2016.12.14:
代码已知bug:
由于类中有全局变量,声明多个对象时,全局变量指向会改变,造成结果错误并且有内存泄漏。因此该份代码只能声明一个Classifier对象。
新的代码已经重新封装,并且做成多标签输出,下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/sinat_30071459/9715053
主要修改:http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_30071459/article/details/53611678
因为caffe-windows-master的代码比较多,看着很乱,所以想到把它封装成一个类来调用做图像分类,这里以GPU版本为例,记录一下自己封装成DLL和如何使用封装后的DLL的过程。
1.打开解决方案
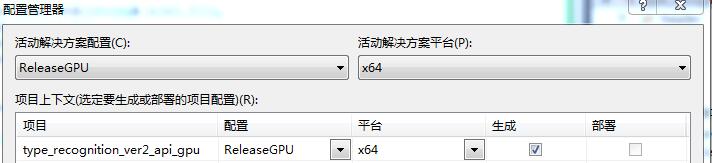
首先,需要修改解决方案配置(默认是Release),我们新建一个叫ReleaseGPU,平台修改为x64(因为用到的其他DLL是64位,配置成win32会出错),如下:
这里我将caffelib的项目名改成了type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu,配置好ReleaseGPU后,右键项目type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu——>属性,配置属性页:
(1)配置属性——常规
(2)C/C++——常规——附加包含目录:
../../3rdparty/include
../../src
../../include
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v7.5\include
预处理器——预处理器定义添加:
TYPE_RECOGNITION_LINK_SHARED
TYPE_RECOGNITION_API_EXPORTS
(3)链接器——常规——附加库目录:
../../3rdparty/lib
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v7.5\lib\x64
(4)链接器——输入——附加依赖项:
kernel32.lib
user32.lib
gdi32.lib
winspool.lib
shell32.lib
ole32.lib
oleaut32.lib
uuid.lib
comdlg32.lib
advapi32.lib
cudart.lib
cublas.lib
curand.lib
libprotobuf.lib
hdf5_tools.lib
hdf5_hl_fortran.lib
hdf5_fortran.lib
hdf5_hl_f90cstub.lib
hdf5_f90cstub.lib
hdf5_cpp.lib
hdf5_hl_cpp.lib
hdf5_hl.lib
hdf5.lib
zlib.lib
szip.lib
opencv_world300.lib
shlwapi.lib
leveldb.lib
cublas_device.lib
cuda.lib
libglog.lib
lmdb.lib
cudnn.lib
libopenblas.dll.a
libgflags.lib
这样就配置好了。
2.添加文件
(1)添加classfy.h和classify.cpp
//classify.h
#pragma once
#include <caffe/caffe.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <iosfwd>
#include <memory>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace caffe; // NOLINT(build/namespaces)
//using namespace boost::property_tree;
using std::string;
/* Pair (number, confidence) representing a prediction. */
typedef std::pair<int, float> Prediction;
class ClassifierImpl {
public:
ClassifierImpl::ClassifierImpl(){};
ClassifierImpl(const string& model_file,
const string& trained_file,
const string& mean_file,
const string& label_file);
std::vector<Prediction> Classify(const cv::Mat& img, int N = 2);
private:
void SetMean(const string& mean_file);
std::vector<float> Predict(const cv::Mat& img);
void WrapInputLayer(std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels);
void Preprocess(const cv::Mat& img,
std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels);
private:
shared_ptr<Net<float> > net_;
cv::Size input_geometry_;
int num_channels_;
cv::Mat mean_;
};//classify.cpp
#include "classify.h"
ClassifierImpl::ClassifierImpl(const string& model_file,
const string& trained_file,
const string& mean_file,
const string& label_file)
{
#ifdef CPU_ONLY
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::CPU);
#else
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::GPU);
#endif
/* Load the network. */
net_.reset(new Net<float>(model_file, TEST));
net_->CopyTrainedLayersFrom(trained_file);
CHECK_EQ(net_->num_inputs(), 1) << "Network should have exactly one input.";
CHECK_EQ(net_->num_outputs(), 1) << "Network should have exactly one output.";
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
num_channels_ = input_layer->channels();
CHECK(num_channels_ == 3 || num_channels_ == 1)
<< "Input layer should have 1 or 3 channels.";
input_geometry_ = cv::Size(input_layer->width(), input_layer->height());
/* Load the binaryproto mean file. */
SetMean(mean_file);
Blob<float>* output_layer = net_->output_blobs()[0];
}
static bool PairCompare(const std::pair<float, int>& lhs,
const std::pair<float, int>& rhs) {
return lhs.first > rhs.first;
}
/* Return the indices of the top N values of vector v. */
static std::vector<int> Argmax(const std::vector<float>& v, int N) {
std::vector<std::pair<float, int> > pairs;
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
pairs.push_back(std::make_pair(v[i], i));
std::partial_sort(pairs.begin(), pairs.begin() + N, pairs.end(), PairCompare);
std::vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
