Java设计模式 - 原型模式
原型模式应用场景:
原型模式是指用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过复制这些原型创建新的对象.适合原型模式的情景如下:程序需要从一个对象出发,得到i若干个和其状态相同,并可独立变化其状态的对象时;对象创建需要独立于它的构造方法和表示时,以原型对象为基础,克隆新的对象,并完善对象实例变量时.
源码下载地址:
https://github.com/godlikecheng/prototype_model
对于浅复制和深复制的概念:
原型模式的实现方式:
1.原型复制具体实现方法 - 利用构造函数方法 - 浅复制
package prototype_model; public class Address { String pro; // 出生省 String city; // 出生市 String zip; // 出生地邮编 public Address(String pro, String city, String zip) { this.pro = pro; this.city = city; this.zip = zip; } public String getPro() { return pro; } public void setPro(String pro) { this.pro = pro; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getZip() { return zip; } public void setZip(String zip) { this.zip = zip; } }
package prototype_model; public class Student { String name; // 姓名 int age; // 年龄 Address add; // 籍贯信息 Student(String na, int a, Address add) { this.name = na; this.age = a; this.add = add; } public Student(Student s) { name = s.getName(); age = s.getAge(); add = s.getAdd(); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Address getAdd() { return add; } public void setAdd(Address add) { this.add = add; } }
测试类:
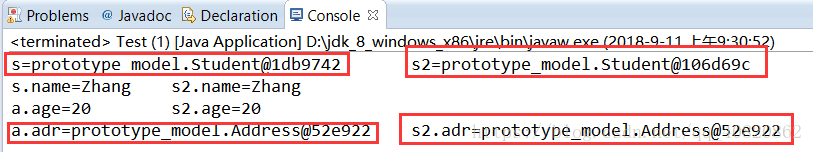
package prototype_model; /** * 测试类 - 浅复制 * @author 张宜成 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Address adr = new Address("liaoning", "dalian","116081"); Student s = new Student("Zhang",20,adr); // 建立学生对象s Student s2 = new Student(s); // 以s为原型,建立复制对象s2 System.out.println("s=" + s + "\ts2=" + s2); System.out.println("s.name=" + s.getName() + "\ts2.name=" + s2.getName()); System.out.println("a.age=" + s.getAge() + "\ts2.age=" + s2.getAge()); System.out.println("a.adr=" + s.getAdd() + "\ts2.adr=" + s2.getAdd()); } }
运行结果:
深复制
package prototype_model_02; public class Address { String pro; // 出生省 String city; // 出生市 String zip; // 出生地邮编 public Address(String pro, String city, String zip) { this.pro = pro; this.city = city; this.zip = zip; } // 深拷贝构造方法 public Address(Address add) { pro = add.getPro(); city = add.getCity(); zip = add.getZip(); } public String getPro() { return pro; } public void setPro(String pro) { this.pro = pro; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getZip() { return zip; } public void setZip(String zip) { this.zip = zip; } }
package prototype_model_02; public class Student { String name; // 姓名 int age; // 年龄 Address add; // 籍贯信息 Student(String na, int a, Address add) { this.name = na; this.age = a; this.add = add; } public Student(Student s) { name = s.getName(); age = s.getAge(); // add = s.getAdd(); // 与浅复制的不同之处 add = new Address(s.getAdd()); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Address getAdd() { return add; } public void setAdd(Address add) { this.add = add; } }
测试类:
package prototype_model_02; /** * 测试类 - 深复制 * @author 张宜成 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Address adr = new Address("liaoning", "dalian","116081"); Student s = new Student("Zhang",20,adr); // 建立学生对象s Student s2 = new Student(s); // 以s为原型,建立复制对象s2 System.out.println("s=" + s + "\ts2=" + s2); System.out.println("s.name=" + s.getName() + "\ts2.name=" + s2.getName()); System.out.println("a.age=" + s.getAge() + "\ts2.age=" + s2.getAge()); System.out.println("a.adr=" + s.getAdd() + "\ts2.adr=" + s2.getAdd()); } }
测试结果:
2.利用Cloneable接口方法
浅复制
package prototype_model_03; public class Address { String pro; // 出生省 String city; // 出生市 String zip; // 出生地邮编 public Address(String pro, String city, String zip) { this.pro = pro; this.city = city; this.zip = zip; } public String getPro() { return pro; } public void setPro(String pro) { this.pro = pro; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getZip() { return zip; } public void setZip(String zip) { this.zip = zip; } }
package prototype_model_03; public class Student implements Cloneable { String name; // 姓名 int age; // 年龄 Address add; // 籍贯信息 Student(String na, int a, Address add) { this.name = na; this.age = a; this.add = add; } public Student(Student s) { name = s.getName(); age = s.getAge(); add = s.getAdd(); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Address getAdd() { return add; } public void setAdd(Address add) { this.add = add; } // 利用Cloneable接口方法 protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
