, 16, 32))
self._anchors = generate_anchors(scales=np.array(anchor_scales))
self._num_anchors = self._anchors.shape[0] ##9
self._feat_stride = layer_params['feat_stride'] ##16
if DEBUG:
print 'anchors:'
print self._anchors
print 'anchor shapes:'
print np.hstack((
self._anchors[:, 2::4] - self._anchors[:, 0::4],
self._anchors[:, 3::4] - self._anchors[:, 1::4],
))
self._counts = cfg.EPS
self._sums = np.zeros((1, 4))
self._squared_sums = np.zeros((1, 4))
self._fg_sum = 0
self._bg_sum = 0
self._count = 0
#设为0,则取出任何超过图像边界的proposals,只要超出一点点,都要去除
self._allowed_border = layer_params.get('allowed_border', 0)
height, width = bottom[0].data.shape[-2:] ## 39,64
if DEBUG:
print 'AnchorTargetLayer: height', height, 'width', width
A = self._num_anchors ## 9
# labels
top[0].reshape(1, 1, A * height, width) ##将labels输出层reshape成(1,1,9×39,64)
# bbox_targets
top[1].reshape(1, A * 4, height, width) ##将bbox_targets输出层reshape成(1,9*4,39,64)
# bbox_inside_weights
top[2].reshape(1, A * 4, height, width) ##将bbox_inside_weights输出层reshape成(1,9*4,39,64)
# bbox_outside_weights
top[3].reshape(1, A * 4, height, width) ##将bbox_outside_weights输出层reshape成(1,9*4,39,64)
def forward(self, bottom, top):...def backward(self, top, propagate_down, bottom):...
def reshape(self, bottom, top):...
我们进入self._anchors = generate_anchors(scales=np.array(anchor_scales))函数来产生anchors,进入该函数。该函数主要是产生9个anchors:
def generate_anchors(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2], scales=2**np.arange(3, 6)): """ Generate anchor (reference) windows by enumerating aspect ratios X scales wrt a reference (0, 0, 15, 15) window. """ base_anchor = np.array([1, 1, base_size, base_size]) - 1 ##设置基础anchor,左上坐标为(1,1),右下坐标为(16,16),即宽为15 ratio_anchors = _ratio_enum(base_anchor, ratios) anchors = np.vstack([_scale_enum(ratio_anchors[i, :], scales) for i in xrange(ratio_anchors.shape[0])]) return anchors
进入ratio_anchors = _ratio_enum(base_anchor, ratios)函数:
def _ratio_enum(anchor, ratios): """ Enumerate a set of anchors for each aspect ratio wrt an anchor. """ w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) ##返回一个anchor的宽,高, xy 中心点 (16,16,7.5,7.5) size = w * h ##size=256 size_ratios = size / ratios ##size_ratios =[ 512. 256. 128.],此时ratios=[0.5, 1, 2] ws = np.round(np.sqrt(size_ratios)) ##ws=[23. 16. 11.] hs = np.round(ws * ratios) ##hs=[ 12. 16. 22.] anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) return anchors def _whctrs(anchor): ##返回一个anchor的宽,高, xy 中心点 """ Return width, height, x center, and y center for an anchor (window). """ w = anchor[2] - anchor[0] + 1 h = anchor[3] - anchor[1] + 1 x_ctr = anchor[0] + 0.5 * (w - 1) y_ctr = anchor[1] + 0.5 * (h - 1) return w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr def _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr): ##根据中心点和尺度ws和hs组成的组合,来创建anchors,返回四个坐标点 """ Given a vector of widths (ws) and heights (hs) around a center (x_ctr, y_ctr), output a set of anchors (windows). """ ws = ws[:, np.newaxis] hs = hs[:, np.newaxis] anchors = np.hstack((x_ctr - 0.5 * (ws - 1), y_ctr - 0.5 * (hs - 1), x_ctr + 0.5 * (ws - 1), y_ctr + 0.5 * (hs - 1))) return anchors
