Listener-监听器
Listener为在Java Web中进行事件驱动编程提供了一整套事件类和监听器接口.Listener监听的事件源分为ServletContext/HttpSession/ServletRequest三个级别:
ServletContext级别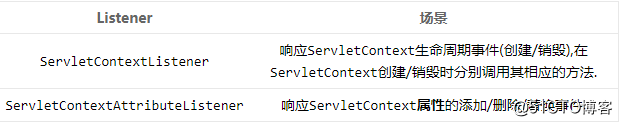
HttpSession级别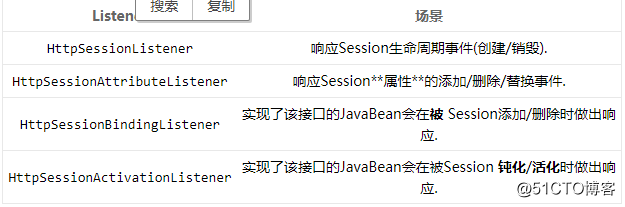
ServletRequest级别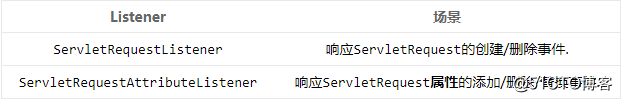
注册
创建监听器只需实现相关接口即可,但只有将其注册到Servlet容器中,才会被容器发现,这样才能在发生事件时,驱动监听器执行.Listener的注册方法有注解和部署描述符两种:
- @WebListener
在Servlet 3.0中, 提供了@WebListener注解:
@WebListener
public class ListenerClass implements ServletContextListener {
// ...
}- 部署描述符
<listener> <listener-class>com.fq.web.listener.ListenerClass</listener-class> </listener>注: 由于HttpSessionBindingListener/HttpSessionActivationListener是直接绑定在JavaBean上, 而并非绑定到Session等域对象, 因此可以不同注册.
示例
加载Spring容器
ContextLoaderListener
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* Close the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}web.xml
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>统计HTTP请求耗时
监控ServletRequest的创建/销毁事件, 以计算HTTP处理耗时
/**
* @author jifang.
* @since 2016/5/4 15:17.
*/
@WebListener
public class PerforationStatListener implements ServletRequestListener {
private static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger("PerforationStatListener");
private static final String START = "Start";
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
ServletRequest request = sre.getServletRequest();
request.setAttribute(START, System.nanoTime());
}
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) sre.getServletRequest();
long start = (Long)request.getAttribute(START);
long ms = (System.nanoTime() - start)/1000;
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
LOGGER.info(String.format("time token to execute %s : %s ms", uri, ms));
}
}HttpSessionBindingListener
当JavaBean实现HttpSessionBindingListener接口后,就可以感知到本类对象被添加/移除Session事件:
Listener```
public class Product implements Serializable, HttpSessionBindingListener {
private int id;
private String name;
private String description;
private double price;
public Product(int id, String name, String description, double price) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.price = price;
}
// ...
public void valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {
System.out.println("bound...");
}
public void valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {
System.out.println("un_bound...");
}}
Servlet
> private static final String FLAG = "flag";
>
> @Override
> protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
> Boolean flag = (Boolean) getServletContext().getAttribute(FLAG);
> if (flag == null || !flag) {
> request.getSession().setAttribute("product", new Product(8, "水晶手链", "VunSun微色天然水晶手链女款", 278.00));
> getServletContext().setAttribute(FLAG, true);
> } else {
> request.getSession().removeAttribute("product");
> getServletContext().setAttribute(FLAG, !flag);
> }
> }
**HttpSessionActivationListener**
为节省内存, Servlet容器可以对Session属性进行迁移或序列化.一般当内存较低时,相对较少访问的对象可以序列化到备用存储设备中(钝化);当需要再使用该Session时,容器又会把对象从持久化存储设备中再反序列化到内存中(活化).HttpSessionActivationListener就用于感知对象钝化/活化事件:
对于钝化/活化,其实就是让对象序列化/反序列化穿梭于内存与持久化存储设备中.因此实现HttpSessionActivationListener接口的JavaBean也需要实现Serializable接口.
