一、Cache缓存的作用
随着时间的积累,应用的使用用户不断增加,数据规模也越来越大,往往数据库查询操作会成为影响用户使用体验的瓶颈,此时使用缓存往往是解决这一问题非常好的手段之一。Spring 3开始提供了强大的基于注解的缓存支持,可以通过注解配置方式低侵入的给原有Spring应用增加缓存功能,提高数据访问性能。在Spring Boot中对于缓存的支持,提供了一系列的自动化配置,使我们可以非常方便的使用缓存。
1.JSR107
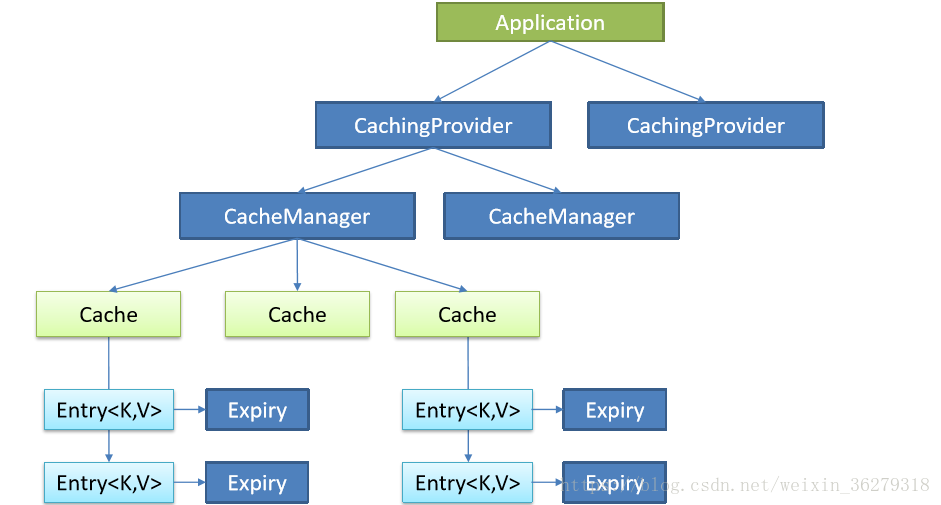
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
示意图:
- CachingProvider定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可 以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
- CacheManager定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache 存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
- Cache是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个 CacheManager所拥有。
- Entry是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
- Expiry 每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期 的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
2.Spring缓存抽象
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache 和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术; 并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发。
- Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合。
- Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache。
- 每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否 已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法 并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
- 使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点:
1.、确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
2、从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据
二、几个重要概念&缓存注解
| Cache | 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有:RedisCache、EhCacheCache、 ConcurrentMapCache等 |
| CacheManager | 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件 |
| @Cacheable | 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存 |
| @CacheEvict | 清空缓存 |
| @CachePut | 保证方法被调用,又希望结果被缓存。 |
| @EnableCaching | 开启基于注解的缓存 |
| keyGenerator | 缓存数据时key生成策略 |
| serialize | 缓存数据时value序列化策略 |
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定 至少一个 |
例如: @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者 @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达 式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数 进行组合 |
例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName” |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存/清除缓存,在 调用方法之前之后都能判断 |
例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userNam e.length()>2”) |
| allEntries (@CacheEvict ) |
是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存 |
例如:@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,allEntries=true) |
| beforeInvocation (@CacheEvict) |
是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,如果指定 为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存, 缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空 缓存 |
例如:@CachEvict(value=”testcache”, beforeInvocation=true) |
| unless (@CachePut) (@Cacheable) | 用于否决缓存的,不像condition,该表达式只在方 法执行之后判断,此时可以拿到返回值result进行判 断。条件为true不会缓存,fasle才缓存 | 例如:@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,unless=”#result == null”) |
| 名字 | 位置 | 描述 | 实例 |
| methodName | root object | 当前被调用的方法名 | #root.methodName |
| method | root object | 当前被调用的方法 | #root.method.name |