建造的anchors如下,行代表三个anchors,列代表2个坐标点(左上xy,右下xy)
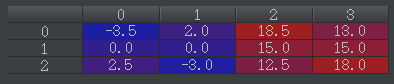
这里得到三个anchors,然后取其中一个anchor为基础建立另三个anchors,另一个anchor为基础建立另三个anchors,这样我们加上原来的3个就得到了9个anchors。
然后我们回到self.solver = caffe.SGDSolver(solver_prototxt),到这里为止我们建立完RoIDataLayer层、AnchorTargetLayer层。代码看上面的class SolverWrapper(object)。
继续后面的程序运行,接着加载预训练模型ZF.v2.caffemodel和加载参数文件stage1_rpn_solver60k80k.pt,接着进入set_roidb(self, roidb)函数。该函数主要对roidb进行顺序打乱。
def set_roidb(self, roidb): """Set the roidb to be used by this layer during training.""" self._roidb = roidb self._shuffle_roidb_inds() ##对水平图+垂直图进行随机打乱 if cfg.TRAIN.USE_PREFETCH: ##跳过 self._blob_queue = Queue(10) self._prefetch_process = BlobFetcher(self._blob_queue, self._roidb, self._num_classes) self._prefetch_process.start() # Terminate the child process when the parent exists def cleanup(): print 'Terminating BlobFetcher' self._prefetch_process.terminate() self._prefetch_process.join() import atexit atexit.register(cleanup)
此时看看sloverwrapper包裹函数的变量:
然后我们进入函数model_paths = sw.train_model(max_iters),从而进入训练。下面的函数大概是每20次显示一次,然后每10000次保存一次快照。
def train_model(self, max_iters): ##80000 """Network training loop.""" last_snapshot_iter = -1 timer = Timer() model_paths = [] while self.solver.iter < max_iters: # Make one SGD update timer.tic() self.solver.step(1) timer.toc() if self.solver.iter % (10 * self.solver_param.display) == 0: ##10000 % 200,具体是每20次显示一次 print 'speed: {:.3f}s / iter'.format(timer.average_time) if self.solver.iter % cfg.TRAIN.SNAPSHOT_ITERS == 0: ##10000 % 10000 ,具体是每10000次保存一次快照 last_snapshot_iter = self.solver.iter model_paths.append(self.snapshot()) if last_snapshot_iter != self.solver.iter: model_paths.append(self.snapshot()) return model_paths
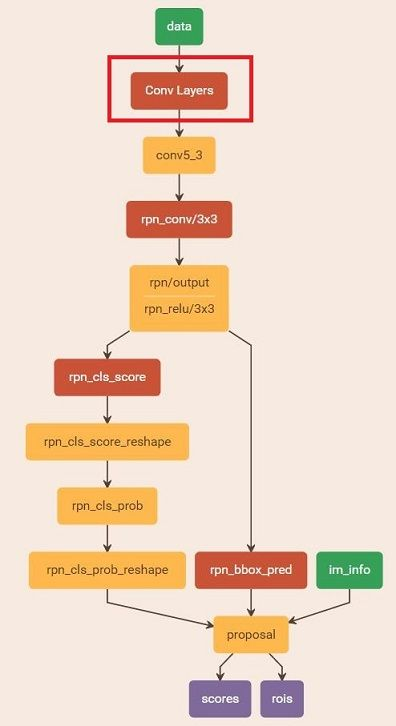
至此,我们已经对第一阶段的训练完成。总的网络图为下图。总览一下,其实就是输入三个[data(pascal_voc格式)、im_info(图片维度)、gt_boxes]; 输出就是分类和回归得分。这里主要目的是获取训练完的模型 zf_rpn_stage1_iter_80000.caffemodel,以便后面的使用。
Stage 1 RPN, init from ImageNet model:
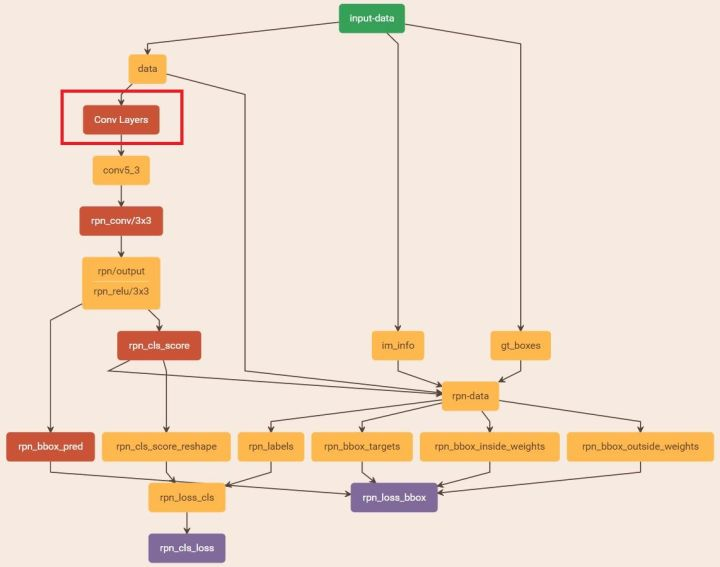
接着我们进入第二阶段的训练。先回到train_faster_rcnn_alt_opt.py函数:
print '~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~' print 'Stage 1 RPN, generate proposals' print '~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~' mp_kwargs = dict( queue=mp_queue, imdb_name=args.imdb_name, rpn_model_path=str(rpn_stage1_out['model_path']), cfg=cfg, rpn_test_prototxt=rpn_test_prototxt) p = mp.Process(target=rpn_generate, kwargs=mp_kwargs) p.start() rpn_stage1_out['proposal_path'] = mp_queue.get()['proposal_path'] p.join()
进入子进程rpn_generate()函数:
def rpn_generate(queue=None, imdb_name=None, rpn_model_path=None, cfg=None, rpn_test_prototxt=None): """Use a trained RPN to generate proposals. """ cfg.TEST.RPN_PRE_NMS_TOP_N = -1 # no pre NMS filtering cfg.TEST.RPN_POST_NMS_TOP_N = 2000 # NMS后保留2000个框 print 'RPN model: {}'.format(rpn_model_path) print('Using config:') pprint.pprint(cfg) ##cfg除了上面改过的两项,其他都不变 import caffe _init_caffe(cfg) # NOTE: the matlab implementation computes proposals on flipped images, too. # We compute them on the image once and then flip the already computed # proposals. This might cause a minor loss in mAP (less proposal jittering). imdb = get_imdb(imdb_name) ##重新获取imdb数据 print 'Loaded dataset `{:s}` for proposal generation'.format(imdb.name) # Load RPN and configure output directory rpn_net = caffe.Net(rpn_test_prototxt, rpn_model_path, caffe.TEST) ##加载rpn_test_prototxt=
##'py-faster-rcnn/models/pascal_voc/ZF/faster_rcnn_alt_opt/rpn_test.pt'
##第一阶段的训练完毕的rpn_model_path=
##py-faster-rcnn/output/faster_rcnn_alt_opt/voc_2007_trainval/zf_rpn_stage1_iter_80000.caffemodel
output_dir = get_output_dir(imdb) ##'py-faster-rcnn/output/faster_rcnn_alt_opt/voc_2007_trainval' print 'Output will be saved to `{:s}`'.format(output_dir) # Generate proposals on the imdb rpn_proposals = imdb_proposals(rpn_net, imdb) # Write proposals to disk and send the proposal file path through the # multiprocessing queue rpn_net_name = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(rpn_model_path))[0] rpn_proposals_path = os.path.join( output_dir, rpn_net_name + '_proposals.pkl') with open(rpn_proposals_path, 'wb') as f: cPickle.dump(rpn_proposals, f, cPickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL) print 'Wrote RPN proposals to {}'.format(rpn_proposals_path) queue.put({'proposal_path': rpn_proposals_path})
进入rpn_net = caffe.Net()函数,该函数主要是创建caffe.Net,里面首先根据pt文件创建网络,网络最后一层是创建层ProposalLayer,进入该类的创建:
class ProposalLayer(caffe.Layer): """ Outputs object detection proposals by applying estimated bounding-box transformations to a set of regular boxes (called "anchors"). """ def setup(self, bottom, top): # parse the layer parameter string, which must be valid YAML layer_params = yaml.load(self.param_str_) ##加载该层参数layer_params={'feat_stride': 16},其实也即16的scale self._feat_stride = layer_params['feat_stride'] ##16 anchor_scales = layer_params.get('scales', (8, 16, 32)) ##(8,16,32) self._anchors = generate_anchors(scales=np.array(anchor_scales)) self._num_anchors = self._anchors.shape[0] ## 9 if DEBUG: print 'feat_stride: {}'.format(self._feat_stride) print 'anchors:' print self._anchors # rois blob: holds R regions of interest, each is a 5-tuple # (n, x1, y1, x2, y2) specifying an image batch index n and a # rectangle (x1, y1, x2, y2) top[0].reshape(1, 5) ##将rois blob输出层reshape成(1,5),列为(图片index,4个坐标值) # scores blob: holds scores for R regions of interest if len(top) > 1: ##如果存在两个输出层,则将 scores blob 输出层reshape 成(1,1,1,1)??? top[1].reshape(1, 1, 1, 1) def forward(self, bottom, top):...def backward(self, top, propagate_down, bottom):... def reshape(self, bottom, top):...
