版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33696779/article/details/69981480
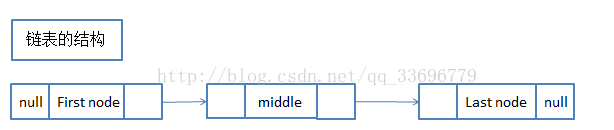
LinkedList底层实现时链表,如上图,如果大家对链表的基本概念不理解,可先行去学习一下链表的基本知识,别的先不多说了,直接上代码:
第一步:定义一个节点类,来表示链表中的节点
package com.collection;
/**
* 定义链表的一个节点
* @author Mrzhang
*
*/
public class Node {
/**
* 前一个节点
*/
private Node privious;
/**
* 当前节点的值
*/
private Object value;
/**
* 后一个节点
*/
private Node nextNode;
public Node getPrivious() {
return privious;
}
public void setPrivious(Node privious) {
this.privious = privious;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(Object value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node getNexttNode() {
return nextNode;
}
public void setNextNode(Node lastNode) {
this.nextNode = lastNode;
}
}
package com.collection;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* 模拟LinkedList基本方法 底层实现是链表
*
* @author Mrzhang
*
* @param <E>
*/
public class MyLinkedList<E> {
// 第一个节点
private Node firstNode;
// 最后一个节点
private Node lastNode;
// 总长度
private int size;
// 增加一个节点
public void add(E value) {
Node node = new Node();
node.setValue(value);
if (firstNode == null) {
node.setPrivious(null);
node.setNextNode(null);
firstNode = node;
lastNode = node;
}
if (firstNode != null) {
node.setPrivious(lastNode);
node.setNextNode(null);
lastNode.setNextNode(node);
lastNode = node;
}
size++;
}
// 在指定位置添加一个节点
public void add(int index, E e) {
rangeCheck(index);
Node node = node(index);
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.setValue(e);
if (node != null) {
if (node == firstNode) {
newNode.setPrivious(null);
newNode.setNextNode(firstNode);
firstNode = newNode;
} else {
Node up = node.getPrivious();
up.setNextNode(newNode);
newNode.setPrivious(up);
newNode.setNextNode(node);
}
size++;
}
}
// 获取链表长度
public int size() {
return size;
}
// 根据索引查询
public E get(int i) {
rangeCheck(i);
Node node = node(i);
return (E) node.getValue();
}
// 根据索引删除
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
Node node = node(index);
if (node == firstNode) {
firstNode = node.getNexttNode();
firstNode.setPrivious(null);
}
if (node == lastNode) {
lastNode = node.getPrivious();
lastNode.setNextNode(null);
} else {
node.getPrivious().setNextNode(node.getNexttNode());
node.getNexttNode().setPrivious(node.getPrivious());
}
size--;
return (E) node.getValue();
}
// 检查是否越界
private void rangeCheck(int i) {
if (i >= size || i < 0) {
try {
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("数组越界");
}
}
}
// 根据索引获取节点(分为前后查询)
private Node node(int index) {
Node node = null;
if(index<(size>>2)){
node = firstNode;
for (int count = 0; count < index; count++) {
node = node.getNexttNode();
}
}
else{
node=lastNode;
for (int count=size-1; count>index; count--) {
node = node.getPrivious();
}
}
return node;
}// 下边是测试代码public static void main(String[] args) {MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();linkedList.add("zhang0");linkedList.add("zhang1");linkedList.add("zhang2");linkedList.add(0, "haha");linkedList.add("zhang3");linkedList.add("zhang4");linkedList.add("zhang5");for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) {System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));}}}
以上就是LinkedList的一些基本方法的实现,这个在笔试的时候也可能会被考到,大家可以多多练习,来增强自身的基本功。
