一、项目目录结构树

二、项目启动
三、往指定的shp文件里写内容
(1) json数据【Post】
{ "name":"test", "path":"c:/test", "geom":"MULTIPOLYGON(((101.870371 25.19228,101.873633 25.188183,101.880564 25.184416,101.886808 25.186028,101.892043 25.189969,101.896592 25.190163,101.903716 25.190785,101.905454 25.193464,101.899897 25.196202,101.894146 25.197911,101.891657 25.19826,101.886078 25.197658,101.884211145538 25.2007060137013,101.88172564506 25.1949712942389,101.87874 25.199619,101.874641 25.200998,101.868547 25.202415,101.863741 25.202415,101.85887 25.202842,101.854557 25.202182,101.852604 25.199736,101.852282 25.19628,101.854492 25.194183,101.855608 25.192668,101.863698 25.192105,101.870371 25.19228)))", "id":1001, "des":"湖泊水面" }
(2)接口调用

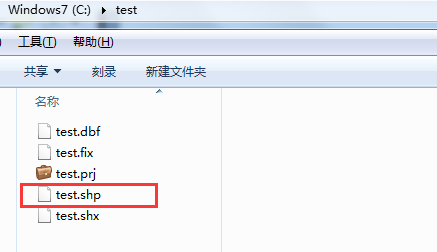
(3)QGIS查看,验证数据有效性

四、读取指定shp文件,并显示内容
(1)接口调用

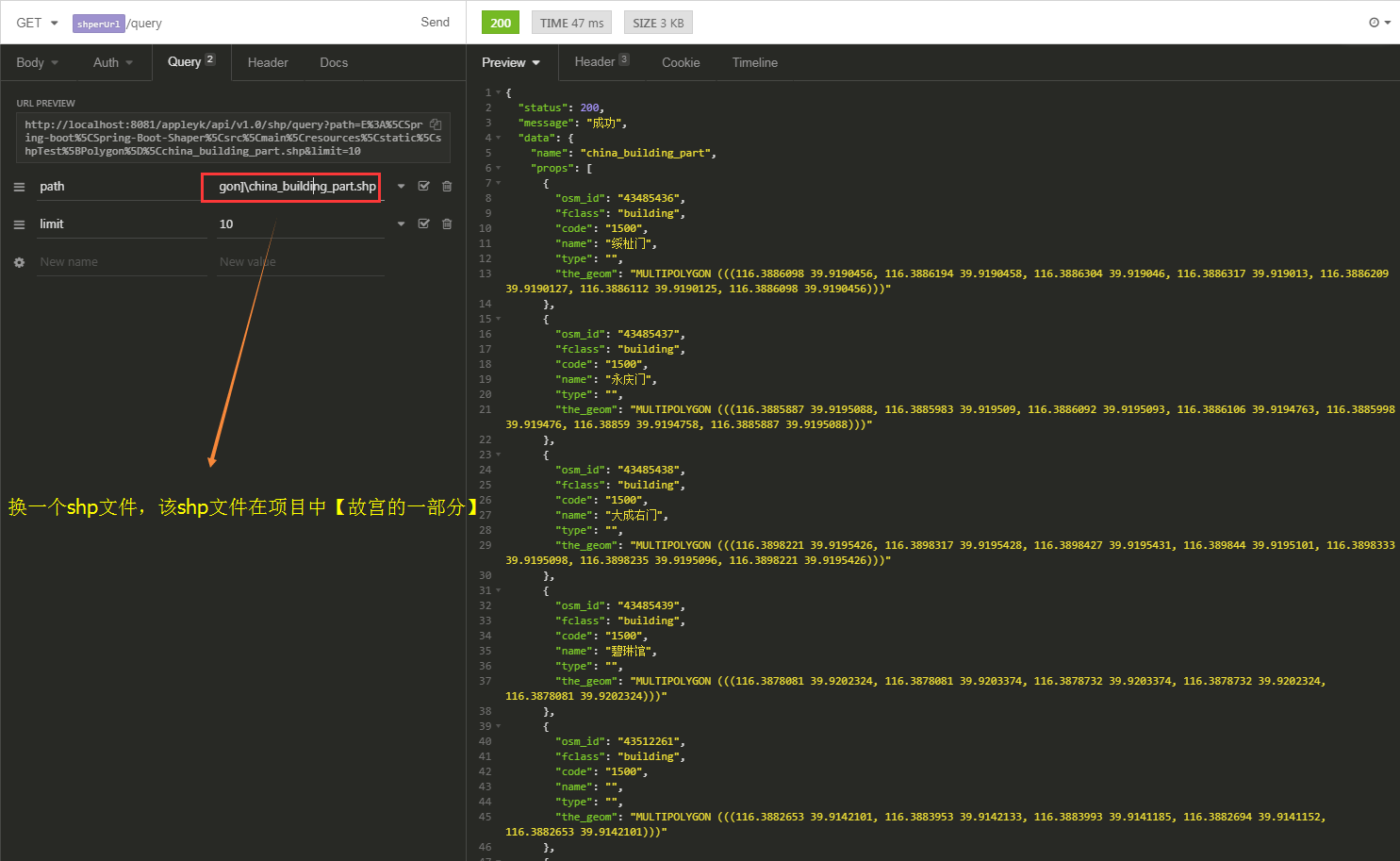
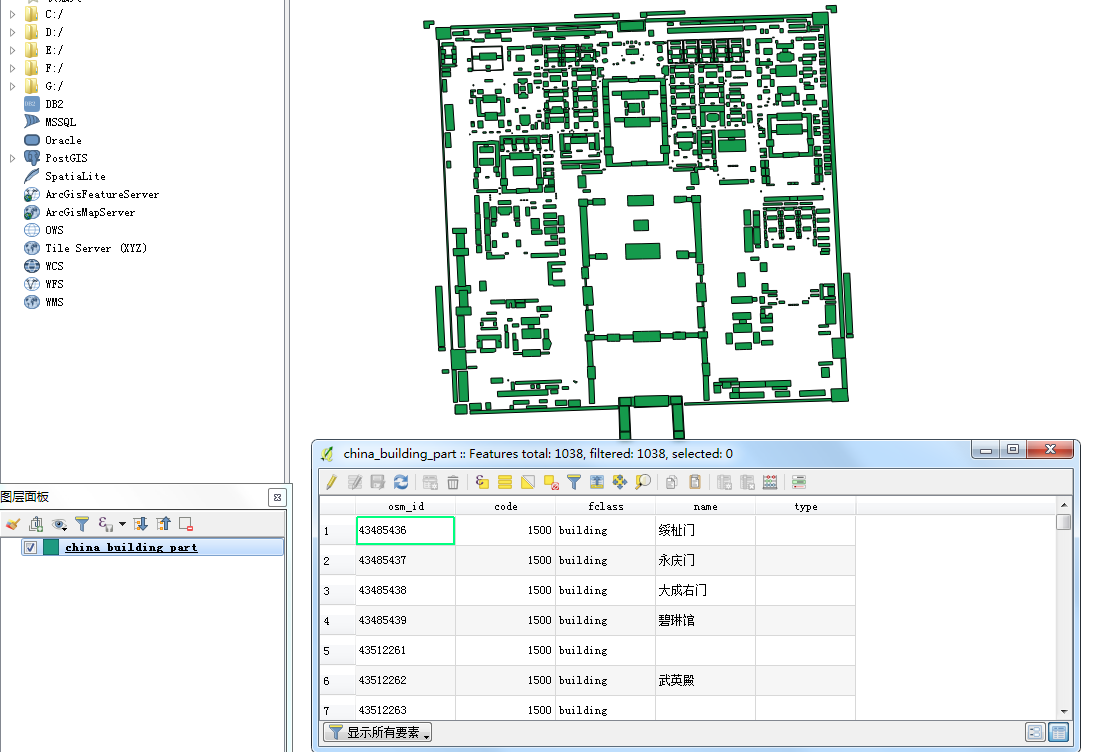
(2)QGIS显示北京故宫【shp文件在项目中的static文件夹下】
五、将指定的shp文件转成image文件或流
(1) 接口调用 === 转image【png】文件
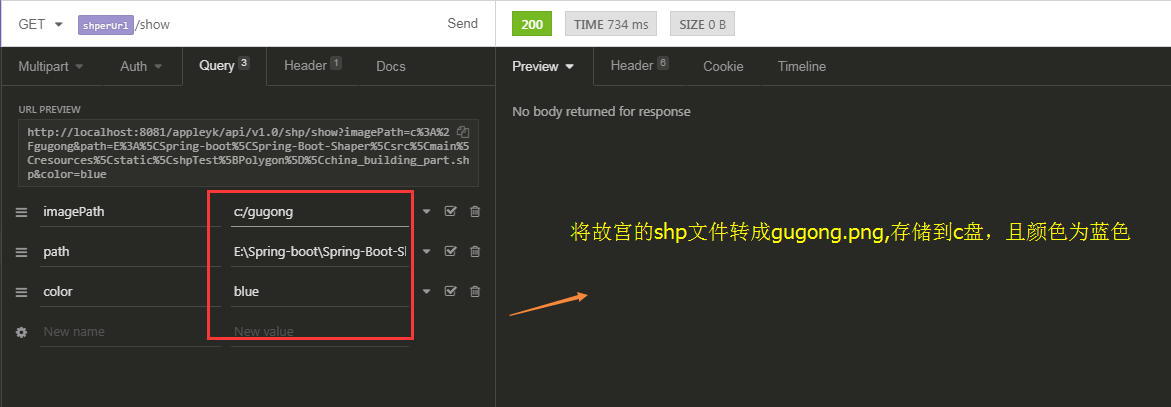
c盘下查看

(2) 接口调用 === 转image流,输出到客户端
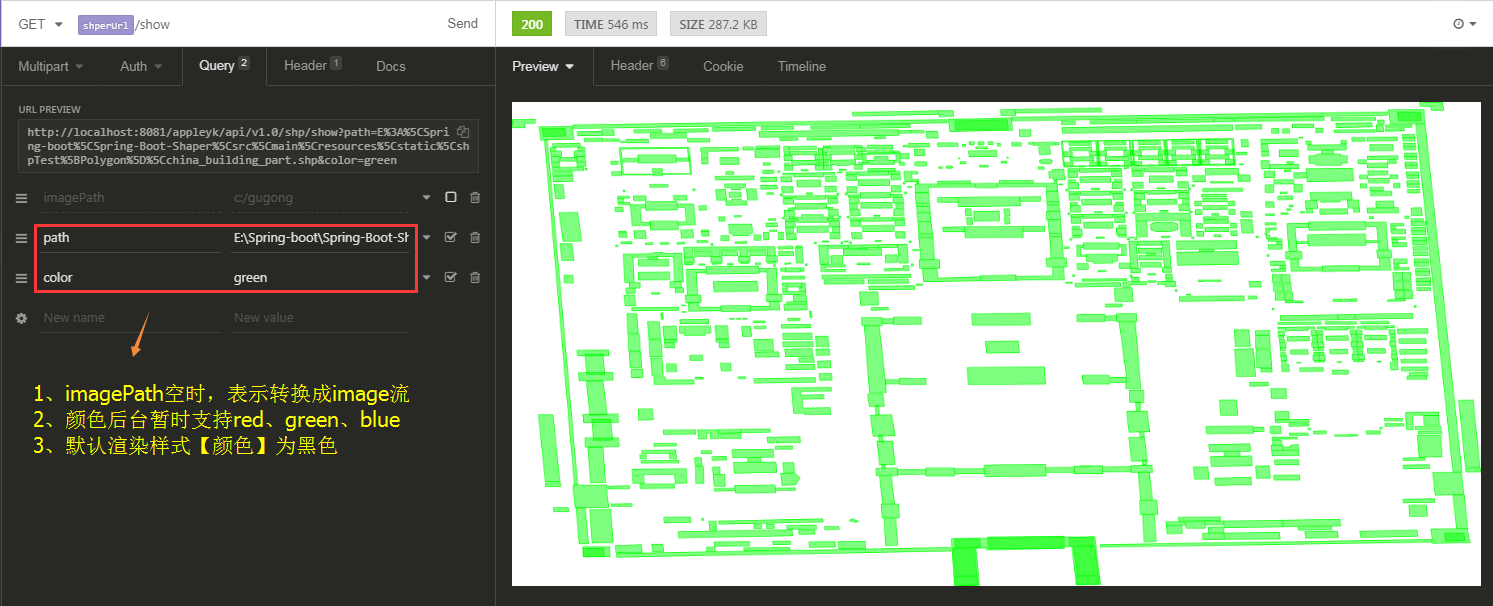
六、核心工具类【ShpTools】
package com.appleyk.geotools; import com.appleyk.IO.StringTokenReader; import com.appleyk.pojos.ShpDatas; import com.appleyk.pojos.ShpInfo; import com.appleyk.result.ResponseMessage; import com.appleyk.result.ResponseResult; import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.*; import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Point; import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Polygon; import org.geotools.data.*; import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStore; import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStoreFactory; import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureSource; import org.geotools.feature.FeatureCollection; import org.geotools.feature.FeatureIterator; import org.geotools.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.ReferencedEnvelope; import org.geotools.map.FeatureLayer; import org.geotools.map.Layer; import org.geotools.map.MapContent; import org.geotools.referencing.crs.DefaultGeographicCRS; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.StreamingRenderer; import org.geotools.styling.SLD; import org.geotools.styling.Style; import org.geotools.swing.JMapFrame; import org.geotools.swing.data.JFileDataStoreChooser; import org.opengis.feature.Property; import org.opengis.feature.simple.SimpleFeature; import org.opengis.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureType; import org.springframework.util.ResourceUtils; import javax.imageio.ImageIO; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.image.BufferedImage; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Serializable; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * <p>shapefile读写工具类</p> * @author Appleyk * @blob https://blog.csdn.net/appleyk * @date Created on 上午 11:54 2018-10-12 */ public class ShpTools { /** * 集合对象构造器【自定义的】 */ private static GeometryCreator gCreator = GeometryCreator.getInstance(); /** * 边界 */ private static ReferencedEnvelope bounds; // 画布的宽度 private static final int IMAGE_WIDTH = 2400; // 画布的高度 private static final int IMAGE_HEIGHT = 1200; /** * 通过shp文件路径,读取shp内容 * @param filePath * @throws Exception */ public static ShpDatas readShpByPath(String filePath,Integer limit) throws Exception { // 一个数据存储实现,允许从Shapefiles读取和写入 ShapefileDataStore shpDataStore = new ShapefileDataStore(new File(filePath).toURI().toURL()); // 设置编码【防止中文乱码】 shpDataStore.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8")); // getTypeNames:获取所有地理图层,这里我只取第一个【如果是数据表,取出的就是表名】 String typeName = shpDataStore.getTypeNames()[0]; System.out.println("shp【图层】名称:"+typeName); FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> result = getFeatures(shpDataStore, typeName); // 迭代特征集合 FeatureIterator<SimpleFeature> iterator = result.features(); ShpDatas shpDatas = new ShpDatas(); shpDatas.setName(typeName); shpDatas.setShpPath(filePath); buildShpDatas(limit, iterator, shpDatas); iterator.close(); return shpDatas; } /** * 根据数据源及图层名称拿到特征集合 * @param shpDataStore * @param typeName * @return * @throws IOException */ private static FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> getFeatures(ShapefileDataStore shpDataStore, String typeName) throws IOException { // 通过此接口可以引用单个shapefile、数据库表等。与数据存储进行比较和约束 FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> featureSource = shpDataStore.getFeatureSource(typeName); // 一个用于处理FeatureCollection的实用工具类。提供一个获取FeatureCollection实例的机制 FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> result = featureSource.getFeatures(); System.out.println("地理要素【记录】:"+result.size()+"个"); System.out.println("=================================="); return result; } /** * 构建shpDatas对象 * @param limit * @param iterator * @param shpDatas */ private static void buildShpDatas(Integer limit, FeatureIterator<SimpleFeature> iterator, ShpDatas shpDatas) { // 这里我们只迭代前limit个 int stop = 0; while (iterator.hasNext()) { if (stop > limit) { break; } // 拿到一个特征 SimpleFeature feature = iterator.next(); // 取出特征里面的属性集合 Collection<Property> p = feature.getProperties(); // 遍历属性集合 Map<String,Object> prop = new HashMap<>(); for (Property pro : p) { String key = pro.getName().toString(); String val = pro.getValue().toString(); prop.put(key, val); System.out.println("key【字段】:"+key+"\t|| value【值】:"+val); } System.out.println("\n============================ 序号:"+stop+"\n"); shpDatas.addProp(prop); stop++; } // end 最外层 while } /** * 将一个几何对象写进shapefile * @param filePath * @param geometry */ public static void writeShpByGeom(String filePath, Geometry geometry) throws Exception{ ShapefileDataStore ds = getshpDS(filePath, geometry); FeatureWriter<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> writer = ds.getFeatureWriter(ds.getTypeNames()[0], Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT); // Interface SimpleFeature:一个由固定列表值以已知顺序组成的SimpleFeatureType实例。 SimpleFeature feature = writer.next(); feature.setAttribute("name", "XXXX名称"); feature.setAttribute("path", "c:/test"); feature.setAttribute("the_geom", geometry); feature.setAttribute("id", 1010L); feature.setAttribute("des", "XXXX描述"); System.out.println("========= 写入【"+geometry.getGeometryType()+"】成功 !========="); // 写入 writer.write(); // 关闭 writer.close(); // 释放资源 ds.dispose(); } /** * 将一个几何对象写进shapefile * @param shpInfo */ public static ResponseResult writeShpByGeom(ShpInfo shpInfo) throws Exception{ // 特殊字符串解析器 StringTokenReader reader = new StringTokenReader(); // 根据几何对象的wkt字符串,反解【解析】成Geometry对象 Geometry geometry = reader.read(shpInfo.getGeom()); // 拿到shp对象所在的目录【文件夹】 String path = shpInfo.getPath(); File file = new File(path); if(!file.exists()){ file.mkdir(); } if(!file.isDirectory()){ return new ResponseResult(ResponseMessage.BAD_REQUEST,"path不是有效的文件夹" ); } String filePath = shpInfo.getPath()+"/"+shpInfo.getName()+".shp"; ShapefileDataStore ds = getshpDS(filePath, geometry); String typeName = ds.getTypeNames()[0]; FeatureWriter<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> writer ; if(shpInfo.isAppendWrite()){ // 追加写几何对象 writer = ds.getFeatureWriterAppend(typeName, Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT); }else{ // 覆盖写几何对象 writer = ds.getFeatureWriter(typeName, Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT); } // Interface SimpleFeature:一个由固定列表值以已知顺序组成的SimpleFeatureType实例。 SimpleFeature feature = writer.next(); feature.setAttribute("name", shpInfo.getName()); feature.setAttribute("path", shpInfo.getPath()); feature.setAttribute("the_geom", geometry); feature.setAttribute("id", shpInfo.getId()); feature.setAttribute("des", shpInfo.getDes()); System.out.println("========= 写入【"+geometry.getGeometryType()+"】成功 !========="); // 写入 writer.write(); // 关闭 writer.close(); // 释放资源 ds.dispose(); // 返回创建成功后的shp文件路径 return new ResponseResult(ResponseMessage.OK,filePath); } /** * 拿到配置好的DataStore * @param filePath * @param geometry * @return * @throws IOException */ private static ShapefileDataStore getshpDS(String filePath, Geometry geometry) throws IOException { // 1.创建shape文件对象 File file = new File(filePath); Map<String, Serializable> params = new HashMap<>(); // 2、用于捕获参数需求的数据类 URLP:url to the .shp file. params.put(ShapefileDataStoreFactory.URLP.key, file.toURI().toURL()); // 3、创建一个新的数据存储【如果存在,则不创建】 ShapefileDataStore ds = (ShapefileDataStore) new ShapefileDataStoreFactory().createNewDataStore(params); // 4、定义图形信息和属性信息 -- SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder 构造简单特性类型的构造器 SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder tBuilder = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder(); // 5、设置 -- WGS84:一个二维地理坐标参考系统,使用WGS84数据 tBuilder.setCRS(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84); tBuilder.setName("shapefile"); // 添加名称 tBuilder.add("name", String.class); // 添加shp所在目录名称 tBuilder.add("path", String.class); // 添加 一个几何对象 tBuilder.add("the_geom", geometry.getClass()); // 添加一个id tBuilder.add("id", Long.class); // 添加描述 tBuilder.add("des", String.class); // 设置此数据存储的特征类型 ds.createSchema(tBuilder.buildFeatureType()); // 设置编码 ds.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8")); return ds; } /** * 打开shp文件,获取地图内容 * @param filePath 文件路径 * @param isOpenByChoose 是否自定义打开shp文件 * @throws Exception */ public static MapContent getMapContentByPath(String filePath,boolean isOpenByChoose,String color) throws Exception{ File file; if(isOpenByChoose){ // 1.1、 数据源选择 shp扩展类型的 file = JFileDataStoreChooser.showOpenFile("shp", null); }else{ // 1.2、根据路径拿到文件对象 file = new File(filePath); } if(file==null){ return null; } // 2、得到打开的文件的数据源 FileDataStore store = FileDataStoreFinder.getDataStore(file); // 3、设置数据源的编码,防止中文乱码 ((ShapefileDataStore)store).setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8")); /** * 使用FeatureSource管理要素数据 * 使用Style(SLD)管理样式 * 使用Layer管理显示 * 使用MapContent管理所有地图相关信息 */ // 4、以java对象的方式访问地理信息 -- 简单地理要素 SimpleFeatureSource featureSource = store.getFeatureSource(); bounds = featureSource.getBounds(); // 5、创建映射内容,并将我们的shapfile添加进去 MapContent mapContent = new MapContent(); // 6、设置容器的标题 mapContent.setTitle("Appleyk's GeoTools"); Color color1; if(color == null || "".equals(color)){ color1 = Color.BLACK; }else if("red".equals(color)){ color1 = Color.RED; }else if("green".equals(color)){ color1 = Color.GREEN; }else if("blue".equals(color)){ color1 = Color.BLUE; }else{ color1 = Color.ORANGE; } // 7、创建简单样式 【颜色填充】 Style style = SLD.createSimpleStyle(featureSource.getSchema(),color1); // 8、显示【shapfile地理信息+样式】 Layer layer = new FeatureLayer(featureSource, style); // 9、将显示添加进map容器 mapContent.addLayer(layer); return mapContent; } public static void showMap(MapContent mapContent){ JMapFrame.showMap(mapContent); } /** * shp文件转Image【格式定png】 * @param shpFilePath shp目标文件 * @param destImagePath 转成图片的文件 == 如果没有,转成的图片写进response输出流里 * @param response 响应流 * @throws Exception */ public static void shp2Image(String shpFilePath,String destImagePath,String color, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception{ // 流渲染器 StreamingRenderer renderer = new StreamingRenderer(); MapContent mapContent = getMapContentByPath(shpFilePath,false,color ); renderer.setMapContent(mapContent); Rectangle imageBounds = new Rectangle(0, 0, IMAGE_WIDTH, IMAGE_HEIGHT); BufferedImage dumpImage = new BufferedImage(IMAGE_WIDTH, IMAGE_HEIGHT, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB); Graphics2D g2d = dumpImage.createGraphics(); g2d.fillRect(0, 0, IMAGE_WIDTH, IMAGE_HEIGHT); g2d.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING, RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON); renderer.paint(g2d, imageBounds, bounds); g2d.dispose(); if(destImagePath == null || "".equals(destImagePath)){ ImageIO.write(dumpImage, "png", response.getOutputStream()); }else{ ImageIO.write(dumpImage, "png", new File(destImagePath+".png")); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ File file = ResourceUtils.getFile("classpath:static/shpTest[Point]/dp_tl.shp"); // 从shp文件里面读取属性信息 readShpByPath(file.getAbsolutePath(),10); System.out.println("=================下面开始往shp文件里面写几何对象==================="); // 先创建文件夹test String filePath = "C:/test/test.shp"; String pointWkt="POINT (120.76164848270959 31.22001141278534)"; Point point = gCreator.createPointByWKT(pointWkt); // Polygon【面】 String polygonWkt="POLYGON ((103.859188 34.695908, 103.85661 34.693788, 103.862027 34.69259, 103.863709 34.695078, 103.859188 34.695908))"; Polygon polygon = gCreator.createPolygonByWKT(polygonWkt); // LineString【线】 String linestringWkt="LINESTRING(113.511315990174 41.7274734296674,113.51492087909 41.7284983348307,113.516079593384 41.727649586406,113.515907932007 41.7262243043929,113.514019656861 41.7247989907606,113.512131381714 41.7250872589898,113.51138036319 41.7256637915682,113.511315990174 41.7274734296674)"; LineString lineString = gCreator.createLineByWKT(linestringWkt); // MultiPolygon【多面】 String multiPolyWkt = "MULTIPOLYGON(((101.870371 25.19228,101.873633 25.188183,101.880564 25.184416,101.886808 25.186028,101.892043 25.189969,101.896592 25.190163,101.903716 25.190785,101.905454 25.193464,101.899897 25.196202,101.894146 25.197911,101.891657 25.19826,101.886078 25.197658,101.884211145538 25.2007060137013,101.88172564506 25.1949712942389,101.87874 25.199619,101.874641 25.200998,101.868547 25.202415,101.863741 25.202415,101.85887 25.202842,101.854557 25.202182,101.852604 25.199736,101.852282 25.19628,101.854492 25.194183,101.855608 25.192668,101.863698 25.192105,101.870371 25.19228)))"; MultiPolygon multiPolygon = gCreator.createMulPolygonByWKT(multiPolyWkt); // 几何对象的范围【矩形边界】 Envelope envelope = polygon.getEnvelopeInternal(); System.out.println(envelope); // 往shp文件里面写几何对象 writeShpByGeom(filePath,point); } }
七、联系我
CSDN名: Appleyk
CSDN博客:https://blog.csdn.net/Appleyk
本篇CSDN对应博文:https://blog.csdn.net/Appleyk/article/details/83376510