版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/u012570105/article/details/83506047
实验环境介绍
- gcc:4.8.5
- glibc:glibc-2.17-222.el7.x86_64
- os:Centos7.4
- kernel:3.10.0-693.21.1.el7.x86_64
线程概念
- 忽略(ps:Linux是用进程实现的线程)
- 进程是资源分配的基本单位,线程是调度的基本单位。
线程标识
- 忽略
线程创建
- 线程创建时不会保证哪个线程先执行
- 新创建的线程会继承调用线程的浮点环境和信号屏蔽字,但是该新线程的挂起信号集会被清楚,测试代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void sig_int(int signo);
void *func(void *arg);
void pr_mask(const char *str);
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (signal(SIGINT, sig_int) == SIG_ERR) {
printf("register signal INT error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// block INT
sigset_t bset;
sigemptyset(&bset);
sigaddset(&bset, SIGINT);
// 更新进程屏蔽信号状态字
if (sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK, &bset, NULL) != 0) {
printf("sigprocmask() failed !\n");
return -1;
}
printf("%d: now sleep for 10 sec for waitint SIGINT\n", pthread_self());
sleep(30);
// create a thread
pthread_t thr1;
if(pthread_create(&thr1,NULL,func, NULL)!=0) {
printf("create thread failed!\n");
return -1;
}
printf("%d: now wake and create thread over. unblock SIGINT signal\n", pthread_self());
sigset_t set;
if (sigaddset(&set, SIGINT) != 0) {
printf("thread add set error\n");
}
// 主线程这里解除INT信号的阻塞,这样主线就会调用信号处理函数
if (sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK, &set, NULL) != 0) {
printf("thread sigprocmask() failed !\n");
return -1;
}
printf("%d: after unblocking SIGINT, main thread sleep\n", pthread_self());
while (1) sleep(1);
return 0;
}
void
sig_int(int signo) /* interrupts pause() */
{
printf("%d: SIGINT received\n", pthread_self());
}
void *func(void *arg)
{
pr_mask("before unblock:");
while (1) sleep(1);
sigset_t set;
if (sigaddset(&set, SIGINT) != 0) {
printf("thread add set error\n");
}
// 这里会接触INT信号的阻塞,但是该线程被挂起的信号集会被清楚
// 所以该线程不会调用信号处理函数
if (sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK, &set, NULL) != 0) {
printf("thread sigprocmask() failed !\n");
return (void *)-1;
}
printf("%d: child thread over\n", pthread_self());
while (1) sleep(1);
return NULL;
}
void pr_mask( const char *str ){
sigset_t set;
int errno_save; //get the pre errno
errno_save = errno;
if( sigprocmask( 0, NULL , &set ) == -1 )
printf("%d: sigprocmask error\n", pthread_self());
else {
printf( "\n%s" , str );
if(sigismember(&set, SIGQUIT))
printf( " SIGQUIT" );
if(sigismember(&set, SIGINT))
printf( " SIGINT" );
if(sigismember(&set, SIGUSR1))
printf( " SIGUSR1" );
if( sigismember( &set , SIGALRM ) )
printf( " SIGALRM" );
}
printf("\n");
errno = errno_save ;
}
// kill -2 8379
// kill -2 8379
// kill -2 8379
result:
-1168320768: now sleep for 10 sec for waitint SIGINT
-1168320768: now wake and create thread over. unblock SIGINT signal
before unblock: SIGINT
-1168320768: SIGINT received
-1168320768: after unblocking SIGINT, main thread sleep
- 控制终端的信号发送给该进程的主线程,测试代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void *func(void *arg);
void sig_int(int signo); /* interrupts pause() */
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
signal(SIGINT, sig_int);
pthread_t thr1;
printf("%lu: main thread\n", pthread_self());
if(pthread_create(&thr1,NULL,func, NULL)!=0) {
printf("create thread failed!\n");
return -1;
}
while (1) sleep(1);
return 0;
}
void
sig_int(int signo) /* interrupts pause() */
{
printf("%lu: SIGINT received\n", pthread_self());
}
void *func(void *arg)
