MyBatis在操作数据库时,主要分为8大步骤:
(1) 读取MyBatis配置文件mabatis-config.xml,mabatis-config.xml作为MaBatis的全局配置文件,配置了MyBatis的运行环境等信息,其主要是获取数据库连接。
(2) 加载映射文件Mapper.xml。Mapper.xml即SQL映射文件,该文件配置了操作数据库的SQL语句,需要在mybatis-config.xml中加载才能执行。mybatis-config.xml可以添加多个配置文件,每个配置文件对应数据库中的一张表。
(3) 构建会话工厂。通过MyBatis的环境等配置信息构建会话工厂SqlSessionFactory。
(4) 创建SqlSession对象。由会话工厂创建SqlSession对象。,该对象中包含执行SQL的所有方法。
(5) MyBatis底层定义的一个Executor接口会根据SqlSession传递的参数动态生成SQL语句,同时负责查询缓存的维护。
(6) 根据生成的SQL语句生成MappedStatement对象。
(7) 向MappedStatement输入映射对象,这里的输入参数的映射过程就相当于JDBC编程中对preparedStatement对象设置参数的过程。
(8) 执行SQL语句,对MappedStatement对象返回的结果进行处理。
下面通过一个入门程序来理解。
1.根据学号查询学生信息
(1)这里用sql server数据库。
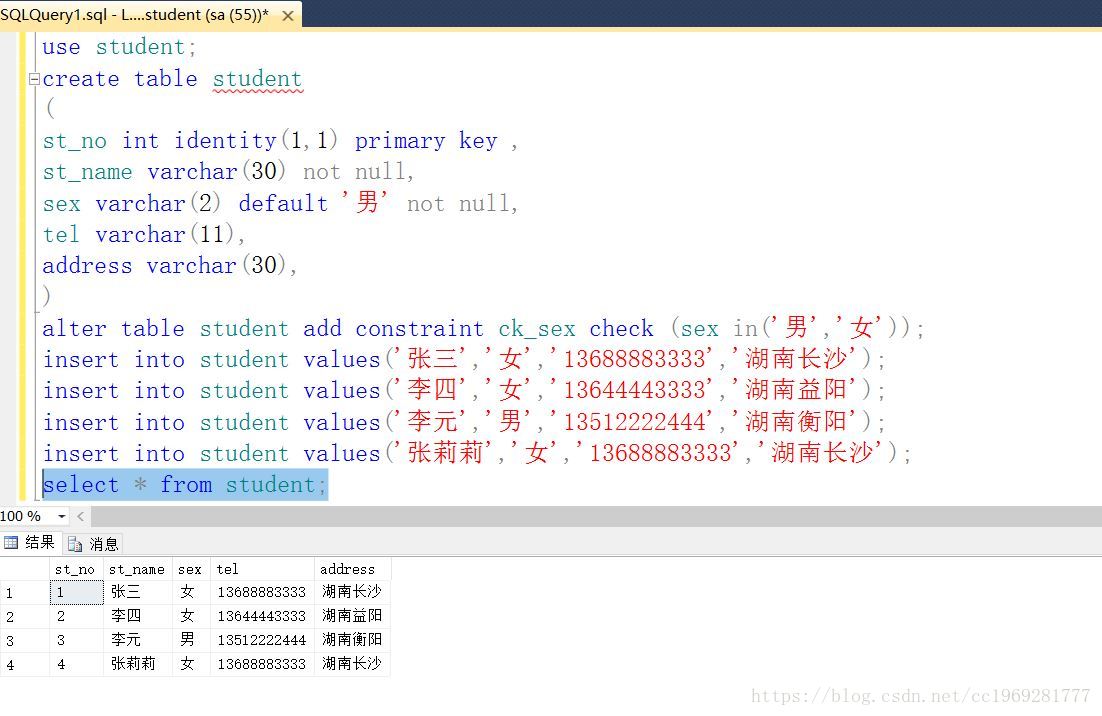
在SQL Server数据库中,创建一个名为student的数据库,创建一个student表,并插入几条数据。
创建代码:
create database student;
use student;
create table student
(
st_no int identity(1,1) primary key ,
st_name varchar(30) not null,
sex varchar(2) default '男' not null,
tel varchar(11),
address varchar(30),
)
alter table student add constraint ck_sex check (sex in('男','女'));
insert into student values('张三','女','13688883333','湖南长沙');
insert into student values('李四','女','13644443333','湖南益阳');
insert into student values('李元霸','男','13512222444','湖南衡阳');
insert into student values('张莉莉','女','13688883333','湖南长沙');
select * from student;
(2)在Myeclipse创建一个名为project01的Web项目,将MyBatis的核心jar包、依赖包,以及Sql Server数据库驱动添加到项目的lib目录下。
(3)在src目录下创建log4j.properties文件,内容如下 :
# Global logging configuration
log4j.rootLogger=ERROR, stdout
# MyBatis logging configuration...
log4j.logger.cn.swjd=DEBUG
# Console output...
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%nMyBatis默认使用log4j输出日志信息,如果要在控制台查看sql语句,就必须
在src目录下创建log4j.properties文件。
(4)在src目录下创建cn.swjd.entries包,在该包下创建持久化类Student。
package cn.swjd.entries;
//学生持久化类
public class Student {
//主键学号
private Integer st_no;
//姓名,性别,年龄,电话 ,地址
private String st_name, sex, tel, address;
public Integer getSt_no() {
return st_no;
}
public void setSt_no(Integer st_no) {
this.st_no = st_no;
}
public String getSt_name() {
return st_name;
}
public void setSt_name(String st_name) {
this.st_name = st_name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [st_no=" + st_no + ", st_name=" + st_name + ", sex="
+ sex + ", tel=" + tel + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
}
(5)在src目录下。创建cn.swjd.mapper包,在包里创建映射文件StudentMapper.xml。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="cn.swjd.mapper.StudentMapper">
<select id="findStudentById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="cn.swjd.entries.Student">
select * from student where st_no= #{st_no}
</select>
</mapper>
说明:<mapper>元素是配置文件的根元素,它包含一个namespace属性,该属性指定了<mapper>的唯一命名空间,通常设置为“包名+SQL映射文件名”的形式。
子元素<select>中的信息是用于执行查询操作的配置,id是唯一标识符。
parameterType:指定传入参数的类型。
resultType:指定返回结果的类型。
#{}:表示一个占位符,相当于jdbc中的?,其里面的内容为接受参数的名称。
(6)在src目录下,创建MyBatis的核心配置文件mybatis-config.xml。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="sqlserver">
<environment id="sqlserver">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- 配置数据库连接池 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;DataBaseName=student"/>
<property name="username" value="sa"/>
<property name="password" value="123"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="cn/swjd/mapper/StudentMapper.xml"/>
</mappers> </configuration> 说明:
<environments>下可配置多个运行环境,default属性用于设置默认运行环境。
(7)在src目录下,创建一个cn.swjd.test包,创建测试类MyBatisTest,再编写一个方法findStudentByIdTest(int st_id),并在main方法里调用。
package cn.swjd.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import cn.swjd.entries.Student;
public class MyBatisTest {
public static void findStudentByIdTest(int st_id) throws Exception{
//1.读取配置文件
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputstream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//2.根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputstream);
//3.通过SqlSessionFactory构建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlsession=factory.openSession();
//4.SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回其映射结果
Student s=sqlsession.selectOne("cn.swjd.mapper.StudentMapper.findStudentById",st_id);
//打印输出结果
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
findStudentByIdTest(1);
}
}
运行结果:
2.根据姓名模糊查询学生信息
修改映射文件StudentMapper.xml,添加一个<select>
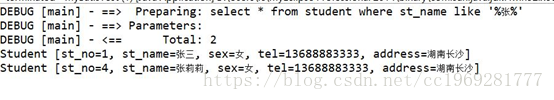
<select id="findStudentByName" parameterType="String" resultType="cn.swjd.entries.Student">
select * from student where st_name like '%${value}%'
</select>
这里传入参数为什么不设置为#{}而用${}呢?
假设传入参数在程序里为 String value=”张”;
如果使用的是#{},最终的sql语句就会变成:
select * from student where st_name like ‘’张’’
使用${},最终的sql语句就会变成:
select * from student where st_name like ‘张’
原因:如果使用的是#{},传入参数?就会根据配置文件<select>中parameterType属性(即数据类型)自动变换,如果parameterType="String",就会自动加入’’, 如果parameterType="Integer",就不会加’’。
而使用${} 不管parameterType属性为何值,都不会自动加’’。
在类MyBatisTest,编写一个方法findStudentByNameTest(String value),并在main方法里调用。
public static void findStudentByNameTest(String st_name) throws Exception{
//1.读取配置文件
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputstream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//2.根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputstream);
//3.通过SqlSessionFactory构建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlsession=factory.openSession();
//4.SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回其映射结果
List<Student> s=sqlsession.selectList("cn.swjd.mapper.StudentMapper.findStudentByName",st_name);
/*selectList方法第一个参数为<Mapper>的namespace属性+<select>的id属性,后面接传入参数*/
//打印输出结果
for(Student stu:s)
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
findStudentByNameTest("张");
}
运行结果:
结果出来了,但是这里有一个问题,使用“${}”拼接字符串,无法防止sql注入问题。
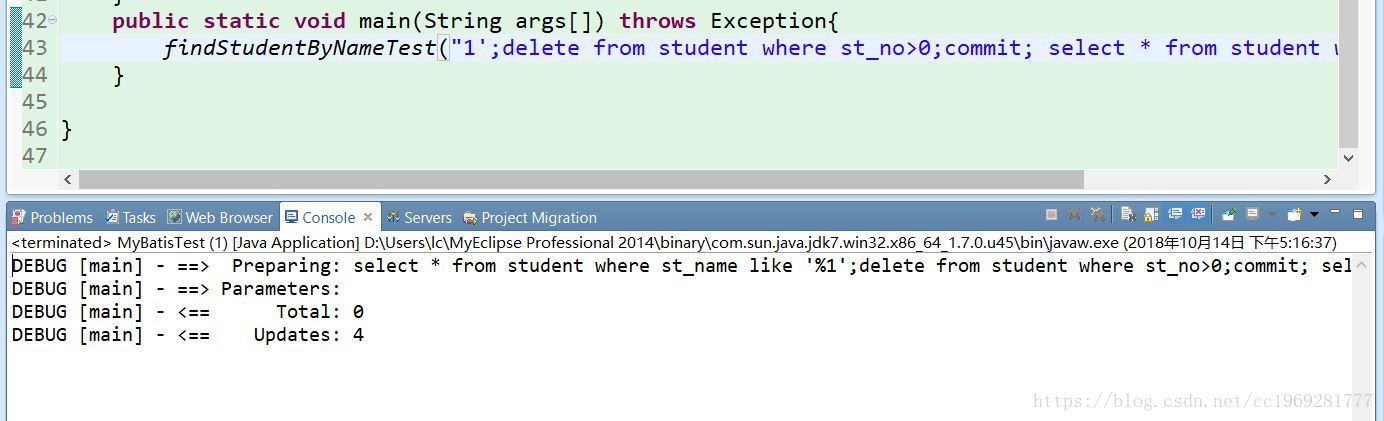
比如这里,如果把方法调用改成:
findStudentByNameTest("1';delete from student where st_no>0;commit; select * from student where st_name like '”);
它竟然可以操作数据库!把表所有内容都删除了。显然,实际项目开发中,是不能出现这种bug的,你永远不知道用户会输入什么东西。
所以,为了安全性,这里不能用${},只能用#{},我们可以用SqlServer中的拼接函数concat()。
修改后:
select * from student where st_name like concat('%',#{value},'%')
修改、删除、增加操作都差不多
相比于查询,就是多了sqlsession.commit()提交事务这一步骤而已
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="cn.swjd.mapper.StudentMapper">
<!-- 根据学号查询学生信息 -->
<select id="findStudentById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="cn.swjd.entries.Student">
select * from student where st_no= #{st_no}
<!-- 根据姓名模糊查询学生信息 -->
</select>
<select id="findStudentByName" parameterType="String" resultType="cn.swjd.entries.Student">
select * from student where st_name like concat('#',#{value},'#')
</select>
<!-- 更新学生信息 -->
<update id="updateStudent" parameterType="cn.swjd.entries.Student"
>
update student set st_name=#{st_name},sex=#{sex},tel=#{tel},address=#{address} where st_no=#{st_no}
</update>
<!-- 删除学生信息 -->
<delete id="deleteStudent" parameterType="Integer">
delete from student where st_no=#{id}
</delete>
<!-- 增加学生信息 -->
<insert id="addStudent" parameterType="cn.swjd.entries.Student">
insert into student values (#{st_name},#{sex},#{tel},#{address})
</insert>
</mapper>package cn.swjd.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import cn.swjd.entries.Student;
public class MyBatisTest {
//根据学号查找学生
public static void findStudentByIdTest(int st_id) throws Exception{
//1.读取配置文件
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputstream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//2.根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputstream);
//3.通过SqlSessionFactory构建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlsession=factory.openSession();