接着我们进入rpn_proposals = imdb_proposals(rpn_net, imdb)函数,该函数作用是读取所有图片并返回每张图片的imdb_boxes[i], scores:
def imdb_proposals(net, imdb): """Generate RPN proposals on all images in an imdb.""" _t = Timer() imdb_boxes = [[] for _ in xrange(imdb.num_images)] for i in xrange(imdb.num_images): im = cv2.imread(imdb.image_path_at(i)) _t.tic() imdb_boxes[i], scores = im_proposals(net, im) _t.toc() print 'im_proposals: {:d}/{:d} {:.3f}s' \ .format(i + 1, imdb.num_images, _t.average_time) if 0: dets = np.hstack((imdb_boxes[i], scores)) # from IPython import embed; embed() _vis_proposals(im, dets[:3, :], thresh=0.9) plt.show() return imdb_boxes
接着我们进入imdb_boxes[i], scores = im_proposals(net, im)函数:
def im_proposals(net, im): """Generate RPN proposals on a single image.""" blobs = {} blobs['data'], blobs['im_info'] = _get_image_blob(im) net.blobs['data'].reshape(*(blobs['data'].shape)) net.blobs['im_info'].reshape(*(blobs['im_info'].shape)) blobs_out = net.forward( data=blobs['data'].astype(np.float32, copy=False), im_info=blobs['im_info'].astype(np.float32, copy=False)) scale = blobs['im_info'][0, 2] boxes = blobs_out['rois'][:, 1:].copy() / scale scores = blobs_out['scores'].copy() return boxes, scores
继续进入blobs['data'], blobs['im_info'] = _get_image_blob(im)函数:
def _get_image_blob(im): """Converts an image into a network input. Arguments: im (ndarray): a color image in BGR order Returns: blob (ndarray): a data blob holding an image pyramid im_scale_factors (list): list of image scales (relative to im) used in the image pyramid """ im_orig = im.astype(np.float32, copy=True) im_orig -= cfg.PIXEL_MEANS im_shape = im_orig.shape ##(375,500,3) im_size_min = np.min(im_shape[0:2]) im_size_max = np.max(im_shape[0:2]) processed_ims = [] assert len(cfg.TEST.SCALES) == 1 target_size = cfg.TEST.SCALES[0] im_scale = float(target_size) / float(im_size_min) ##下面主要意思是图的最大边不能超过1000,目标是宽或高为600,另一个高或宽低于1000就行 # Prevent the biggest axis from being more than MAX_SIZE if np.round(im_scale * im_size_max) > cfg.TEST.MAX_SIZE: im_scale = float(cfg.TEST.MAX_SIZE) / float(im_size_max) im = cv2.resize(im_orig, None, None, fx=im_scale, fy=im_scale, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) ##对原始图片进行扩充,这里采用线性插值的方法 im_info = np.hstack((im.shape[:2], im_scale))[np.newaxis, :] ##[[ 600. 800. 1.6]] processed_ims.append(im) # Create a blob to hold the input images blob = im_list_to_blob(processed_ims) ##转化图片成blob格式 return blob, im_info ##返回该图片的blob格式数据和im_info图片信息,比如(600,800,3)
继续进入blob = im_list_to_blob(processed_ims)函数:
def im_list_to_blob(ims): """Convert a list of images into a network input. Assumes images are already prepared (means subtracted, BGR order, ...). """ max_shape = np.array([im.shape for im in ims]).max(axis=0) num_images = len(ims) ## 1张图 blob = np.zeros((num_images, max_shape[0], max_shape[1], 3), dtype=np.float32) for i in xrange(num_images): ##将所有图片转换成caffe中blob的格式 im = ims[i] blob[i, 0:im.shape[0], 0:im.shape[1], :] = im # Move channels (axis 3) to axis 1 # Axis order will become: (batch elem, channel, height, width) channel_swap = (0, 3, 1, 2) ##交换axis=3和axis=1 列 blob = blob.transpose(channel_swap) ##最终变为(batch elem, channel, height, width),注意这里的高和宽放到了后面,这是caffe中blob的格式 return blob