| target | root object | 当前被调用的目标对象 | #root.target |
| targetClass | root object | 当前被调用的目标对象类 | #root.targetClass |
| args | root object | 当前被调用的方法的参数列表 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | root object | 当前方法调用使用的缓存列表(如@Cacheable(value={"cache1", "cache2"})),则有两个cache。 |
#root.caches[0].name |
| argument name |
evaluation context | 方法参数的名字. 可以直接 #参数名 ,也可以使用 #p0或#a0 的 形式,0代表参数的索引。 |
#a0、#p0 |
| result | evaluation context | 方法执行后的返回值(仅当方法执行之后的判断有效,如 ‘unless’,’cache put’的表达式 ’cache evict’的表达式 beforeInvocation=false) |
#result |
三、SpringBoot缓存工作原理以及@Cacheable运行流程
1.如果需要分析自动配置的原理就需要分析自动配置类:CacheAutoConfiguration:
2.这个自动配置中导入了一个类CacheConfigurationImportSelector,这个类会引入一些缓存配置类。
3.在配置文件中设置属性debug=true,这样就会打印所有的配置报告。
4.通过打印日志可以看出SimpleCacheConfiguration配置类默认生效。这个配置类给容器中注册了一个CacheManager。
5.缓存方法运行之前,先按照cacheNames查询缓存组件,第一次获取缓存如果没有缓存创建一个。
6.Cache中查找缓存的内容会使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数。如果没有参数使用SimpleKey生成。
四、SpringBoot中Cache缓存的使用
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>2.@EnableCaching开启缓存
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"com.wang.cache.dao"})
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching // 开启缓存注解
public class SpringbootCacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootCacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
3.@Cacheable缓存注解的使用 (标注在service业务层方法上)
执行流程:先执行@Cacheable注解中的getCache(String name)方法,根据name判断ConcurrentMap中是否有此缓存,如果没有缓存那么创建缓存并保存数据,另外service层的方法也会执行。如果有缓存不再创建缓存,另外service层的方法也不会执行。
总结:先执行@Cacheable----->再执行service层的方法
@Cacheable注解的属性如下:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Cacheable {
@AliasFor("cacheNames")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String key() default "";
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
String condition() default "";
String unless() default "";
boolean sync() default false;
}service层代码
第一次查询数据库打印service类方法日志,并把数据保存到Cahce中
第二次传入相同参数不再执行service类方法,不会打印日志,查询的数据直接从缓存中获取
@Service
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
PersonDao personDao;
/*1. @Cacheable的几个属性详解:
* cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字
* key:缓存数据使用的key,可以用它来指定。默认使用方法参数的值,一般不需要指定
* keyGenerator:作用和key一样,二选一
* cacheManager和cacheResolver作用相同:指定缓存管理器,二选一
* condition:指定符合条件才缓存,比如:condition="#id>3"
* 也就是说传入的参数id>3才缓存数据
* unless:否定缓存,当unless为true时不缓存,可以获取方法结果进行判断
* sync:是否使用异步模式*/
//@Cacheable(cacheNames= "person")
//@Cacheable(cacheNames= "person",key="#id",condition="#id>3")
@Cacheable(cacheNames= "person",key="#id")
public Person queryPersonById(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询"+id+"号员工信息");
Person person=new Person();
person.setId(id);
return personDao.query(person);
}
}4.@CachePut必须结合@Cacheable一起使用,否则没什么意义
@CachePut的作用:即调用方法,又更新缓存数据 ,修改了数据库中的数据,同时又更新了缓存!
@Service
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
PersonDao personDao;
/**
* @CachePut:即调用方法,又更新缓存数据
* 修改了数据库中的数据,同时又更新了缓存
*
*运行时机:
* 1.先调用目标方法
* 2.将目标方法返回的结果缓存起来
*
* 测试步骤:
* 1.查询1号的个人信息
* 2.以后查询还是之前的结果
* 3.更新1号的个人信息
* 4.查询一号员工返回的结果是什么?
* 应该是更新后的员工
* 但只更新了数据库,但没有更新缓存是什么原因?
* 5.如何解决缓存和数据库同步更新?