//4.SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回其映射结果
Student s=sqlsession.selectOne("cn.swjd.mapper.StudentMapper.findStudentById",st_id);
/*selectOne方法第一个参数为<Mapper>的namespace属性+<select>的id属性,后面接传入参数*/
//打印输出结果
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//根据姓名模糊查找学生
public static void findStudentByNameTest(String st_name) throws Exception{
//1.读取配置文件
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputstream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//2.根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputstream);
//3.通过SqlSessionFactory构建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlsession=factory.openSession();
//4.SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回其映射结果
List<Student> s=sqlsession.selectList("cn.swjd.mapper.StudentMapper.findStudentByName",st_name);
/*selectList方法第一个参数为<Mapper>的namespace属性+<select>的id属性,后面接传入参数*/
//打印输出结果
for(Student stu:s)
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
//更新学生信息
public static void updateStudent(Student s) throws IOException{
//1.读取配置文件
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputstream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//2.根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputstream);
//3.通过SqlSessionFactory构建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlsession=factory.openSession();
//4.SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回其映射结果
int i = sqlsession.update("cn.swjd.mapper.StudentMapper.updateStudent", s);
//提交事务
sqlsession.commit();
if(i>0){
System.out.println("更新学号为"+s.getSt_no()+"学生信息成功!");
}
}
//删除学生信息
public static void deleteStudent(int st_no) throws IOException{
//1.读取配置文件
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputstream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//2.根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputstream);
//3.通过SqlSessionFactory构建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlsession=factory.openSession();
//4.SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回其映射结果
int i = sqlsession.delete("cn.swjd.mapper.StudentMapper.deleteStudent", st_no);
//5.提交事务
sqlsession.commit();
if(i>0){
System.out.println("删除学号为"+st_no+"的学生信息成功!");
}
}
//增加学生信息
public static void addStudent(Student s) throws IOException{
//1.读取配置文件
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputstream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//2.根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputstream);
//3.通过SqlSessionFactory构建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlsession=factory.openSession();
//4.SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回其映射结果
int i = sqlsession.insert("cn.swjd.mapper.StudentMapper.addStudent", s);
//5.提交事务
sqlsession.commit();
if(i>0){
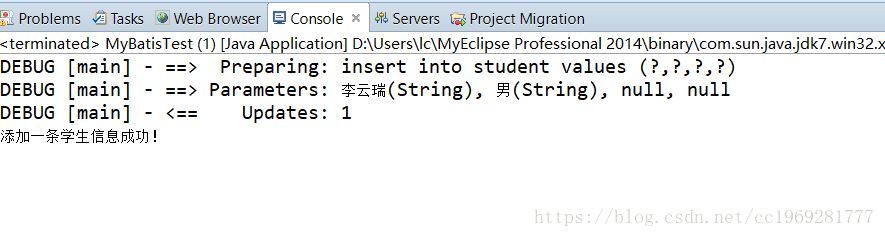
System.out.println("添加一条学生信息成功!");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
Student s=new Student();
s.setSt_name("李云瑞");
s.setSex("男");
addStudent(s);
}
}