在conf/context.xml配置钝化时间
> <Context>
> <WatchedResource>WEB-INF/web.xml</WatchedResource>
>
> <Manager className="org.apache.catalina.session.PersistentManager" maxIdleSwap="1">
> <Store className="org.apache.catalina.session.FileStore" directory="sessions"/>
> </Manager>
> </Context>
JavaBean
> public class Product implements Serializable, HttpSessionActivationListener {
>
> private int id;
> private String name;
> private String description;
> private double price;
>
> // ...
>
> public void sessionWillPassivate(HttpSessionEvent se) {
> System.out.println("passivate...");
> }
>
> public void sessionDidActivate(HttpSessionEvent se) {
> System.out.println("Activate...");
> }
> }
将Product加入Session一分钟不访问后, 该对象即会序列化到磁盘, 并调用sessionWillPassivate()方法, 当再次使用该对象时, Servlet容器会自动活化该Session, 并调用sessionDidActivate()方法.
**Filter-过滤器**
Filter是指拦截请求,并可以对ServletRequest/ServletResponse进行处理的一个对象.由于其可配置为拦截一个或多个资源,因此可用于处理登录/加(解)密/会话检查/图片适配等问题.
Filter中常用的有Filter/FilterChain/FilterConfig三个接口:

过滤器必须实现Filter接口, 当应用程序启动时,Servlet容器自动调用过滤器init()方法;当服务终止时,自动调用destroy()方法.当每次请求与过滤器资源相关资源时,都会调用doFilter()方法;由于doFilter()可以访问ServletRequest/ServletResponse,因此可以在Request中添加属性,或在Response中添加一个响应头,甚至可以对Request/Response进行修饰/替换,改变他们的行为(详见下).

FilterChain中只有一个doFilter()方法, 该方法可以引发调用链中下一过滤器或资源本身被调用.如果没有在Filter的doFilter()中调用FilterChain的doFilter()方法,那么程序的处理将会在此处停止,不会再继续请求.
示例: Filter解决GET/POST编码问题/**
- @author jifang.
@since 2016/5/2 11:55.
*/
public class CharsetEncodingFilter implements Filter {private static final String IGNORE_URI = "ignore_uri";
private static final String URI_SEPARATOR = ",";
private Set<String> ignoreUris = new HashSet<String>();
public void init(FilterConfig config) throws ServletException {
String originalUris = config.getInitParameter(IGNORE_URI);
if (originalUris != null) {
String[] uris = originalUris.split(URI_SEPARATOR);
for (String uri : uris) {
this.ignoreUris.add(uri);
}
}
}public void destroy() {
}public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp, FilterChain chain) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
if (!ignoreUris.contains(uri)) {
if (request.getMethod().equals("GET")) {
request = new EncodingRequest(request);
} else {
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
}
}
chain.doFilter(request, resp);
}private static final class EncodingRequest extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
public EncodingRequest(HttpServletRequest request) { super(request); } @Override public String getParameter(String name) { String value = super.getParameter(name); if (value != null) { try { value = new String(value.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "UTF-8"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } return value; }}
}
注: HttpServletRequestWrapper介绍见Decorator-装饰者部分.
注册/配置
编写好过滤器后, 还需对其进行注册配置,配置过滤器的目标如下:
确定过滤器要拦截的目标资源;
传递给init()方法的启动初始值;
为过滤器命名.
web.xml
<filter>
<filter-name>CharsetEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.fq.web.filter.CharsetEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>ignore_uri</param-name>
<param-value>/new_servlet.do,/hello_http_servlet.do</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharsetEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>也可用@WebFilter注解,其配置方式简单且与部署描述符类似,因此在此就不再赘述
.