* 这样写:@CachePut(cacheNames = "person",key = "#person.id")
* @CachePut(cacheNames = "person",key = "#result.id")
*/
@CachePut(cacheNames = "person",key = "#result.id")
public Person updatePerson(Person person){
System.out.println("修改"+person.getId()+"号员工信息");
personDao.update(person);
return person;
}
}
5.@CacheEvict也是结合@Cacheable一起使用才有意义
@CacheEvict的作用:清除缓存中的指定数据或清除缓存中所有数据
@CacheEvict的属性
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface CacheEvict {
@AliasFor("cacheNames")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String key() default "";
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
String condition() default "";
boolean allEntries() default false;
boolean beforeInvocation() default false;
}
service层代码
@Service
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
PersonDao personDao;
/**
* @CacheEvict:清除缓存
* 1.key:指定要清除缓存中的某条数据
* 2.allEntries=true:删除缓存中的所有数据
* beforeInvocation=false:默认是在方法之后执行清除缓存
* 3.beforeInvocation=true:现在是在方法执行之前执行清除缓存,
* 作用是:只清除缓存、不删除数据库数据
*/
//@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "person",key = "#id")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "person",allEntries=true)
public void deletePerson(Integer id){
System.out.println("删除"+id+"号个人信息");
//删除数据库数据的同时删除缓存数据
//personDao.delete(id);
/**
* beforeInvocation=true
* 使用在方法之前执行的好处:
* 1.如果方法出现异常,缓存依旧会被删除
*/
//int a=1/0;
}
}
6.@Caching是@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict注解的组合
@Caching的作用:此注解用于复杂的缓存操作
@Caching的属性
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Caching {
Cacheable[] cacheable() default {};
CachePut[] put() default {};
CacheEvict[] evict() default {};
}
service层代码
@Service
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
PersonDao personDao;
/**
* @Caching是 @Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict注解的组合
* 以下注解的含义:
* 1.当使用指定名字查询数据库后,数据保存到缓存
* 2.现在使用id、age就会直接查询缓存,而不是查询数据库
*/
@Caching(
cacheable = {@Cacheable(value = "person",key="#name")},
put={ @CachePut(value = "person",key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(value = "person",key = "#result.age")
}
)
public Person queryPersonByName(String name){
System.out.println("查询的姓名:"+name);
return personDao.queryByName(name);
}
}7.@CacheConfig主要用于配置该类中会用到的一些共用的缓存配置
@CacheConfig的作用:抽取@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict的公共属性值
@CacheConfig的属性
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CacheConfig {
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
}
servive层代码
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "person") //将cacheNames抽取出来
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
PersonDao personDao;
/*1. @Cacheable的几个属性详解:
* cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字
* key:缓存数据使用的key,可以用它来指定。默认使用方法参数的值,一般不需要指定
* keyGenerator:作用和key一样,二选一
* cacheManager和cacheResolver作用相同:指定缓存管理器,二选一
* condition:指定符合条件才缓存,比如:condition="#id>3"
* 也就是说传入的参数id>3才缓存数据
* unless:否定缓存,当unless为true时不缓存,可以获取方法结果进行判断
* sync:是否使用异步模式*/
//@Cacheable(cacheNames= "person")
//@Cacheable(cacheNames= "person",key="#id",condition="#id>3")
@Cacheable(key="#id")
public Person queryPersonById(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询"+id+"号员工信息");
Person person=new Person();
person.setId(id);
return personDao.query(person);
}
/**
* @CachePut:即调用方法,又更新缓存数据
* 修改了数据库中的数据,同时又更新了缓存
*
*运行时机:
* 1.先调用目标方法
* 2.将目标方法返回的结果缓存起来
*
* 测试步骤:
* 1.查询1号的个人信息
* 2.以后查询还是之前的结果
* 3.更新1号的个人信息
* 4.查询一号员工返回的结果是什么?
* 应该是更新后的员工
* 但只更新了数据库,但没有更新缓存是什么原因?
* 5.如何解决缓存和数据库同步更新?
* 这样写:@CachePut(cacheNames = "person",key = "#person.id")
* @CachePut(cacheNames = "person",key = "#result.id")
*/
@CachePut(key = "#result.id")
public Person updatePerson(Person person){
System.out.println("修改"+person.getId()+"号员工信息");
personDao.update(person);
return person;
}
/**
* @CacheEvict:清除缓存
* 1.key:指定要清除缓存中的某条数据
* 2.allEntries=true:删除缓存中的所有数据
* beforeInvocation=false:默认是在方法之后执行清除缓存
* 3.beforeInvocation=true:现在是在方法执行之前执行清除缓存,
* 作用是:只清除缓存、不删除数据库数据
*/
//@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "person",key = "#id")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "person",allEntries=true)
public void deletePerson(Integer id){
System.out.println("删除"+id+"号个人信息");
//删除数据库数据的同时删除缓存数据
//personDao.delete(id);
/**
* beforeInvocation=true
* 使用在方法之前执行的好处:
* 1.如果方法出现异常,缓存依旧会被删除
*/
//int a=1/0;
}
/**
* @Caching是 @Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict注解的组合
* 以下注解的含义:
* 1.当使用指定名字查询数据库后,数据保存到缓存
* 2.现在使用id、age就会直接查询缓存,而不是查询数据库
*/
@Caching(
cacheable = {@Cacheable(key="#name")},
put={ @CachePut(key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(key = "#result.age")
}
)
public Person queryPersonByName(String name){
System.out.println("查询的姓名:"+name);
return personDao.queryByName(name);
}
}