{
while (1) sleep(1);
return NULL;
}
result:
140463559870208: main thread
^C140463559870208: SIGINT received
^C140463559870208: SIGINT received
^C140463559870208: SIGINT received
^\Quit
线程终止
- 线程终止的方式:
- 如果任意线程调用exit、_Exit或者_exit,那么整个进程就会终止
- 如果默认的动作是终止进程,那么,发送到该线程的信号会终止整个进程(12章再来讨论信号和线程)
- 单个线程有三种退出方式
- 线程可以从启动例程中返回,返回值是线程的退出码
- 线程可以被同一进程中的其他线程取消
- 线程调用pthread_exit来结束
- 相关函数:pthread_exit、pthread_join


- pthread_join可以获取到pthread_exit的rval_ptr,如果线程是被取消的,则pthread_join的rval_ptr指向的内存单元为PTHREAD_CANCELED
- pthread_join也自动把线程置于分离状态
- pthread_join可以回收同一个进程的其他线程
注意在线程函数中返回的指针是合法的,该指针的数据分配不该是在线程函数的栈上分配。这样在别的线程中进行进行join的时候,该地址已经不合法
- pthread_cancel函数
- 该函数并不等待线程终止,它仅仅提出请求
- pthread_cleanup_push函数可以注册线程退出清理函数,这些清理函数被pthread_cleanup_push函数调度,pthread_cleanup_pop函数是删除线程的清理函数
- pthread_cleanup_push函数注册的函数的调用时机为:
- pthread_exit时
- 被别的线程进行pthread_cancel时
- pthread_cleanup_pop的参数非0时
- 测试代码如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAXLINE 2048
static void
err_doit(int errnoflag, int error, const char *fmt, va_list ap)
{
char buf[MAXLINE];
vsnprintf(buf, MAXLINE-1, fmt, ap);
if (errnoflag)
snprintf(buf+strlen(buf), MAXLINE-strlen(buf)-1, ": %s",
strerror(error));
strcat(buf, "\n");
fflush(stdout); /* in case stdout and stderr are the same */
fputs(buf, stderr);
fflush(NULL); /* flushes all stdio output streams */
}
void
err_exit(int error, const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
err_doit(1, error, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
exit(1);
}
void
cleanup(void *arg)
{
printf("cleanup: %s\n", (char *)arg);
}
void *
thr_fn1(void *arg)
{
printf("thread 1 start\n");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup, "thread 1 first handler");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup, "thread 1 second handler");
printf("thread 1 push complete\n");
if (arg)
return((void *)1); // 这里不会调用清理函数,在别的平台上在这里发会可能会产生未定义的行为,应该使用pthread_exit来返回,但是这样就会执行清理函数
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
return((void *)1);
}
void *
thr_fn2(void *arg)
{
printf("thread 2 start\n");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup, "thread 2 first handler");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup, "thread 2 second handler");
printf("thread 2 push complete\n");
if (arg)
pthread_exit((void *)2); // 这里会触发调用清理函数
// 如果走到这里,则清理函数不会调用
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
pthread_exit((void *)2);
}
int
main(void)
{
int err;
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
void *tret;
err = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thr_fn1, (void *)1);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't create thread 1");
err = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thr_fn2, (void *)1);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't create thread 2");
err = pthread_join(tid1, &tret);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't join with thread 1");
printf("thread 1 exit code %ld\n", (long)tret);
err = pthread_join(tid2, &tret);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't join with thread 2");
printf("thread 2 exit code %ld\n", (long)tret);
exit(0);
}
result:
thread 1 start
thread 1 push complete
thread 2 start
thread 2 push complete
thread 1 exit code 1
cleanup: thread 2 second handler
cleanup: thread 2 first handler
thread 2 exit code 2
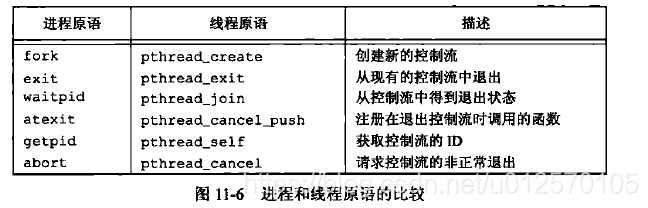
- 进程和线程的原语比较: