一、解析封装property-placeholder相关的BeanDefinition
有两种方式:
(1)在XML配置格式如下
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:xxxx.properties"/>
(2)注解配置如下:
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:xxx.properties")
public class PropertiesWithJavaConfig {
@Bean
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer() {
return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
}
}
java类中
@Value( "${jdbc.url}" )
private String jdbcUrl;
下面分析的是XML方式(Spring的自定义标签解析可参考:
Spring自定义XML标签解析及其原理分析)
查看spring-context源码模块下的spring.handlers文件可以得知其解析的类为如下
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context=org.springframework.context.config.ContextNamespaceHandler
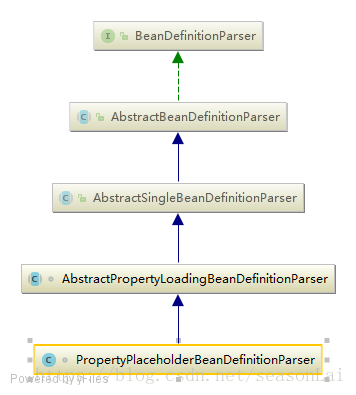
进入ContextNamespaceHandler类中可以看到解析property-placeholder标签委托给了PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser类
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-placeholder", new PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser());
PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser类继承图如下:
解析自定义标签最终是调用BeanDefinitionParser的parse方法的,其在AbstractBeanDefinitionParser中有实现
public final BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
//调用parseInternal进行解析
AbstractBeanDefinition definition = parseInternal(element, parserContext);
...
return definition;
}
parseInternal方法在AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser类中实现
protected final AbstractBeanDefinition parseInternal(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition();
//拿到父节点名称
String parentName = getParentName(element);
if (parentName != null) {
builder.getRawBeanDefinition().setParentName(parentName);
}
//【标记1】拿到bean的类型
Class<?> beanClass = getBeanClass(element);
if (beanClass != null) {
builder.getRawBeanDefinition().setBeanClass(beanClass);
}
else {
//拿到类名
String beanClassName = getBeanClassName(element);
if (beanClassName != null) {
builder.getRawBeanDefinition().setBeanClassName(beanClassName);
}
}
...
//【标记2】解析标签
doParse(element, parserContext, builder);
return builder.getBeanDefinition();
}
Spring会把XML配置文件中配置的bean封装成BeanDefinition,用于后面的实例化。而上面是通过BeanDefinitionBuilder来构建一个BeanDefinition进行返回。
【标记1】拿到bean的类型

先看看上面【标记1】的地方,那里决定了返回的BeanDefinition具体类型是什么。PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser类覆写了该方法。
protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {
//3.1及之后版本的xsd文件默认值是这个
if (SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_DEFAULT.equals(element.getAttribute(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_ATTRIBUTE))) {
return PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.class;
}
//3.0或之前版本的xsd返回这个
return PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.class;
}
返回结果和spring-context.xsd有关系,3.0或之前版本返回PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.class,3.1及之后版本返回PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.class。
【标记2】解析标签
PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser类覆写了该方法
protected void doParse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
//调用父类解析一部分标签属性
super.doParse(element, parserContext, builder);
builder.addPropertyValue("ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders",
Boolean.valueOf(element.getAttribute("ignore-unresolvable")));
String systemPropertiesModeName = element.getAttribute(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(systemPropertiesModeName) &&
!systemPropertiesModeName.equals(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_DEFAULT)) {
//3.1及之后的版本进这里
builder.addPropertyValue("systemPropertiesModeName", "SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_" + systemPropertiesModeName);
