版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处。 https://blog.csdn.net/dahaohan/article/details/51397220
前言
上篇博文介绍了Android Studio的基础入门配置
而要了解学习一个新的IDE,更需要了解其对项目的管理以及对项目的构建配置等,本博文就基于此目的做一个简要介绍。PS. Android Studio偶尔简称AS
Eclipse Workspace Vs AS Project
Eclipse项目组织形式由两层工程目录结构组成,Workspace以及其包含的Project;其中Workspace工作空间目录负责管理把控其包含的所有具体的Project一些通用设置,而一个具体的Project则代表了一个Android应用/Library。
具体的一些配置关系请参考:http://blog.csdn.net/exbob/article/details/6428229
Android Studio则有对应的层级:Project以及其包含的Module;这里Project管理所有Module一些通用的构建配置,而一个module则对应于具体的Application/library。
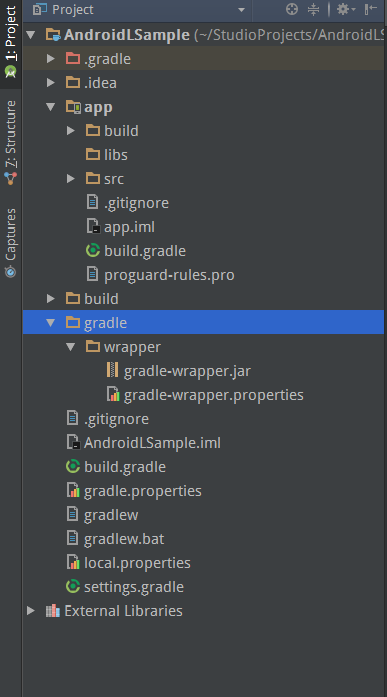
AS 项目结构
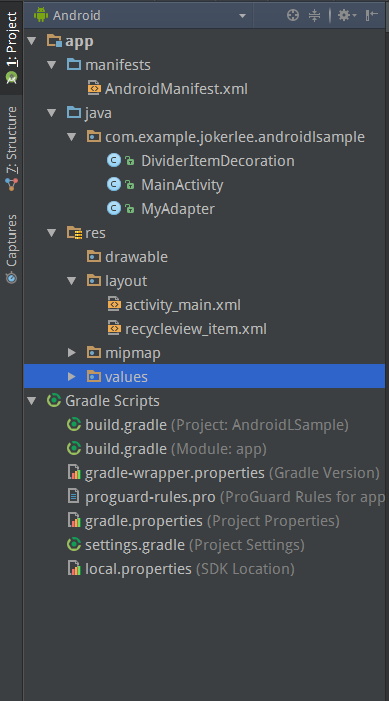
AS提供了多种视图来查看一个project,常用的为:
.gradle/ & .idea/ 目录
gradle插件以及AS生成的一些设置文件目录。
app/ module目录
build/
module编译过程结果输出目录,包含编译打包生成的apk,编译后的资源文件等。
libs/
module依赖的本地第三方库文件目录。
src/
module所有的源文件以及资源文件所在目录。
androidTest/ & test/
module所有测试相关代码所在目录。
java/
module下所有java源文件所在目录。
res/ & assets/
module下所有资源文件所在目录。
jni/
module下实现jni的C/C++源文件所在目录。
build.gradle (module)
gradle构建工具构建module时所依据的构建文件,后续构建步骤会详细介绍其内容。
app.iml (module)
module项目的配置文件,其内容指定了该module的源码路径/依赖的库文件等基础信息:
gradle.properties(project)
整个Project工程的gradle属性配置文件,如配置gradle是否支持ndk等。
local.properties (project)
本地构建环境的配置文件,指定了如SDK/NDK的路径等,由AS IDE自动生成。
build.gradle (project)
整个Project工程的gradle构建文件,其定义的构建配置会应用到所有的module上。
settings.gradle (project)
the gradle.settings file, located in the root project directory, tells Gradle which modules it should include when building your app.
