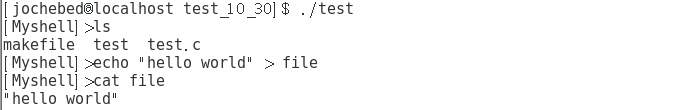
- Linux系统的shell作为操作系统的外壳,为用户提供使用操作系统的接口。
- 它是命令语言、命令解释程序及程序设计语言的统称。
- 相当于bash的一个子进程,父进程等待,子进程进行程序替换。
- shell充当一个桥梁:将使用者的命令翻译给核心(kernel)处理;同时,将核心的处理结果翻译给使用者。
- shell在你成功地登录进入系统后启动,并始终作为你与系统内核的交互手段直至你退出系统。
- 你系统上的每位用户都有一个缺省的shell,每个用户的缺省shell在系统里的/etc/passwd文件里被指定。

写一个简易的shell需要以下操作:
- 获取命令行
- 解析命令行(strtok:将字符串打散)
- 建立一个子进程(fork)
- 替换子进程(execve)
- 父进程等待子进程(wait)

代码实现:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main()
{
while(1)
{
printf("[Myshell]>");
fflush(stdout);
//解析输入到shell上的字符串 ls -a -l
char buffer[1024];
int read_size = read(1, buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1);
if (read_size > 0)
{
buffer[read_size - 1] = 0;
}
char* shell_argv[32] = {NULL};
int shell_index = 0;
char* start = buffer;
while (*start != '\0')
{
while (*start != '\0' && isspace(*start))
{
start++;
}
}
//创建子进程来exec
pid_t pid = vfork();
if (pid < 0)
{
printf("vfork failure\n");
exit(1);
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
//考虑重定向 >
//在字符串数组中找重定向标志
int i = 0;
int flag = 0;
for (; shell_argv[i] != NULL; ++i )
{
if (strcmp(">", shell_argv[i]) == 0)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
int copyFd;
shell_argv[i] = NULL;
if (flag)
{
if (shell_argv[i+1] == NULL)
{
printf("command error\n");
exit(1);
}
close(1);
int fd = open(shell_argv[i+1], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0777
);
copyFd = dup2(1, fd);
}
execvp(shell_argv[0], shell_argv);
if (flag)
{
close(1);
dup2(copyFd, 1);
}
exit(1);
}
else //father process
{
int status = 0;
int ret = waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
if (ret == pid)
{
if (WIFEXITED(status))
{
// printf("exitCode is %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(statu
s));
}
else if (WIFSIGNALED(status))
{
printf("signal is %d\n", WTERMSIG(status));
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}