FilterConfig
前面介绍了Filter/FilterChain两个接口,下面介绍FilterConfig接口, 其最常用的方法是getInitParameter(), 获取过滤器的初始化参数, 以完成更精细化的过滤规则.不过他还提供了如下实用方法:

拦截方式
过滤器的拦截方式有四种: REQUEST / FORWARD / INCLUDE / ERROR
REQUEST : (默认)直接访问目标资源时执行(地址栏直接访问/表单提交/超链接/重定向等只要在地址栏中可看到目标资源路径,就是REQUEST)
FORWARD : 转发访问执行(RequestDispatcher中forward()方法)
INCLUDE : 包含访问执行(RequestDispatcher中include()方法)
ERROR : 当目标资源在web.xml中配置为中时,并且出现异常,转发到目标资源时, 执行该过滤器.
<filter>
<filter-name>CharsetEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.fq.web.filter.CharsetEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>ignore_path</param-name>
<param-value>/new_servlet.do</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharsetEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
<dispatcher>REQUEST</dispatcher>
<dispatcher>INCLUDE</dispatcher>
</filter-mapping>Decorator-装饰者
Servlet中有4个包装类ServletRequestWrapper/ServletResponseWrapper/HttpServletRequestWrapper/HttpServletResponseWrapper,可用来改变Servlet请求/响应的行为, 这些包装类遵循装饰者模式(Decorator).
由于他们为所包装的Request/Response中的每一个对等方法都提供了默认实现,因此通过继承他们, 只需覆盖想要修改的方法即可.没必要实现原始ServletRequest/ServletResponse/…接口的每一个方法.
实例-页面静态化
HttpServletRequestWrapper在解决GET编码时已经用到, 下面我们用HttpServletResponseWrapper实现页面静态化.
页面静态化是在第一次访问时将动态生成的页面(JSP/Servlet/Velocity等)保存成HTML静态页面文件存放到服务器,再有相同请求时,不再执行动态页面,而是直接给用户响应已经生成的静态页面.
Filter & Decorator
/**
* @author jifang.
* @since 2016/5/7 9:40.
*/
public class PageStaticizeFilter implements Filter {
private static final String HTML_PATH_MAP = "html_path_map";
private static final String STATIC_PAGES = "/static_pages/";
private ServletContext context;
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
this.context = filterConfig.getServletContext();
this.context.setAttribute(HTML_PATH_MAP, new HashMap<String, String>());
}
public void destroy() {
}
@SuppressWarnings("All")
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) resp;
Map<String, String> htmlPathMap = (Map<String, String>) context.getAttribute(HTML_PATH_MAP);
String htmlName = request.getServletPath().replace("/", "_") + ".html";
String htmlPath = htmlPathMap.get(htmlName);
// 尚未生成静态页面
if (htmlPath == null) {
htmlPath = context.getRealPath(STATIC_PAGES) + "/" + htmlName;
htmlPathMap.put(htmlName, htmlPath);
PageStaticizeResponse sResponse = new PageStaticizeResponse(response, htmlPath);
chain.doFilter(request, sResponse);
sResponse.close();
}
String redirectPath = context.getContextPath() + STATIC_PAGES + htmlName;
response.sendRedirect(redirectPath);
}
private static final class PageStaticizeResponse extends HttpServletResponseWrapper {
private PrintWriter writer;
public PageStaticizeResponse(HttpServletResponse response, String path) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
super(response);
writer = new PrintWriter(path, "UTF-8");
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getWriter() throws IOException {
return this.writer;
}
public void close() {
this.writer.close();
}
}
}注册
<filter>
<filter-name>PageStaticzeFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.fq.web.filter.PageStaticizeFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>PageStaticzeFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>注: 在此只是提供一个页面静态化思路, 由于代码中是以Servlet-Path粒度来生成静态页面, 粒度较粗, 细节方面肯定会有所疏漏(但粒度过细又会导致生成HTML页面过多), 因此这份代码仅供参考, 不可用于实际项目(关于该Filter所拦截的jsp页面, 可参考上篇博客的购物车案例).