原题
B Red Black Tree
BaoBao has just found a rooted tree with n vertices and (n−1) weighted edges in his backyard. Among the vertices, m of them are red, while the others are black. The root of the tree is vertex 1 and it's a red vertex.
Let's define the cost of a red vertex to be 0, and the cost of a black vertex to be the distance between this vertex and its nearest red ancestor.
Recall that
- The length of a path on the tree is the sum of the weights of the edges in this path.
- The distance between two vertices is the length of the shortest path on the tree to go from one vertex to the other.
- Vertex u is the ancestor of vertex v if it lies on the shortest path between vertex v and the root of the tree (which is vertex 1 in this problem).
As BaoBao is bored, he decides to play q games with the tree. For the i-th game, BaoBao will select ki vertices vi,1,vi,2,...,vi,ki on the tree and try to minimize the maximum cost of these ki vertices by changing at most one vertex on the tree to a red vertex.
Note that
- BaoBao is free to change any vertex among all the n vertices to a red vertex, NOT necessary among the ki vertiecs whose maximum cost he tries to minimize.
- All the q games are independent. That is to say, the tree BaoBao plays with in each game is always the initial given tree, NOT the tree modified during the last game by changing at most one vertex.
Please help BaoBao calculate the smallest possible maximum cost of the given kivertices in each game after changing at most one vertex to a red vertex.
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of the input is an integer T, indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
The first line contains three integers n, m and q (2≤m≤n≤105, 1≤q≤2×105), indicating the size of the tree, the number of red vertices and the number of games.
The second line contains m integers r1,r2,...,rm (1=r1<r2<...<rm≤n), indicating the red vertices.
The following (n−1) lines each contains three integers ui, vi and wi (1≤ui,vi≤n, 1≤wi≤109), indicating an edge with weight wi connecting vertex ui and vi in the tree.
For the following q lines, the i-th line will first contain an integer ki (1≤ki≤n). Then ki integers vi,1,vi,2,...,vi,ki follow (1≤vi,1<vi,2<...<vi,ki≤n), indicating the vertices whose maximum cost BaoBao has to minimize.
It's guaranteed that the sum of n in all test cases will not exceed 106, and the sum of ki in all test cases will not exceed 2×106.
Output
For each test case output q lines each containing one integer, indicating the smallest possible maximum cost of the ki vertices given in each game after changing at most one vertex in the tree to a red vertex.
Sample Input
2
12 2 4
1 9
1 2 1
2 3 4
3 4 3
3 5 2
2 6 2
6 7 1
6 8 2
2 9 5
9 10 2
9 11 3
1 12 10
3 3 7 8
4 4 5 7 8
4 7 8 10 11
3 4 5 12
3 2 3
1 2
1 2 1
1 3 1
1 1
2 1 2
3 1 2 3
Sample Output
4
5
3
8
0
0
0
Hint
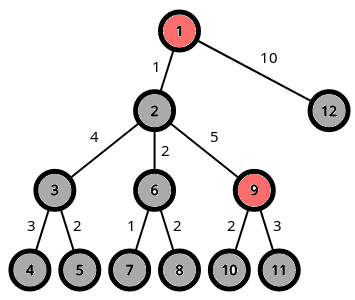
The first sample test case is shown above. Let's denote C(v) as the cost of vertex v.
For the 1st game, the best choice is to make vertex 2 red, so that C(3)=4, C(7)=3 and C(8)=4. So the answer is 4.
For the 2nd game, the best choice is to make vertex 3 red, so that C(4)=3, C(5)=2, C(7)=4 and C(8)=5. So the answer is 5.
For the 3rd game, the best choice is to make vertex 6 red, so that C(7)=1, C(8)=2, C(10)=2 and C(11)=3. So the answer is 3.
For the 4th game, the best choice is to make vertex 12 red, so that C(4)=8, C(5)=7 and C(12)=0. So the answer is 8.
作者: 浙江大学竞赛命题组
单位: ACMICPC
时间限制: 2500 ms
内存限制: 128 MB
代码长度限制:
思路
先说题意,给了n nn个节点,n?1 n-1n?1条边的树,树上的点有m mm个点是红色的,其余的点是黑色的,题目已知树根1这个点的颜色一定是红色的。我们定义每个点的花费为:
红点:花费为0
黑点:花费为这个点与它离这个红色的点的最短距离。
现在要进行q qq次游戏,也就是说每一次的游戏相互独立,一个不会影响另一个的结果,每个游戏选出了k kk个点,你有一次机会,可以把一个黑色的点变成红色的点,题目让你在改变一个点后使得选出的点的代价最小的情况下,求出点的最大值。
思路就是二分+LCA.