回到im_proposals(net, im)函数,现在我们获得一张图片的blobs['data']和blobs['im_info'],继续往下运行。
def im_proposals(net, im): """Generate RPN proposals on a single image.""" blobs = {} blobs['data'], blobs['im_info'] = _get_image_blob(im) net.blobs['data'].reshape(*(blobs['data'].shape)) ##将第一阶段的网络模型更改下输入结构,改成该图片的维度结构,比如(1,3,600,800) net.blobs['im_info'].reshape(*(blobs['im_info'].shape)) ##(1,3) blobs_out = net.forward( data=blobs['data'].astype(np.float32, copy=False), im_info=blobs['im_info'].astype(np.float32, copy=False)) scale = blobs['im_info'][0, 2] ##1.6 boxes = blobs_out['rois'][:, 1:].copy() / scale scores = blobs_out['scores'].copy() return boxes, scores ##返回2000个boxes的坐标和得分
接着进入net.forward()函数,执行该网络的前向传播函数。在终端的显示是im_proposals: 1/5011 2476.064s,即有5011张图片,每张返回2000个propals和boxes。
这些proposals保存在文件'output/faster_rcnn_alt_opt/voc_2007_trainval/zf_rpn_stage1_iter_80000_proposals.pkl' 中,留着等下面的训练。最后把该路径通过进程传给下一个进程。总的网络图:
Stage 1 RPN, generate proposal
终于来到最后一个阶段了。先看看主代码:
print '~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~' print 'Stage 1 Fast R-CNN using RPN proposals, init from ImageNet model' print '~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~' cfg.TRAIN.SNAPSHOT_INFIX = 'stage1' mp_kwargs = dict( queue=mp_queue, imdb_name=args.imdb_name, init_model=args.pretrained_model, solver=solvers[1], max_iters=max_iters[1], cfg=cfg, rpn_file=rpn_stage1_out['proposal_path']) p = mp.Process(target=train_fast_rcnn, kwargs=mp_kwargs) p.start() fast_rcnn_stage1_out = mp_queue.get() p.join()
我们进入子进程train_fast_rcnn()函数,其实这里的大部分内容和前面的相似,就不重复累述。
def train_fast_rcnn(queue=None, imdb_name=None, init_model=None, solver=None, max_iters=None, cfg=None, rpn_file=None): """Train a Fast R-CNN using proposals generated by an RPN. """ cfg.TRAIN.HAS_RPN = False # 这次训练不需要RPN层了 cfg.TRAIN.PROPOSAL_METHOD = 'rpn' # 使用之前的propasals来训练 cfg.TRAIN.IMS_PER_BATCH = 2 print 'Init model: {}'.format(init_model) print 'RPN proposals: {}'.format(rpn_file) print('Using config:') pprint.pprint(cfg) import caffe _init_caffe(cfg) roidb, imdb = get_roidb(imdb_name, rpn_file=rpn_file) ##不重复分析了,就是获取图片集的roidb和imdb格式的数据 output_dir = get_output_dir(imdb) print 'Output will be saved to `{:s}`'.format(output_dir) # Train Fast R-CNN model_paths = train_net(solver, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model=init_model, max_iters=max_iters) # Cleanup all but the final model for i in model_paths[:-1]: os.remove(i) fast_rcnn_model_path = model_paths[-1] # Send Fast R-CNN model path over the multiprocessing queue queue.put({'model_path': fast_rcnn_model_path})
最后阶段的图如下所示:
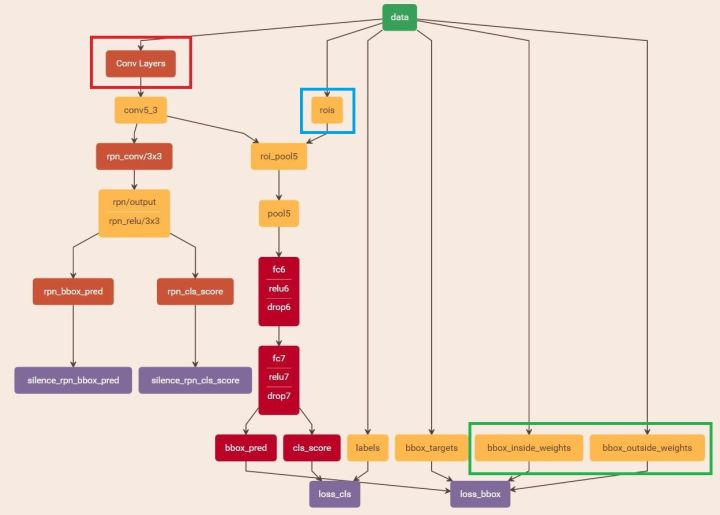
由图知我们设置不使用rpn层,将提取的proposals作为rois和前面VGG16(或者ZF)网络提取的最后特征(conv5_3)传入网络,计算bbox_inside_weights+bbox_outside_weights,作用与RPN一样,传入soomth_L1_loss layer,如图绿框。
这样就可以训练最后的识别softmax与最终的bounding box regression了。