Python安装Mongo DB驱动。首先通过“pip list”命令,查看是否安装了Mongo。
D:\Python\Python36>python -m pip install pymongo
Collecting pymongo
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/0f/54/ec07858c625460027536aefe8bbe1d0f319b62b5884ec8650e1c2649dccb/pymongo-3.7.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl (309kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 317kB 194kB/s
Installing collected packages: pymongo
Successfully installed pymongo-3.7.0注:Mongo DB驱动源代码地址是https://github.com/mongodb/mongo-python-driver。
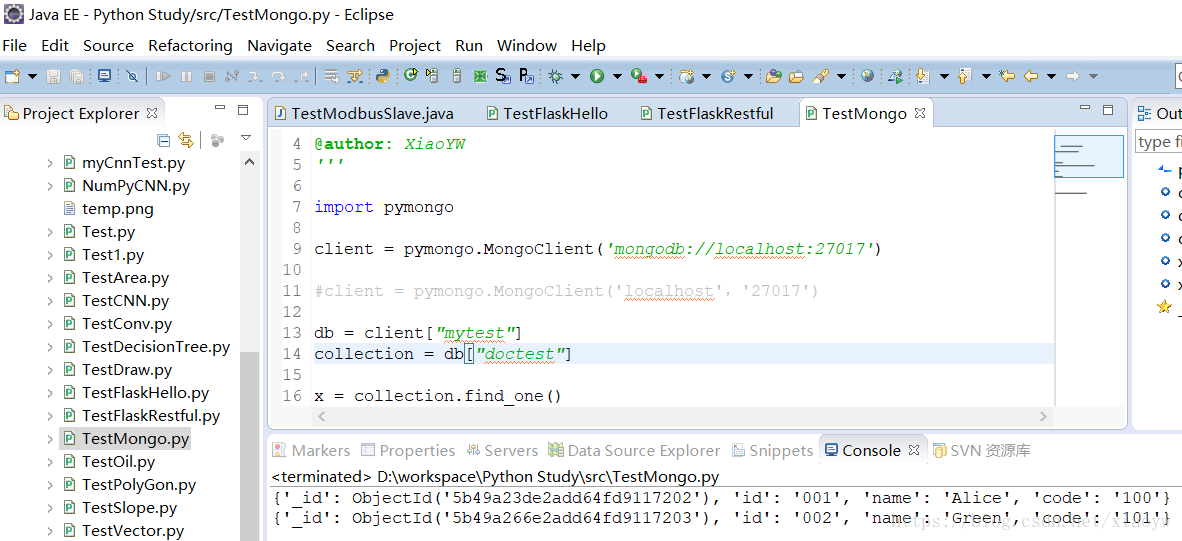
Python操作Mongo数据库示例程序如下所示。
import pymongo
client = pymongo.MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017')
#client = pymongo.MongoClient('localhost','27017')
db = client["mytest"]
collection = db["doctest"]
x = collection.find_one()
x1 = collection.find_one({"name":"Green"})
print(x)
print(x1)代码说明:
client = pymongo.MongoClient(‘mongodb://localhost:27017’) ,创建Mongo数据库连接;
db = client[“mytest”] ,打开数据库,详见后附所描述的操作(创建了“mytest”数据库);
collection = db[“doctest”] ,打开数据集合(可以理解为Table),详见后附所描述的操作(创建了“doctest”集合);
x = collection.find_one() , 从集合“doctest”中查询数据,返回一条记录。
x1 = collection.find_one({“name”:”Green”}), 从集合“doctest”中查询条件为:”name”=”Green”数据,返回一条记录。
附:
安装MongoDB,下载地址为win32/mongodb-win32-x86_64-2008plus-ssl-v4.0-latest.zip
1). 命令方式
首先创建数据库目录,例如D:\mongodb\data。然后运行命令
mongod –dbpath D:\mongodb\data
2). 配置文件方式
在任意位置创建一个配置文件,例如D:\mongodb\conf的目录下创建一个名为mongod.cfg的文件,内容为dbpath=D:\mongodb\data。然后运行命令
D:\mongodb\bin>mongod -config d:\mongodb\conf\mongod.cfg
数据库操作示例内容如下:
D:\mongodb\bin>mongo
MongoDB shell version v4.0.0
connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
MongoDB server version: 4.0.0
Welcome to the MongoDB shell.
MongoDB Enterprise > show dbs
admin 0.000GB
config 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
MongoDB Enterprise > use mytest
switched to db mytest
MongoDB Enterprise > db.createCollection("doctest")
{ "ok" : 1 }
MongoDB Enterprise > show collections
doctest
MongoDB Enterprise > db.doctest.save({id:"001",name:"Alice",code:"100"});
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
MongoDB Enterprise > db.doctest.save({id:"002",name:"Green",code:"101"});
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
MongoDB Enterprise > db.doctest.find();
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5b49a23de2add64fd9117202"), "id" : "001", "name" : "Alice", "code" : "100" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5b49a266e2add64fd9117203"), "id" : "002", "name" : "Green", "code" : "101" }
MongoDB Enterprise > db.doctest.find({"name":"Green"});
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5b49a266e2add64fd9117203"), "id" : "002", "name" : "Green", "code" : "101" }
MongoDB Enterprise >参考:
《初学MongoDB实践笔记——安装、创建数据库、保存及查询数据》 CSDN博客 肖永威 2015年1月