我们首先把这个图进行一遍dfs,然后求出两个数组,dis[i] dis[i]dis[i]:表示i点离树根的距离,close[i] close[i]close[i]:表示父亲节点中离i点最近的红色的点,求出这两个我们可以用dis[i]-dis[close[i]]来求出这个点离与他最近的红色的点的距离。
对于每一次选出来的k个点,我们从中找出二分的右端点,就是这个点集中离红色的点距离最长的这个点。
在进行二分判断的时候,从这个点集中找出那些离红色的点的距离大于二分值mid的点,然后求lca.这个点就是当前我们选择的最优点。把这个点涂成红色,然后判断这些点中是否还存在离红色的点的距离大于二分值mid的点,如果存在就证明当前值不可以,否则可以。(我下面求lca的代码用的树剖)
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
typedef long long ll;
const ll N = 1e5 + 10;
ll first[N], tot, r[N];
ll fa[N], dep[N], siz[N], son[N], top[N];
ll close[N], dis[N];
ll vv[N], vis[N];
ll n, m, q, k;
struct edge
{
ll v, w, next;
} e[N * 2];
void add_edge(ll u, ll v, ll w)
{
e[tot].v = v, e[tot].w = w;
e[tot].next = first[u];
first[u] = tot++;
}
void init()
{
mem(first, -1);
mem(r, 0);
mem(vis, 0);
tot = 0;
}
void dfs1(ll u, ll f, ll deep)
{
fa[u] = f;
dep[u] = deep;
siz[u] = 1;
son[u] = 0;
ll maxson = -1;
for (ll i = first[u]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
ll v = e[i].v;
if (v == f)
continue;
dfs1(v, u, deep + 1);
siz[u] += siz[v];
if (siz[v] > maxson)
{
son[u] = v;
maxson = siz[v];
}
}
}
void dfs2(ll u, ll topf)
{
top[u] = topf;
if (!son[u])
return;
dfs2(son[u], topf);
for (ll i = first[u]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
ll v = e[i].v;
if (v == fa[u] || v == son[u])
continue;
dfs2(v, v);
}
}
ll qlca(ll x, ll y)
{
while (top[x] != top[y])
{
if (dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]])
swap(x, y);
x = fa[top[x]];
}
return dep[x] < dep[y] ? x : y;
}
void dfs(ll u, ll red)
{
close[u] = red;
for (ll i = first[u]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
ll v = e[i].v, w = e[i].w;
if (v == fa[u])
continue;
dis[v] = dis[u] + w;
if (r[v])
dfs(v, v);
else
dfs(v, red);
}
}
ll judge(ll mid)
{
ll lca = -1;
for (ll i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
ll v = vv[i];
if (dis[v] - dis[close[v]] > mid) //如果当前点离红色的点的距离大于枚举的值的时候
{
vis[v] = 1;
if (lca == -1)
lca = v;
else
{
ll u = lca;
lca = qlca(lca, v);
}
}
else
vis[v] = 0;
}
if (lca == -1)
return 1;
//lca为当前找的最优点
for (ll i = 1; i <= k; i++)
if (vis[vv[i]])
{
ll v = vv[i];
if (dis[v] - dis[lca] > mid)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
void solve()
{
ll x, u, v, w;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &n, &m, &q);
init();
for (ll i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
scanf("%lld", &x);
r[x] = 1;
}
for (ll i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++)
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &u, &v, &w);
add_edge(u, v, w);
add_edge(v, u, w);
}
dfs1(1, 0, 1);
dfs2(1, 1);
dfs(1, 1);
while (q--)
{
scanf("%lld", &k);
for (ll i = 1; i <= k; i++)
scanf("%lld", &vv[i]);
ll l = 0, r = 0;
for (ll i = 1; i <= k; i++)
r = max(r, dis[vv[i]] - dis[close[vv[i]]]); //找出没修改之前离红点最大的值
while (l < r)
{
ll mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (judge(mid))
r = mid;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
printf("%lld\n", l);
}
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
ll t;
scanf("%lld", &t);
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}