开发环境:Visual Studio 2015 + Python 3.7.0
一、在C++代码中写Python脚本
在C++中含有调用Python脚本的API函数,在C++代码中嵌入Python脚本代码,是通过PyRun_SimpleString()函数实现。它允许将Python脚本代码写成字符串,作为PyRun_SimpleString()函数参数,从而实现Python脚本的解析与运行,这种方法适用于Python脚本简短的情形,其主要流程如下图所示:
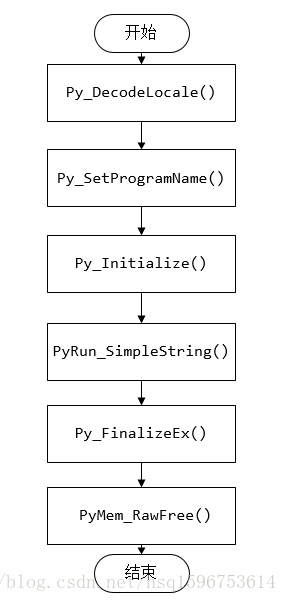
下面通过一则实例演示C++调用Python的这种方式。
(1)C++代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <Python.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
wchar_t *program = Py_DecodeLocale(argv[0], NULL);
if (program == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Fatal error: cannot decode argv[0]\n");
exit(1);
}
//The Py_SetProgramName() function should be called before Py_Initialize()
//to inform the interpreter about paths to Python run-time libraries
Py_SetProgramName(program); //optional but recommended
// the Python interpreter is initialized with Py_Initialize()
Py_Initialize();
//pass a string containing Python statements to PyRun_SimpleString()
PyRun_SimpleString("from time import time,ctime\n"
"print('Today is', ctime(time()))\n");
//the Py_FinalizeEx() call shuts the interpreter down
if (Py_FinalizeEx() < 0) {
exit(120);
}
PyMem_RawFree(program);
//system("pause");
//return 0;
return getchar();
}(2)程序运行结果:

二、C++调用本地Python脚本文件
在很多情形,Python脚本并不是那么简短,在C++代码中直接嵌入Python脚本代码虽然也可以达到需求,但这样的代码往往不易阅读与维护。因此,C++ 中的Python API允许通过加载本地Python脚本文件的方式调用Python。下面通过一则实例演示C++调用Python的这种方式
(1)C++代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <Python.h>
using namespace std;
/*
This code loads a Python script using argv[1], and calls the function named in argv[2].
Its integer arguments are the other values of the argv array.
*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
PyObject *pName, *pModule, *pFunc;
PyObject *pArgs, *pValue;
if (argc < 3)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: call pythonfile funcname [args]\n");
return 1;
}
// initializing the interpreter
Py_Initialize();
pName = PyUnicode_DecodeFSDefault(argv[1]);
/* Error checking of pName left out */
// the script is loaded using PyImport_Import()
pModule = PyImport_Import(pName);
Py_DECREF(pName);
if (pModule != NULL)
{
// Once the script is loaded, the name we’re looking for is retrieved using PyObject_GetAttrString()
pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, argv[2]);
/* pFunc is a new reference */
if (pFunc && PyCallable_Check(pFunc))
{
pArgs = PyTuple_New(argc - 3);
for (int i = 0; i < argc - 3; ++i)
{
pValue = PyLong_FromLong(atoi(argv[i + 3]));
if (!pValue)
{
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot convert argument\n");
return 1;
}
/* pValue reference stolen here: */
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, i, pValue);
}
pValue = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, pArgs);
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
if (pValue != NULL)
{
printf("Result of call: %ld\n", PyLong_AsLong(pValue));
Py_DECREF(pValue);
}
else
{
Py_DECREF(pFunc);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr, "Call failed\n");
return 1;
}
}
else
{
if (PyErr_Occurred())
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot find function \"%s\"\n", argv[2]);
}
Py_XDECREF(pFunc);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
}
else
{
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to load \"%s\"\n", argv[1]);
return 1;
}
if (Py_FinalizeEx() < 0)
{
return 120;
}
return getchar();
}(2)Python脚本文件MyMultiply.py代码:
def multiply(a,b):
print("Will compute", a, "times", b)
c = 0
for i in range(0, a):
c = c + b
return c(3)VS命令行参数:
MyMultiply multiply 5 3(4)程序运行结果:
