Oracle的介绍
1. Oracle的创始人----拉里•埃里森
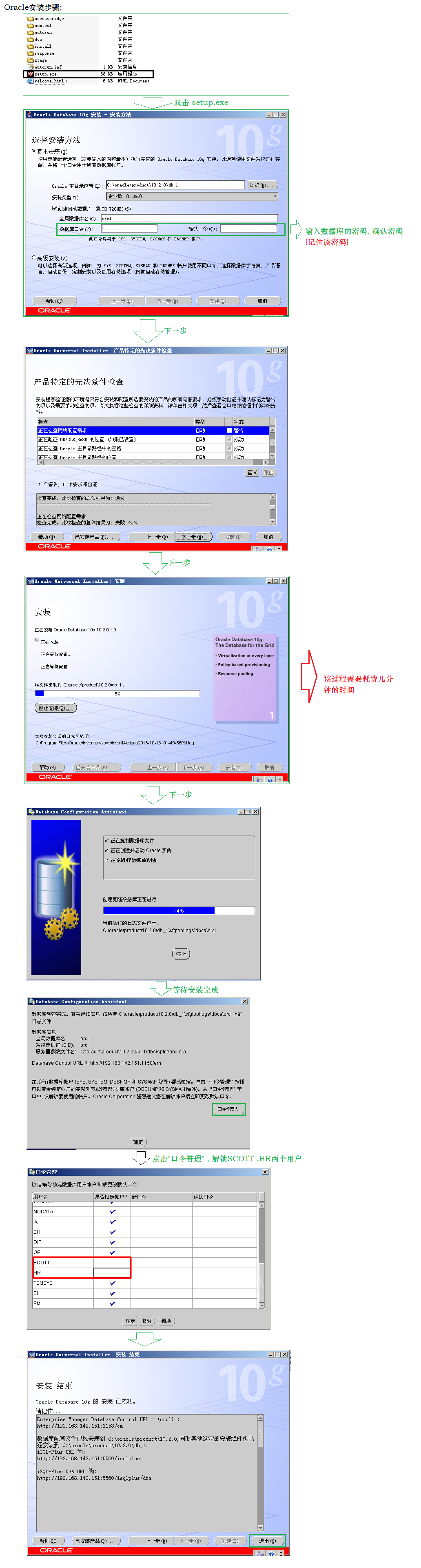
2. oracle的安装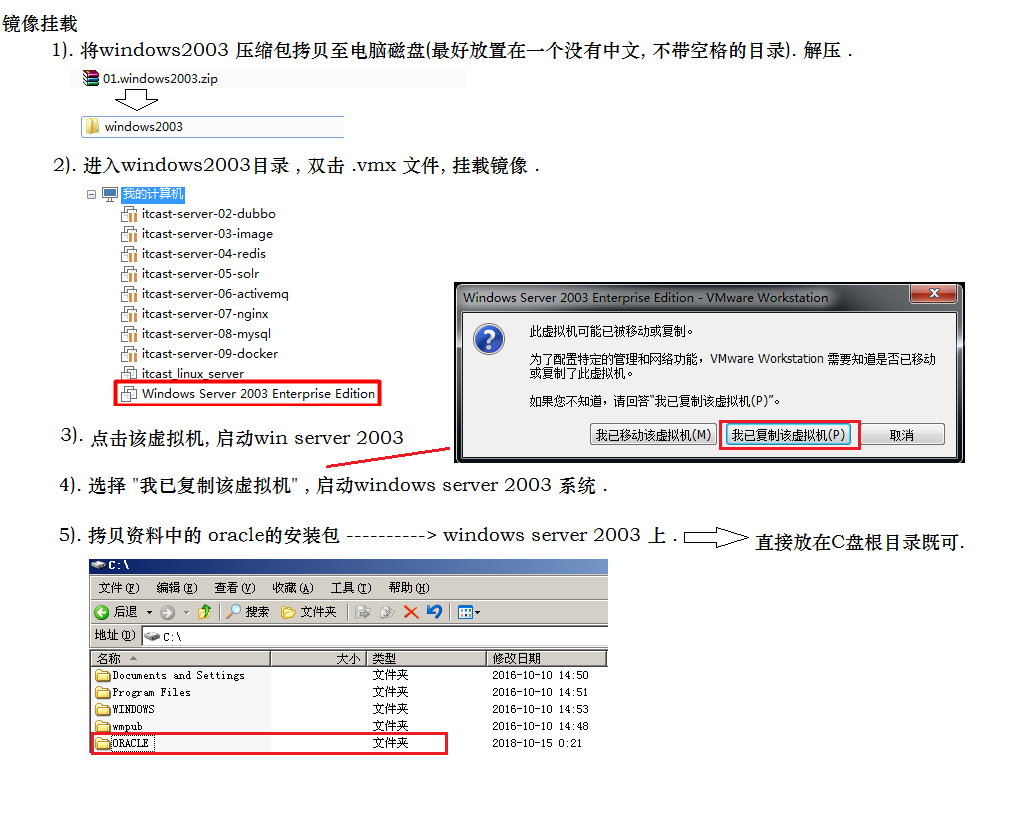
[连接Oracle步骤](](https://img2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1224549/201810/1224549-20181017214101430-1777213931.png)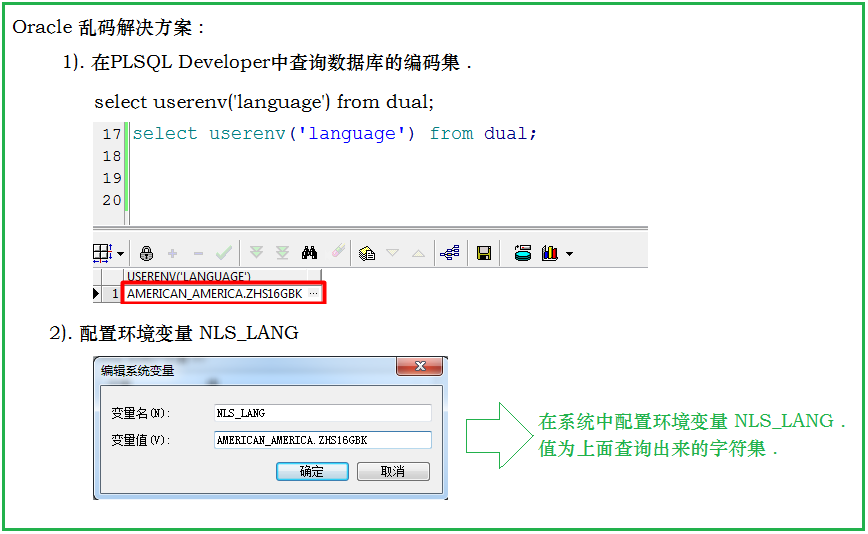
3. oracle的体系结构:
数据库: 在oracle中,数据库只有一个,就是全局数据库(orcl)---不同模块的表结构,通过用户区分
实例
表空间(datafile 'C:/db1.dbf'): 一个逻辑概念,就是用来存储数据库表的 用户 数据文件: 用来具体存储数据信息的,磁盘上的具体文件 准备工作:
1. 创建表空间:
create tablespace 名称
datafile 'c:\itheima.dbf'
size 100m -- 大小 autoextend on -- on 表示自动扩充 next 10m -- 每次扩充的大小 2. 删除表空间 drop tablespace 名称; 3. 创建用户: create user 用户名 identified by 用户名 -- 设置密码 default tablespace 用户名; -- 指定用户所属的表空间 4. 用户授权: connect -- 连接角色 resource --开发者角色 dba --超级管理员角色 grant dba to 用户名 -- 赋予权限表的基本操作:
常用数据类型: varchar, varchar2,date,number(10,2)==>10是总长度,2表示小数点后的位数 1. 创建表 create table person( pid number(20), pname varchar2(10) ); 2. 修改表 1. 添加一列 alter table person add gender number(1); 2. 添加多列 alter table person add (gender number(1),(age number(3))); 3. 修改列类型: alter table person modify gender char(1); 4. 修改列名称: alter table person rename column gender to sex; 5. 删除一列: alter table person drop column sex; 增删改基本操作:
1. 增加
insert into person (pid,pname) values (1,'小明'); commit; 2. 修改 update person set pname = '小马' where pid = 1; commit; 3. 删除 delete from person; ---删除表中全部记录 drop table person; ---删除表结构 truncate table person; ---先删除表,再次创建表,效果等同于删除表中的全部记录修改字符集:
select userenv('language') from dual; 配置环境变量: NLS_LANG 值为查询出的结果序列:默认从1开始,依次递增,为主键赋值使用(Mysql的自增)
1. 创建
create sequence s_person;
2. 查看(序列不属于任何一张表,但是可以逻辑和表做绑定)
select s_person.nextval from dual; --- dual表示的是虚表,补全语法,没有任何意义 select s_person.currval from dual; 3. 基本使用: insert into person (pid,pname) values (s_person.nextval,'王智'); 解锁用户
1. alter user scott account unlock; ------------> 解锁scott用户,如果在安装的时候已经解锁,可以不需要设置 2. alter user scott identified by tiger; --解锁scott用户的密码【此句也可以用来重置密码】 单行函数:作用于一行,返回一个值