result.push_back(pairs[i].second);
return result;
}
/* Return the top N predictions. */
std::vector<Prediction> ClassifierImpl::Classify(const cv::Mat& img, int N) {
std::vector<float> output = Predict(img);
std::vector<int> maxN = Argmax(output, N);
std::vector<Prediction> predictions;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int idx = maxN[i];
predictions.push_back(std::make_pair(idx, output[idx]));
}
return predictions;
}
/* Load the mean file in binaryproto format. */
void ClassifierImpl::SetMean(const string& mean_file) {
BlobProto blob_proto;
ReadProtoFromBinaryFileOrDie(mean_file.c_str(), &blob_proto);
/* Convert from BlobProto to Blob<float> */
Blob<float> mean_blob;
mean_blob.FromProto(blob_proto);
CHECK_EQ(mean_blob.channels(), num_channels_)
<< "Number of channels of mean file doesn't match input layer.";
/* The format of the mean file is planar 32-bit float BGR or grayscale. */
std::vector<cv::Mat> channels;
float* data = mean_blob.mutable_cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < num_channels_; ++i) {
/* Extract an individual channel. */
cv::Mat channel(mean_blob.height(), mean_blob.width(), CV_32FC1, data);
channels.push_back(channel);
data += mean_blob.height() * mean_blob.width();
}
/* Merge the separate channels into a single image. */
cv::Mat mean;
cv::merge(channels, mean);
/* Compute the global mean pixel value and create a mean image
* filled with this value. */
cv::Scalar channel_mean = cv::mean(mean);
mean_ = cv::Mat(input_geometry_, mean.type(), channel_mean);
}
std::vector<float> ClassifierImpl::Predict(const cv::Mat& img) {
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
input_layer->Reshape(1, num_channels_,
input_geometry_.height, input_geometry_.width);
/* Forward dimension change to all layers. */
net_->Reshape();
std::vector<cv::Mat> input_channels;
WrapInputLayer(&input_channels);
Preprocess(img, &input_channels);
net_->ForwardPrefilled();
/* Copy the output layer to a std::vector */
Blob<float>* output_layer = net_->output_blobs()[0];
const float* begin = output_layer->cpu_data();
const float* end = begin + output_layer->channels();
return std::vector<float>(begin, end);
}
/* Wrap the input layer of the network in separate cv::Mat objects
* (one per channel). This way we save one memcpy operation and we
* don't need to rely on cudaMemcpy2D. The last preprocessing
* operation will write the separate channels directly to the input
* layer. */
void ClassifierImpl::WrapInputLayer(std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels) {
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
int width = input_layer->width();
int height = input_layer->height();
float* input_data = input_layer->mutable_cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < input_layer->channels(); ++i) {
cv::Mat channel(height, width, CV_32FC1, input_data);
input_channels->push_back(channel);
input_data += width * height;
}
}
void ClassifierImpl::Preprocess(const cv::Mat& img,
std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels) {
/* Convert the input image to the input image format of the network. */
cv::Mat sample;
if (img.channels() == 3 && num_channels_ == 1)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, CV_BGR2GRAY);
else if (img.channels() == 4 && num_channels_ == 1)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, CV_BGRA2GRAY);
else if (img.channels() == 4 && num_channels_ == 3)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, CV_BGRA2BGR);
else if (img.channels() == 1 && num_channels_ == 3)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, CV_GRAY2BGR);
else
sample = img;
cv::Mat sample_resized;
if (sample.size() != input_geometry_)
cv::resize(sample, sample_resized, input_geometry_);
else
sample_resized = sample;
cv::Mat sample_float;
if (num_channels_ == 3)
sample_resized.convertTo(sample_float, CV_32FC3);
else
sample_resized.convertTo(sample_float, CV_32FC1);
cv::Mat sample_normalized;
cv::subtract(sample_float, mean_, sample_normalized);