该文件用于指定Project工程下的哪些module需要最终加入构建编译,多module project可能需要使用该文件配置需要最终构建打包生成应用的module。
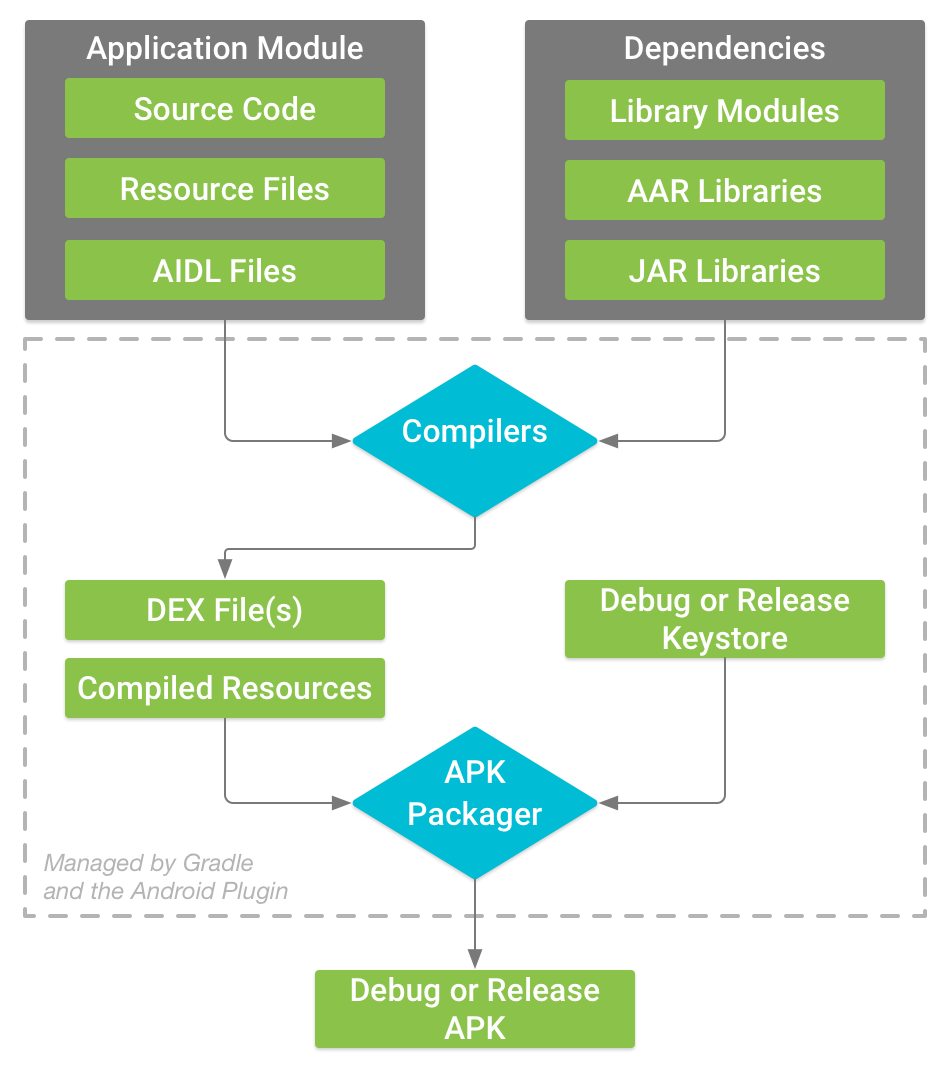
AS构建简介
The Top-level Build File
位于Project根目录下的build.gradle构建文件为顶层构建文件,定义了应用于所有需要构建的module的构建配置。通常情况该文件使用 buildscript {}给所有的module定义通用的Gradle仓库和依赖。
/**
* The buildscript {} block 是Gradle用于配置自身的仓库和依赖的地方,你不应该将应用的
* 依赖配置写在此处。
*/
buildscript {
/**
* The repositories {} block 配置Gradle用于搜索和下载依赖的仓库;
* Gradle预制的配置支持JCenter, Maven Central, and Ivy等远程仓库,默认定义JCenter
* 作为Gradle搜索下载依赖的仓库。
*/
repositories {
jcenter()
}
/**
*The dependencies {} block configures the dependencies Gradle needs to use
* to build your project. The following line adds Android Plugin for Gradle
* version 2.0.0 as a classpath dependency.
*/
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:2.0.0'
}
}
/**
* The allprojects {} block 是用于给所有的module配置仓库和依赖
* Dependencies that are not required by all the modules in the
* project should be configured in module-level build.gradle files. For new
* projects, Android Studio configures JCenter as the default repository, but it
* does not configure any dependencies.
*/
allprojects {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
/**
*为所有的module添加自己的maven仓库
*/
maven {
url 'http://mvnrepo.xxx.com/mvn/repository'
}
}
The Module-level Build File
位于module目录下的build.gradle构建文件,定义单独一个module的构建配置。
/**
* 告诉Gradle使用Android plugin进行构建,并且使得android {}能应用于android的具体构建选项。
*/
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
/**
* The android {} block is where you configure all your Android-specific
* build options.
*/
android {
compileSdkVersion 23
buildToolsVersion "23.0.3"
/**
* The defaultConfig {} block encapsulates default settings and entries for all
* build variants, and can override some attributes in main/AndroidManifest.xml
* dynamically from the build system. You can configure product flavors to override
* these values for different versions of your app.
*/
defaultConfig {
/**
* applicationId uniquely identifies the package for publishing.
* However, your source code should still reference the package name
* defined by the package attribute in the main/AndroidManifest.xml file.
*/
applicationId 'com.example.myapp'
// Defines the minimum API level required to run the app.
minSdkVersion 14
// Specifies the API level used to test the app.
targetSdkVersion 23
// Defines the version number of your app.
versionCode 1
// Defines a user-friendly version name for your app.
versionName "1.0"
}
/**
* The buildTypes {} block is where you can configure multiple build types.
* By default, the build system defines two build types: debug and release. The
* debug build type is not explicitly shown in the default build configuration,
* but it includes debugging tools and is signed with the debug key. The release
* build type applies Proguard settings and is not signed by default.
*/
buildTypes {
/**
* By default, Android Studio configures the release build type to enable code
* shrinking, using minifyEnabled, and specifies the Proguard settings file.
*/
release {
minifyEnabled true // Enables code shrinking for the release build type.
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
/**
* The productFlavors {} block is where you can configure multiple product
* flavors. This allows you to create different versions of your app that can
* override defaultConfig {} with their own settings. Product flavors are
* optional, and the build system does not create them by default. This example
* creates a free and paid product flavor. Each product flavor then specifies
* its own application ID, so that they can exist on the Google Play Store, or
* an Android device, simultaneously.
*/
productFlavors {
free {
applicationId 'com.example.myapp.free'
}
paid {
applicationId 'com.example.myapp.paid'
}
}
}
/**
* The dependencies {} block in the module-level build configuration file
* only specifies dependencies required to build the module itself.
*/
dependencies {
compile project(":lib")
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:22.0.1'
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
}