1. 字符函数
select upper('yes') from dual; ==== 小写变大写
select lower('yes') from dual; ==== 大写变小写 CONCAT : 拼接两个字符串,与 || 相同 select concat('Hello',' Oracle') from dual; INITCAP : 将字符串的第一个字母变为大写 select INITCAP('hello') from dual; 2. 数值函数 select round(26.18, 1) from dual; ==== 四舍五入,后面的参数表示保留的小数点后的位置,如果是-1呢?自行测试 select trunc(26.18, 1) from dual;直接截取 select mod(10, 3) from dual; ==== 求余数 3. 日期函数: select sysdate - e.hiredate from emp e; === 查询emp表所有员工入职到现在多少天了,sysdate表示当前时间 select sysdate + 1 from dual; === 算出明天此刻(运算操作都是针对天) select months_between(sysdate,e.hiredate) from emp e; 查询emp表所有员工入职到现在多少月了 如果算年呢? 礼拜呢? 考虑使用上面两个例子的基础上修改 select months_between(sysdate,e.hiredate) / 12 from emp e; select (sysdate - e.hiredate) / 7 from emp e; 4. 转换函数: select to_char(sysdate,'fm yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') from dual; === 日期转字符串,去掉fm试试?去掉24试试? select to_date('2018-6-7 16:39:50','fm yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') from dual; === 字符串转日期 5. 通用函数: select e.sal * 12 + nvl(e.comm,0) from emp e; === 算出emp表中所有员工的年薪(由于comm奖金有null值,所以需要排除掉null值,nvl表示判断第一个数是否为null,是则返回第二个参数,不是返回第一个参数) select e.sal * 12 + nvl2(e.comm,e.comm,0) from emp e;=== 第一个参数是判定值,第二个是不为null的返回值,第三个是为null的返回值 条件表达式(1和2是mysql和oracle通用):
1. 给emp表中员工起中文名称:
select e.ename,
case e.ename
when 'SMITH' then '曹操' when 'WARD' then '诸葛' else '无名' end from emp e; 2. 判断emp表中员工工资,高于3000,显示高收入,1500-3000中等,其余低等 select e.ename, case when e.ename > 3000 then '高收入' when e.ename > 1500 then '中等收入' else '低收入' end from emp e; 3. oracle专用: select e.ename, decode(e.ename 'SMITH' , '曹操' , 'WARD' , '诸葛' , '无名') 中文名 from emp e; 中文名表示起别名,在oracle中,除了起别名,都用单引号,别名可以不用引号或者使用双引号多行/聚合函数:作用于多行,返回一个值
select count(1) from emp; -- 查询总数量 select sum(sal) from emp; -- 工资总和 select max(sal) from emp; -- 最大工资 select min(sal) from emp; -- 最低工资 select avg(sal) from emp; -- 平均工资分组查询
1. 查询出每个部门的平均工资:
select e.deptno,avg(e.sal)
from emp e
group by e.deptno 2. select [字段列表] from 表名 where 条件 group by 字段 having 条件; --- 字段列表: group by之后的字段和聚合统计函数 3. where和having的区别: where: 在group by分组之前进行条件的过滤 having: 在group by分组之后进行条件的过滤 多表查询
1. 笛卡尔积(没有任何意义)
2. 等值连接
select * from emp e, dept d where e.deptno = d.deptno;
3. 内连接
select * from emp e inner join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno; 4. 外连接(左/右) select * from emp e left join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno; select * from emp e right join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno; select * from emp e full join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;自连接查询:
关键在于起别名
查询出员工的姓名和员工领导的姓名
select e1.ename. e2.ename from emp e1. emp e2 where e1.mgr = e2.empno;子查询(尽量使用多表查询,不要使用子查询-----sql优化)
子查询返回一个值(=)
子查询返回一个集合(in)
子查询返回一张表(子查询,把查询出的结果看作一个表起别名来使用)
Oracle的分页:
rownum伪列,配合三层嵌套子查询完成
条件中的rownum是从1开始的,不能设置大于某个数字,所以考虑使用别名
select * from (
select rownum rn,t.* from ( select e.* from emp e order by sal desc ) t where rownum < 11 ) where rn > 5;视图和索引
视图:
1. 视图的概念:
提供一个查询窗口,所有数据来自于原表
2. 视图的操作:
创建视图(必须有dba权限)
create or replace view v_name as 查询语句;
使用视图
select * from v_name; 视图修改字段(可以修改,但是不推荐) update v_emp set job='CLERK' where ename='ALLEN'; commit; 创建只读视图 create view v_name as 查询语句 with read only; 3. 视图的作用: 1. 视图可以屏蔽掉敏感字段(数据安全) 2. 方便操作,数据的统一 4. 创建表(将查询结果存入表中): create table table_name as 查询语句; ----- create table emp as select * from scott.emp; 索引: 1. 索引的概念: 在表的列上构建一个二叉树,达到大幅度提高查询效率的目的,但是索引会影响增删改的效率 2. 索引创建的时机: 1. 数据量大的表 2. 经常查询的表 3. 针对什么样的字段建立索引: 经常在where条件后的字段 4. 索引的分类: * 单列索引 1. 创建: create index idx_name on table_name(column_name); 2. 触发规则(单行函数,模糊查询都会影响索引的触发,也就是不会触发索引): 单列索引触发规则,条件必须是索引列中的原始值 * 复合索引 1. 创建: create index idx_name on table_name(column_name1,column_name2); 2. 触发规则: 复合索引第一列为优先检索列. 如果要触发复合索引,必须包含有优先检索列中的原始值pl/sql编程语言
1. 概念:
pl/sql编程语言对sql语言的扩展,使得sql语言具有过程化编程的特性.
主要用来编写存储过程和存储函数的.
2. 声明方法:
declare
i number(2) := 10; ====> 定义普通变量 s varchar2(10) := '小明'; ena table_name.column_name%type; ====> 定义引用型变量,类型与表的字段类型一样 emprow emp%rowtype; ====> 记录型变量 begin dbms_output.put_line(i); ====> 输出 dbms_output.put_line(s); select ename into ena from emp where empno = 1; ====> 使用查询语句为变量赋值 dbms_output.put_line(ena); select * into emprow from emp where empno = 1; -- 不能直接输出emprow,输出emprow.column来输出内容 dbms_output.put_line(emprow.ename || '工作为' || emprow.job); end; 3. if判断: declare i number(3) := &i; ====> 输入值,将值给i begin if 条件1 then 条件1满足执行的逻辑 elsif 条件2 then 条件2满足执行的逻辑 else 条件都不满足执行的逻辑 end if; end; -------------------------------------------- declare -- 输入值 i number(2) := &i; begin if i < 18 then dbms_output.put_line('未成年'); elsif i < 30 then dbms_output.put_line('青年'); elsif i < 50 then dbms_output.put_line('壮年'); else dbms_output.put_line('老年'); end if; end; 4. loop循环: 1. while循环: declare i number(2) := 1; ===> 如果i递增越界,会报异常 begin while 条件 loop 执行逻辑(输出等); 条件变量的改变; ===> i := i+1; end loop; end; 2. exit循环(掌握掌握): declare i number(2) := 1; begin loop exit when 条件; ===> 条件符合,退出循环 执行逻辑(输出等); 条件变量的改变; end loop; end; 3. for循环 decalre begin for i in 1..10 loop ===> 两个点代表范围 执行逻辑; end loop; end; 5. 游标的使用: 游标: 可以存放多个对象,多行记录(临时存放多行数据). declare cursor c1 is select * from emp; ====> 定义游标 emprow emp%rowtype; begin open c1; ===> 打开游标 loop fetch c1 into emprow; ====> 获取游标中的一行记录 exit when c1%notfound; ====> 查找不到对象的时候自动退出(notfound是游标中的属性,用来判断是否还有数据) dbms_output.put_line(emprow.ename); end loop; close c1; ===> 关闭游标 end; -------------------------------------------------------- 为指定部门涨工资 declare cursor c3(dno emp.deptno%type) is select empno from emp where deptno = dno; eno emp.empno%type; begin open c3(20); loop fetch c3 into eno; exit when c3%notfound; update emp set sal=sal + 100 where empno = eno; commit; end loop; close c3; end;存储过程和存储函数
1. 存储过程(提高复用性,提高业务逻辑的执行效率):
1. 概念: 提前已经编译好的一段pl/sql片段,放置在数据库端,可以直接被调用,这一段pl/sql一般都是固定步骤的业务.
2. 创建语法(参数类型不能加长度):
create or replace procedure 过程名(参数名 in/out 数据类型) ===> in可以省略 AS/IS 变量的声明; begin PLSQL子程序体; end; ------------------------------------------------------ 给指定员工涨工资: create or replace procedure p1(eno in emp.empno%type) as begin update emp set sal=sal+100 where empno = eno; commit; end; 3. 调用存储过程(两种) 通过PL/SQL进行调用 declare begin p1(1); end; 通过java程序调用 2. 存储函数: 1. 创建(返回的参数类型和参数的类型不能加长度): create or replace function fun_name(参数名 in type,....) return 参数类型 is 变量名 变量类型; begin 执行逻辑; return 结果变量; end 函数名; ---------------- 存储函数算年薪 create or replace function fun_salyear(eno in number) return number is yearsal number(10); begin select sal*12+nvl(comm,0) into yearsal from emp where empno = eno; return yearsal; end; 2. 调用: 存储函数在调用的时候返回值必须接受. declare 返回变量的声明 begin 返回变量 := 函数名(参数); 逻辑处理; end; ----------------- declare yearsal number(10); begin yearsal := fun_salyear(7788); dbms_output.put_line(yearsal); end; 3. out参数的使用: 存储过程算年薪: --------- 使用存储过程测试out参数的使用 create or replace procedure pro_yearsal(eno in emp.empno%type,yearsal out number) is begin select sal*12+nvl(comm,0) into yearsal from emp where empno = eno; end; ----------- 测试 declare yearsal number(10); begin pro_yearsal(7788,yearsal); dbms_output.put_line(yearsal); end; 另外一种写法: ---- 存储过程计算年薪的另外一种写法 create or replace procedure pro_yearsal2(eno in emp.empno%type,yearsal out number) is s number(10); c emp.comm%type; begin select sal*12,nvl(comm,0) into s,c from emp where empno = eno; yearsal := s + c; end; ---- 调用存储过程 declare yearsal number(10); begin pro_yearsal2(7788,yearsal); dbms_output.put_line(yearsal); end; 4. in和out的参数区别是什么? in: 输入的参数(默认值) out: 输出参数(对外暴露的变量) 调用的时候需要传入的值就是输入参数,调用的时候不需要传入值并且在执行完成后还需要获取的值是输出参数. 5. 存储过程和存储函数的区别 1. 语法区别: * 关键字不一样: procedure和function * 存储函数比存储过程多了两个return 2. 本质区别: 存储函数有返回值,存储过程没有返回值. > 实际开发中,还是存储过程用的比较多. 触发器
1. 触发器的概念:
制定一个规则,在我们做增删改操作前(before)后(after),只要满足规则,自动触发,无需调用.