测试类:
package prototype_model_03; /** * 测试类 - 浅复制 - 利用Cloneable接口方法 * @author 张宜成 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Address adr = new Address("liaoning", "dalian","116081"); Student s = new Student("Zhang",20,adr); // 建立学生对象s 原型对象 // Student s2 = new Student(s); // 以s为原型,建立复制对象s2 Student s2 = (Student) s.clone(); //克隆对象 System.out.println("s=" + s + "\ts2=" + s2); System.out.println("s.name=" + s.getName() + "\ts2.name=" + s2.getName()); System.out.println("a.age=" + s.getAge() + "\ts2.age=" + s2.getAge()); System.out.println("a.adr=" + s.getAdd() + "\ts2.adr=" + s2.getAdd()); } }
测试结果:
深复制
package prototype_model_04; public class Address implements Cloneable { String pro; // 出生省 String city; // 出生市 String zip; // 出生地邮编 public Address(String pro, String city, String zip) { this.pro = pro; this.city = city; this.zip = zip; } public String getPro() { return pro; } public void setPro(String pro) { this.pro = pro; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getZip() { return zip; } public void setZip(String zip) { this.zip = zip; } // 深拷贝 protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Address s = (Address)super.clone(); return s; } }
package prototype_model_04; public class Student implements Cloneable { String name; // 姓名 int age; // 年龄 Address add; // 籍贯信息 Student(String na, int a, Address add) { this.name = na; this.age = a; this.add = add; } public Student(Student s) { name = s.getName(); age = s.getAge(); add = s.getAdd(); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Address getAdd() { return add; } public void setAdd(Address add) { this.add = add; } // 利用Cloneable接口方法 protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student s = (Student)super.clone(); s.setAdd((Address)add.clone()); return s; } }
测试类:
package prototype_model_04; /** * 测试类 - 深复制 - 利用Cloneable接口方法 * @author 张宜成 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Address adr = new Address("liaoning", "dalian","116081"); Student s = new Student("Zhang",20,adr); // 建立学生对象s 原型对象 // Student s2 = new Student(s); // 以s为原型,建立复制对象s2 Student s2 = (Student) s.clone(); //克隆对象 System.out.println("s=" + s + "\ts2=" + s2); System.out.println("s.name=" + s.getName() + "\ts2.name=" + s2.getName()); System.out.println("a.age=" + s.getAge() + "\ts2.age=" + s2.getAge()); System.out.println("a.adr=" + s.getAdd() + "\ts2.adr=" + s2.getAdd()); } }
测试结果:
利用Serializable序列化接口方法
深复制
package prototype_model_05; import java.io.Serializable; // 实现Serializable接口 public class Address implements Serializable{ String pro; // 出生省 String city; // 出生市 String zip; // 出生地邮编 public Address(String pro, String city, String zip) { this.pro = pro; this.city = city; this.zip = zip; } public String getPro() { return pro; } public void setPro(String pro) { this.pro = pro; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getZip() { return zip; } public void setZip(String zip) { this.zip = zip; } }
package prototype_model_05; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.io.Serializable; // 实现Serializable, Cloneable接口 public class Student implements Cloneable,Serializable { String name; // 姓名 int age; // 年龄 Address add; // 籍贯信息 Student(String na, int a, Address add) { this.name = na; this.age = a; this.add = add; } public Student(Student s) { name = s.getName(); age = s.getAge(); add = s.getAdd(); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Address getAdd() { return add; } public void setAdd(Address add) { this.add = add; } // 利用Serializable序列化接口方法 protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Object obj = null; try { ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos); oos.writeObject(this); // 从流里读回来 ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis); obj = ois.readObject(); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return obj; } }
