1.为什么要选择Spring Security
同事曾经说过,他喜欢用Shiro多过使用Spring Security,笔者也曾经使用过Shiro,对于那个时候的我来说Shiro足够简单让我接入到开发的系统当中,如果单从单体应用来说可能使用Shiro进行权限控制可能更加好,但是如果到了分布式系统中需要考虑多服务之间的鉴权需要使用Oauth的时候Spring Security 结合Spring Security Oauth会有更好的支持。Shiro在github已经有1年多没更新了,而Spring Security依在持续更新当中,此外Spring Security有更好的社区支持。在现在注重安全和不断变化的系统要求下,除了大公司自研自己一套适合自己业务的权限框架外,不断更新的Spring Security会比Shiro更适合进行完后开发。
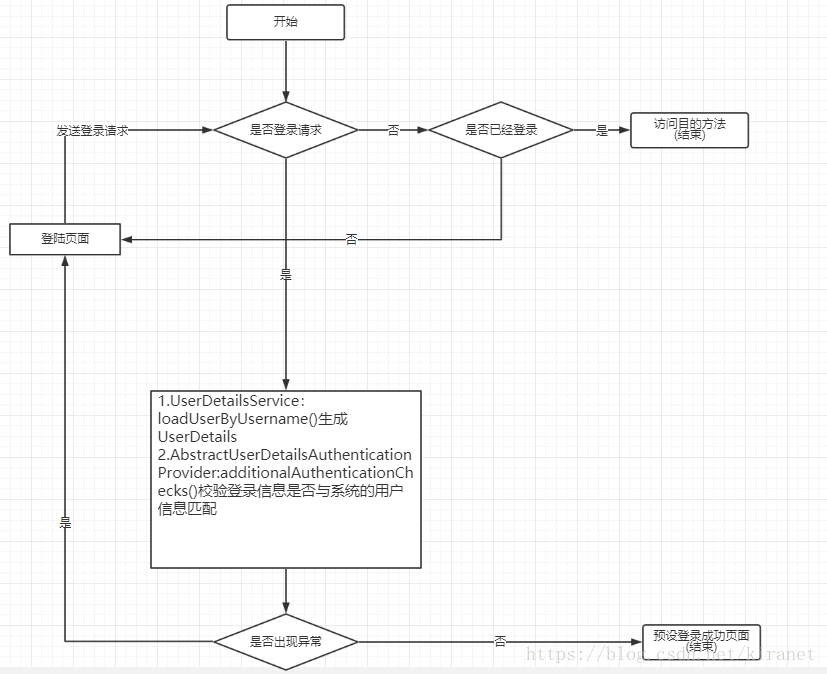
2.Spring Security运行流程图
3.主要组件
3.1 UserDetails
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
String getPassword();
String getUsername();
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
boolean isEnabled();
}UserDetails作为Spring Security整个登录过程的pojo接口,在登录中我们必须继承他构建符合我们需要的实体类,其中username和password用于登录,而authorities则用于接口的权限控制。
3.2 UserDetailsService
public interface UserDetailsService {
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}用于生成UserDetails,在常规的开发当中都会继承这个接口并组装出完后使用的UserDetails类。
3.3 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
Authentication authResult;
try {
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
// authentication
return;
}
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
logger.error(
"An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.",
failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
// Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter用于登录进行过滤在他的doFilter方法中,首先通过requiresAuthentication方法确认当前的访问url是否约定的登录处理接口,如果不是约定的登录接口就让请求往下一个过滤器传递,如果是则继续玩下执行,则会使用初始化中的AuthenticationManager的AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider的authenticate方法进行校验。
3.4 AuthenticationManager
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器中会使用AuthenticationManager的authenticate方法进行登录校验,而Spring Security提供了一个实现ProviderManager给我们使用,而ProviderManager会通过自己的AuthenticationProvider数组,调用其authenticate方法进行校验。
3.5 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication,
messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports",
"Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported"));
// Determine username
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
logger.debug("User '" + username + "' not found");
if (hideUserNotFoundExceptions) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
else {
throw notFound;
}
}
Assert.notNull(user,
"retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract");
}
try {
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
else {
throw exception;
}
}
postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}在AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider中的authenticate中,代码首先会通过retrieveUser方法使用我们定义的UserDetailsService的生成对应的UserDetails,获得UserDetails后,我们在使用自身的additionalAuthenticationChecks方法去验证数据库的用户信息和登录信息是否一致。如果additionalAuthenticationChecks没有报错,那么请求就会带着UserDetails的权限成功登陆。