2. 分类
语句级触发器: 在insert/update/delete语句的时候触发一次,不包含有for each row的就是语句级触发器. 行级触发器: 在insert/update/delete语句的时候影响多少行就触发多少次,包含有for each row的就是行级触发器. 3. 伪记录变量: 一般在修改的删除的时候用的多,用于备份,下面两个只能用于行级触发器. :old,获取操作前的数据 :new,获取操作后的数据 4. 创建语句级触发器 create or replace trigger trigger_name before/after insert/update/delete on table_name declare begin 逻辑的执行; end; ---------------------------------------------- ---- 创建语句级触发器 create or replace trigger tri_name after insert on person declare begin dbms_output.put_line('插入一条数据'); end; ---- 满足条件即可触发触发器 insert into person values(s_person.nextval,'b'); 5. 触发器的触发: 只要满足条件就触发. 6. 创建行级别的触发器: create or replace trigger trigger_name before/after insert/update/delete on table_name for each row declare begin 逻辑的执行; end; --------------------------------------------- ---- 创建行级插入触发器触发器,输出插入的id值 create or replace trigger tri_id after insert on person for each row declare begin dbms_output.put_line('插入的数据id是:' || :new.pid); end; ---- 满足条件即可触发触发器 insert into person values(s_person.nextval,'b'); 7. pl/sql抛出异常(第一个参数是异常的编码,第二个是异常的提示信息) raise_application_error(-20001~-20999之间,'提示信息'); 8. 触发器实现主键自增(行级触发器) create or replace trigger trigger_name before insert on table_name for each row declare begin select seq_person.nextval into :new.主键名 from dual; end; ---------------------------------- ---- 创建主键自增的触发器(主键自增一定是行级触发器,并且在插入之前) create or replace trigger auid before insert on person for each row declare begin select s_person.nextval into :new.pid from dual; end; ---- 使用主键自增的触发器 insert into person(pname) values ('小zhi'); select * from person; 存储函数和触发器的两个小例子:
---- 创建不能给员工降薪的触发器
create or replace trigger tri_raise_sal before update on emp for each row declare begin if :old.sal > :new.sal then raise_application_error(-20001,'不能给员工降薪'); end if; end; update emp set sal = sal - 1 where empno = 7788; ---- 使用存储函数实现提供部门id,查询部门名称 create or replace function fun_ename_dname(dno dept.deptno%type) return dept.dname%type is dna dept.dname%type; begin select dname into dna from dept where deptno = dno; return dna; end; ---- 使用上面的存储函数 select e.ename, fun_ename_dname(e.deptno) from emp e; select e.ename, d.dname from emp e, dept d where e.deptno=d.deptno;java程序连接Oracle数据库
oracle10g----> ojdbc14.jar
oracle11g----> ojdbc6.jar
与mysql相比,不同的地方在于驱动包不同,url不同.
1. 首先需要注意的是oracle的ojdbc的驱动jar包从maven中央仓库下载不下来,所以只能手动向本地仓库进行安装:
mvn install:install-file -DgroupId=com.oracle -DartifactId=ojdbc14 -Dversion=10.2.0.4.0 -Dpackaging=jar -Dfile=D:/ojdbc14.jar --- 后面的Dfile是你本地的ojdbc14.jar存放的位置 2. 使用java连接oracle的步骤: // 加载数据的驱动 Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"); // 获取数据库的连接,ip是oracle服务所在服务器的ip,username表示用户名,password表示密码 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@ip:1521:orcl","username","password";) // 得到预编译的Statement对象(增删改查的时候使用) PreparedStatement ps = connection.preparedStatement("sql语句"); // 设置预编译sql语句中的占位符 preparedStatement.setObject(1,"值"); // 执行数据库查询操作 ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); // 处理结果集 while(rs.next()){ 逻辑处理; } // 释放资源 rs.close(); ps.close(); connection.close(); 3. 使用java执行存储过程和存储函数 /** * java调用存储过程 * {?= call <procedure-name>[(<arg1>,<arg2>, ...)]} 调用存储函数使用 * {call <procedure-name>[(<arg1>,<arg2>, ...)]} 调用存储过程使用 * @throws Exception */ @Test public void testProcedure() throws Exception{ // 加载数据库驱动 Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"); // 得到连接 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@192.168.88.131:1521:orcl", "itheima", "itheima"); // 得到预编译的Statement对象 CallableStatement cs = connection.prepareCall("{call pro_yearsal(?,?)}"); // 替换占位符 cs.setObject(1,7788); cs.registerOutParameter(2, OracleTypes.NUMBER); // 执行查询操作 cs.executeQuery(); // 输出结果 System.out.println(cs.getObject(2)); // 释放资源 cs.close(); connection.close(); } /** * java调用存储过程 * {?= call <procedure-name>[(<arg1>,<arg2>, ...)]} 调用存储函数使用 * {call <procedure-name>[(<arg1>,<arg2>, ...)]} 调用存储过程使用 * @throws Exception */ @Test public void testFunction() throws Exception{ // 加载数据库驱动 Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"); // 得到连接 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@192.168.88.131:1521:orcl", "itheima", "itheima"); // 得到预编译的Statement对象 CallableStatement cs = connection.prepareCall("{?=call fun_salyear(?)}"); // 替换占位符 cs.setObject(2,7788); cs.registerOutParameter(1, OracleTypes.NUMBER); // 执行查询操作 cs.executeQuery(); // 输出结果 System.out.println(cs.getObject(1)); // 释放资源 cs.close(); connection.close(); }
转载地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wadmwz/p/9806854.html