测试类:
package prototype_model_05; /** * 测试类 - 深复制 - 利用Serializable接口方法 * @author 张宜成 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Address adr = new Address("liaoning", "dalian","116081"); Student s = new Student("Zhang",20,adr); // 建立学生对象s 原型对象 // Student s2 = new Student(s); // 以s为原型,建立复制对象s2 Student s2 = (Student) s.clone(); //克隆对象 System.out.println("s=" + s + "\ts2=" + s2); System.out.println("s.name=" + s.getName() + "\ts2.name=" + s2.getName()); System.out.println("a.age=" + s.getAge() + "\ts2.age=" + s2.getAge()); System.out.println("a.adr=" + s.getAdd() + "\ts2.adr=" + s2.getAdd()); } }
测试结果:
应用案例:
原型管理器及其应用
package prototype_demo; import java.util.Hashtable; /** * 原型管理器及其应用 很明显,原型管理器是对原型的管理类,可以添加原型对象,也可以获得原型对象 * @author 张宜成 */ public class PrototypeManager { // 定义一个Hashtable,用于存储原型对象 private Hashtable ht = new Hashtable(); private static PrototypeManager pm = new PrototypeManager(); // 首先通过addPrototype()添加各原型对象 public void addPrototype(String key, Object obj) { ht.put(key, obj); } // 再通过getPropotype()获得所需原型对象即可. public Object getPrototype(String key) { return ht.get(key); } public static PrototypeManager getPrototypeManager() { return pm; } }
package prototype_demo; public class PubInfo implements Cloneable{ // 这里需要实现Cloneable接口 String college; // 所在大学 String city; // 所在城市 String zip; // 邮编 // 构造方法 public PubInfo(String college, String city, String zip) { super(); this.college = college; this.city = city; this.zip = zip; } public String getCollege() { return college; } public void setCollege(String college) { this.college = college; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getZip() { return zip; } public void setZip(String zip) { this.zip = zip; } public String toString() { return "PubInfo [college=" + college + ", city=" + city + ", zip=" + zip + "]"; } // 重写clone的方法 - 浅拷贝 protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }package prototype_demo; /** * 学生类 * * @author 张宜成 */ public class Student implements Cloneable { // 这里需要实现Cloneable的接口 String name; // 学生姓名 int age; // 年龄 PubInfo info; // 公共信息 public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public PubInfo getInfo() { return info; } public void setInfo(PubInfo info) { this.info = info; } public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", info=" + info + "]"; } // 重写clone的方法 - 浅拷贝 protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
测试类:
要求:
现在要求创建m个辽宁师大学生对象,n个大连理工大学学生对象,对重复的公共信息仅输入一次即可, 那么它还如何实现嗯?具体思路如下:
(1) 创建辽宁师大学生原型对象s,要求对象中姓名name,年龄age为默认值,公共信息对象info设置为 "辽宁师范大学, 大连, 116081" 同理创建大连理工大学学生原型对象s2,将s s2添加到原型管理器对象中.(2)从原型管理器获取辽宁师大学生原型对象t,循环m次,在循环体中创建t的克隆对象(对应每一位新创建的学生对象), 仅输入学生姓名,年龄即可.
(3)同理创建n个大连理工公大学学生对象.
package prototype_demo; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Vector; /** * @author 张宜成 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { int m = 3; int n = 3; PrototypeManager pm = PrototypeManager.getPrototypeManager(); PubInfo p = new PubInfo("liaoshi", "dalian", "116081"); Student s = new Student(); // 创建辽师学生原型对象 s.setInfo(p); pm.addPrototype("liaoshi", s); // 加入原型管理器 PubInfo p2 = new PubInfo("dagong", "dalian", "116023"); Student s2 = new Student(); // 创建大连理工学生对象 s2.setInfo(p2); pm.addPrototype("dagong", s2); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); /* * 辽师 */ Vector<Student> vec = new Vector(); // 创建辽师学生集合 Student t = (Student) pm.getPrototype("liaoshi"); // 获取原型对象 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { Student st = (Student) t.clone(); // 通过浅复制创建新学生对象 System.out.println("请输入要录入的辽大姓名:"); st.setName(sc.nextLine()); // 输入并设置姓名 System.out.println("请输入要录入的辽大年龄:"); st.setAge(sc.nextInt()); // 输入并设置年龄 vec.add(st); } Vector<Student> vec2 = new Vector(); Student t2 = (Student) pm.getPrototype("dagong"); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Student st = (Student) t2.clone(); System.out.println("请输入要录入的大工姓名:"); st.setName(sc.nextLine()); System.out.println("请输入要录入的大工年龄:"); st.setName(sc.nextLine()); vec2.add(st); } } }
上一篇: Java设计模式之 工厂模式
下一篇: 待更新...