}
if (element.hasAttribute("value-separator")) {
builder.addPropertyValue("valueSeparator", element.getAttribute("value-separator"));
}
if (element.hasAttribute("trim-values")) {
builder.addPropertyValue("trimValues", element.getAttribute("trim-values"));
}
if (element.hasAttribute("null-value")) {
builder.addPropertyValue("nullValue", element.getAttribute("null-value"));
}
}
doParse方法主要解析配置的相关属性
二、PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer类分析
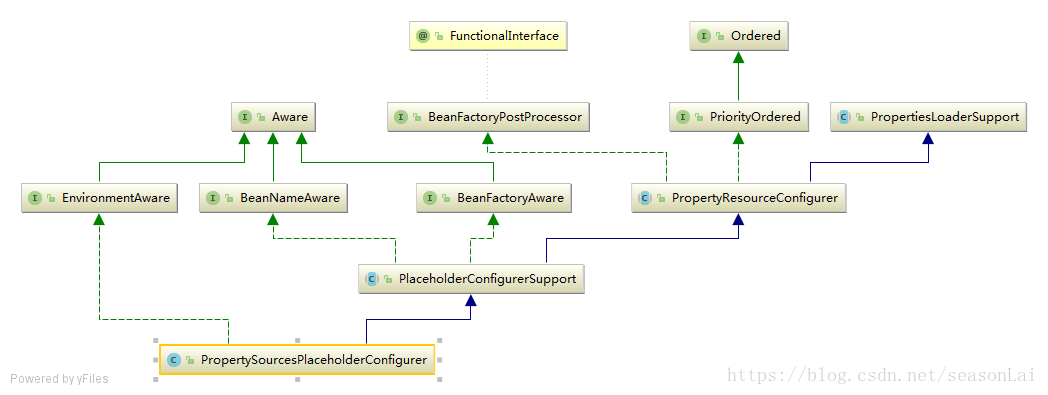
上面介绍了Spring如何解析XML配置中的context:property-placeholder标签封装成BeanDefinition放入容器中。本人写的时候看的是Spring5的源码,所以最后解析该标签得到的BeanDefinition的类的类型是PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer。接下来分析这个类究竟做了什么。
可以看到PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer间接实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,该接口是在Spring解析完所有bean并封装成BeanDefinition的方法在PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer类中实现了
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
//propertySources为空,就会去加载environment中的属性、和XML中指定的文件中的属性
if (this.propertySources == null) {
this.propertySources = new MutablePropertySources();
//添加environment中的属性
if (this.environment != null) {//因为实现了EnvironmentAware接口,environment在该接口方法中赋值
this.propertySources.addLast(
new PropertySource<Environment>(ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, this.environment) {
@Override
@Nullable
public String getProperty(String key) {
return this.source.getProperty(key);
}
}
);
}
try {
//【标记3】进行加载XML中的location属性的文件,并合并props属性
PropertySource<?> localPropertySource =
new PropertiesPropertySource(LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties());
if (this.localOverride) {
//允许本地覆盖,就加在前面,优先级高
this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource);
}
else {
//不允许本地覆盖,就加在后面,优先级低
this.propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource);
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}
//【标记4】处理容器中的BeanDefinition
processProperties(beanFactory, new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources));
//赋值成员变量
this.appliedPropertySources = this.propertySources;
}
上面可以看到,如果propertySources没有被赋值,那就会去加载environment中的属性、和XML中指定的文件中的属性,最后就把propertySources传到PropertySourcesPropertyResolver对象,开始处理容器中的BeanDefinition中需要替换的属性
【标记3】进行加载XML中的location属性的文件,并合并props属性
protected Properties mergeProperties() throws IOException {
Properties result = new Properties();
//localOverride默认为false,表示本地属性的不能覆盖从外部加载属性
if (this.localOverride) {
// 加载location属性的表示的文件,本质是通过java的Properties类进行加载
loadProperties(result);
}
//把本地的属性合并,localProperties可在xml文件中通过props属性进行设置
if (this.localProperties != null) {
for (Properties localProp : this.localProperties) {
CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(localProp, result);
}
}
if (!this.localOverride) {
// 加载location属性的表示的文件,本质是通过java的Properties类进行加载
loadProperties(result);
}
return result;
}
逻辑比较简单,localOverride变量决定是否本地的属性可以覆盖另外加载的属性
【标记4】处理容器中的BeanDefinition
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver) throws BeansException {
//添加替换的前缀,默认是 ${
propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(this.placeholderPrefix);
//添加替换的后缀,默认是 }
propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(this.placeholderSuffix);
//添加默认值分隔符,默认是 :
propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(this.valueSeparator);
//新建一个处理器,替换逻辑就在这
StringValueResolver valueResolver = strVal -> {
//ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders默认为false
String resolved = (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders ?
propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(strVal) :
propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(strVal));
//trimValues默认为false
if (this.trimValues) {
resolved = resolved.trim();
}
//如果设置了nullValue,则如果和nullValue相等,返回null
return (resolved.equals(this.nullValue) ? null : resolved);
};
//开始进行处理
doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver);
}
上面的StringValueResolver是文本替换处理器,实质就是它来把${xx}这些经过处理返回真正的值。
protected void doProcessProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
StringValueResolver valueResolver) {
//把处理器封装到BeanDefinitionVisitor
BeanDefinitionVisitor visitor = new BeanDefinitionVisitor(valueResolver);
//拿到所有bean名字
String[] beanNames = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String curName : beanNames) {
//处理除了自身以外的bean
if (!(curName.equals(this.beanName) && beanFactoryToProcess.equals(this.beanFactory))) {
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinition(curName);
try {
//开始处理
visitor.visitBeanDefinition(bd);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), curName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
}
//处理别名
beanFactoryToProcess.resolveAliases(valueResolver);
//把valueResolver传递给beanFactoryToProcess,供其用于处理注解的解析等
beanFactoryToProcess.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver);
}
遍历容器中的所有BeanDefinition进行处理,把文本处理器又封装进了BeanDefinitionVisitor,所以其visitBeanDefinition方法是真正开始处理BeanDefinition的属性。在方法最后还对别名进行了处理,然后把valueResolver传递给beanFactoryToProcess,供其用于处理注解的解析等
public void visitBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
//处理父类名
visitParentName(beanDefinition);
//处理类名
visitBeanClassName(beanDefinition);
//处理工厂bean名
visitFactoryBeanName(beanDefinition);
//处理工厂方法名
visitFactoryMethodName(beanDefinition);
//处理生命周期
visitScope(beanDefinition);
//处理属性值
if (beanDefinition.hasPropertyValues()) {
visitPropertyValues(beanDefinition.getPropertyValues());
}
//处理构造方法值
if (beanDefinition.hasConstructorArgumentValues()) {
ConstructorArgumentValues cas = beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues();
visitIndexedArgumentValues(cas.getIndexedArgumentValues());
visitGenericArgumentValues(cas.getGenericArgumentValues());
}
}
上面可以看到:visitBeanDefinition对beanDefinition的一些属性进行了处理
上面对beanDefinition的处理最终还是会调用StringValueResolver的resolveStringValue方法(上面用了java8新增的语法),而最终调用的是PropertySourcesPropertyResolver的resolvePlaceholders或resolveRequiredPlaceholders方法(取决于ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders变量)。下面来挑选resolveRequiredPlaceholders方法来分析
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (this.strictHelper == null) {
//创建一个PropertyPlaceholderHelper,参数传false
this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false);
}
return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper);
}
private PropertyPlaceholderHelper createPlaceholderHelper(boolean ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
return new PropertyPlaceholderHelper(this.placeholderPrefix, this.placeholderSuffix,
this.valueSeparator, ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders);
}
PropertyPlaceholderHelper是个工具类
private String doResolvePlaceholders(String text, PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper) {
return helper.replacePlaceholders(text, this::getPropertyAsRawString);
}
public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) {
Assert.notNull(value, "'value' must not be null");
return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, new HashSet<>());
}
上面可以看到传递了getPropertyAsRawString方法(java8语法),而该方法是返回key对应的属性值
protected String parseStringValue(
String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(value);
int startIndex = value.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix);
while (startIndex != -1) {//存在前缀才进入循环
//找到后缀的下标
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex);
if (endIndex != -1) {//是否有后缀包裹
String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex);
String originalPlaceholder = placeholder;
//这里添加不进去Set集合,说明存在循环引用
if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions");
}
//递归解析,拿到最终值?
placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
//调用处理器拿到属性值,其实调用的是getPropertyAsRawString方法
String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder);
if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) {
//为空,可能格式是 xxxx:xxx(冒号后面是默认值)
int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator);
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
//拿到真正的要替换的值
String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex);
//默认值
String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length());
//调用处理器进行处理
propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder);
if (propVal == null) {
propVal = defaultValue;//为空就复制为默认值
}
}
}
if (propVal != null) {
//递归执行,拿到最终的值
propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'");
}
//进行入下次循环
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length());
}
else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
// Proceed with unprocessed value.
//如果ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders为true,说明忽略无法解析的${xxx}
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length());
}
else {
//报错了
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" +
placeholder + "'" + " in value \"" + value + "\"");
}
//处理成功过了,移除
visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder);
}
else {
startIndex = -1;//没有后缀包裹,不用解析了
}
}
return result.toString();
}
代码虽然有点长,但逻辑还是很清晰
- 先拿到要替换的值(即:${xx}中的xx)
- 递归解析,拿到真正要替换的值(即有可能是KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: {{}/xx}这样的)
- 调用placeholderResolver的resolvePlaceholder方法拿到属性值(其实就会调用上面传递的getPropertyAsRawString方法)
- 如果属性值为空,可能是有默认值分隔符(即有:),一番处理后拿到属性值
- 对属性值进行递归解析,拿到最终属性值(即可能是在属性文件中写法:xxx=${xxx},一般是多个属性文件的情况)
- 最终属性值不为空就替换,否则根据 ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders判断是否抛异常还是继续解析
- 把解析成功的要替换的值从visitedPlaceholders中移除
- 继续循环或返回结果