/* This operation will write the separate BGR planes directly to the
* input layer of the network because it is wrapped by the cv::Mat
* objects in input_channels. */
cv::split(sample_normalized, *input_channels);
CHECK(reinterpret_cast<float*>(input_channels->at(0).data)
== net_->input_blobs()[0]->cpu_data())
<< "Input channels are not wrapping the input layer of the network.";
}
然后,我们再写一个导出类即可(如下(2))。
(2)添加type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu.h和type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu.cpp
//type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu.h
#ifndef TYPE_RECOGNITION_API_H_ //保证头文件包含一次
#define TYPE_RECOGNITION_API_H_
#ifdef TYPE_RECOGNITION_LINK_SHARED
#if defined(__GNUC__) && __GNUC__ >= 4
#define TYPE_RECOGNITION_API __attribute__ ((visibility("default")))
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
#define TYPE_RECOGNITION_API
#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
#if defined (TYPE_RECOGNITION_API_EXPORTS)
#define TYPE_RECOGNITION_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define TYPE_RECOGNITION_API __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
#else
#define TYPE_RECOGNITION_API
#endif
#else
#define TYPE_RECOGNITION_API
#endif
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
/* Pair (label, confidence) representing a prediction. */
typedef std::pair<int, float> Prediction;
class TYPE_RECOGNITION_API Classifier //导出类
{
public:
Classifier(){};
~Classifier();
Classifier(const std::string& model_file,
const std::string& trained_file,
const std::string& mean_file,
const std::string& label_file);
std::vector<Prediction> Classify(const cv::Mat& img, int N = 2);
};
#endif//type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu.cpp
#include "type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu.h"
#include "classify.h"
ClassifierImpl *impl = NULL;
Classifier::Classifier(const std::string& model_file,
const std::string& trained_file,
const std::string& mean_file,
const std::string& label_file)
{
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#pragma comment( linker, "/subsystem:windows")
#endif
impl = new ClassifierImpl(model_file, trained_file, mean_file, label_file);
}
Classifier::~Classifier()
{
//impl->~ClassifierImpl();
if (impl)
delete impl;
}
std::vector<Prediction> Classifier::Classify(const cv::Mat& img, int N)
{
return impl->Classify(img, N);
}
用到的文件是dll和lib文件,使用这些文件方法如下。
3.使用DLL
将type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu.dll复制到caffe-windows-master\3rdparty\bin;
将type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu.lib复制到caffe-windows-master\3rdparty\lib;
将type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu.h复制到caffe-windows-master\3rdparty\include;
然后,新建一个控制台项目,配置成x64,
右键项目配置如下:
C/C++——常规——附加包含目录:(这里路径自己修改)
********\3rdparty\include
链接器——常规——附加库目录:
********\3rdparty\lib
链接器——输入——附加依赖项:
将type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu.lib和opencv_world300.lib加进去,
然后,为项目添加一个cpp文件:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include "type_recognition_ver2_api_gpu.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
std::string model_file("./model/deploy.prototxt");
std::string trained_file("./model/net.caffemodel");
std::string mean_file("./model/type_mean.binaryproto");
std::string label_file("./model/typelabels.txt");
Classifier myclassifier(model_file, trained_file, mean_file, label_file);
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("../image/automobile/000001.jpg", -1);
std::vector<Prediction> result = myclassifier.Classify(img);
Prediction p = result[0];
std::cout <<"类别:"<< p.first << "确信度:" << p.second << "\n";
getchar();
return 0;
}
(下面链接的代码有bug,声明多个对象会出问题,新的代码:http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_30071459/article/details/53735600)
封装好的代码加入了opencv显示图像,可通过链接下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/sinat_30071459/9568131 是一个txt文件,因为csdn上传限制,上传到了百度云,txt里面有百度云链接。
将Classification\CLassificationDLL\bin加入环境变量后即可。
效果如下:(把Freetype库也加了进去,标签可以显示中文)