什么是委托?
如果我们把委托当做参数来传递的话,就要用到委托。简单来说,委托是一个类型,这个类型可以赋值一个方法的引用。
声明委托
在C#中使用一个类分两个阶段,首选定义这个类,告诉编译器这个类由什么字段和方法组成的,然后使用这个类实例化对象。在我们使用委托的时候,也需要经过这两个阶段,首先定义委托,告诉编译器我们这个委托可以指向哪些类型的方法,然后,创建该委托的实例。
定义委托的语法如下:
delegate void IntMethodInvoker(int x);
定义了一个委托叫做IntMethodInvoker,这个委托可以指向什么类型的方法呢?
这个方法要带有一个int类型的参数,并且方法的返回值是void的。
定义一个委托要定义方法的参数和返回值,使用关键字delegate定义。
定义委托的其他案例:
delegate double TwoLongOp(long first,longsecond);
delegate string GetAString();
使用委托
privatedelegate string GetAString();
staticvoid Main(){
int x = 40;
GetAString firstStringMethod = newGetAString(x.ToString);
Console.WriteLine(firstStringMethod());
}
在这里我们首先使用GetAString委托声明了一个类型叫做fristStringMethod,接下来使用new对它进行初始化,使它引用到x中的ToString方法上,这样firstStringMethod就相当于x.ToString,我们通过firstStringMethod()执行方法就相当于x.ToString()
通过委托示例调用方法有两种方式
fristStringMethod();
firstStringMethod.Invoke();
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _009_委托
{
class Program
{
private delegate string GetAString();//定义了一个委托类型,这个委托类型的名字叫做GetAString
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 40;
//string s = x.ToString();//toString()方法用来把数据转换成字符串
//使用委托类型 创建实例
GetAString a = new GetAString(x.ToString);//a指向了x中的toString方法
string s = a();//通过委托实例去调用x中的toString方法
Console.WriteLine(s);//通过委托类型调用一个方法,跟直接调用这个方法作用是一样的
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _009_委托
{
class Program
{
private delegate string GetAString();//定义了一个委托类型,这个委托类型的名字叫做GetAString
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//int x = 40;
//string s = x.ToString();//toString()方法用来把数据转换成字符串
//使用委托类型 创建实例
//GetAString a = new GetAString(x.ToString);//a指向了x中的toString方法
//string s = a();//通过委托实例去调用x中的toString方法
//GetAString a = x.ToString;
//string s = a.Invoke();//通过invoke方法调用a所引用的方法
//Console.WriteLine(s);//通过委托类型调用一个方法,跟直接调用这个方法作用是一样的
//实例2 使用委托类型作为方法的参数
PrintString method = Method1;
PrintStr(method);
method = Method2;
PrintStr(method);
Console.ReadKey();
}
private delegate void PrintString();
static void PrintStr(PrintString print)
{
print();
}
static void Method1()
{
Console.WriteLine("method1");
}
static void Method2()
{
Console.WriteLine("method2");
}
}
}
Action委托
除了我们自己定义的委托之外,系统还给我们提供过来一个内置的委托类型,Action和Func
Action委托引用了一个void返回类型的方法,T表示方法参数,先看Action委托有哪些
Action
Action<inT>
Action<inT1,in T2>
Action<in T1,in T2.... inT16>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _010_Action委托
{
class Program
{
static void PrintString()
{
Console.WriteLine("hello world.");
}
static void PrintInt(int i)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
static void PrintString(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
static void PrintDoubleInt(int i1,int i2)
{
Console.WriteLine(i1 + i2);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Action a = PrintString;//action是系统内置(预定义)的一个委托类型,它可以指向一个没有返回值,没有参数的方法
//Action<int> a = PrintInt;//定义了一个委托类型,这个类型可以指向一个没有返回值,有一个int参数的方法
//a(1);
//Action<String> a = PrintString;//定义了一个委托类型,这个类型可以指向一个没有返回值,有一个string参数的方法,在这里系统会自动寻找匹配的方法
//a("hello world");
Action<int, int> a = PrintDoubleInt;
a(2, 3);
}
}
}Func引用了一个带有一个返回值的方法,它可以传递0或者多到16个参数类型,和一个返回类型
Func<outTResult>
Func<inT,out TResult>
Func<intT1,inT2,,,,,,in T16,out TResult>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _011_Func委托
{
class Program
{
static int Test1()
{
return 1;
}
static int Test2(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
return 100;
}
static int Test3(int i,int j)
{
return i + j;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Func<int> a = Test1;//Func中的泛型类型指定的是 方法的返回值类型
//Console.WriteLine(a());
//Func<string, int> a = Test2;//Func中后面可以跟很多类型,最后一个
////类型是返回值类型,前面的类型是参数类型,参数类型必须跟指向的方法的参数类型按照顺序对应
//Func<int, int, int> a = Test3;//func后面必须指定一个返回值类型,参数类型可以有0-16个,先写参数
//类型,最后一个是返回值类型
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
冒泡排序的扩展
雇员薪水的排序
Employee.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _012_冒泡排序扩展
{
class Employee
{
//get 和 set 会在相应的时候自动调用
//主要是为了隐藏程序内的数据结构时用
//get是获取该属性的值,
//set设置该属性的值。
//在用set时有一个特殊的变量value
//就是设置属性时的值
public string Name { get; private set; }
public int Salary { get; private set; }
public Employee(string name,int salary)
{
this.Name = name;
this.Salary = salary;
}
//按照薪水来排序
//如果e1大于e2的话,返回true,否则返回false
public static bool Compare(Employee e1,Employee e2)
{
if (e1.Salary > e2.Salary) return true;
return false;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return Name + ":" + Salary;
}
}
}
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _012_冒泡排序扩展
{
class Program
{
//int型冒泡排序
static void Sort(int[] sortArray)
{
bool swapped = false;
do
{
swapped = false;
for (int i = 0; i < sortArray.Length - 1; i++)
{
if (sortArray[i] > sortArray[i + 1])
{
int temp = sortArray[i];
sortArray[i] = sortArray[i + 1];
sortArray[i + 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
} while (swapped);
}
//通用冒泡排序
static void CommonSort<T>(T[] sortArray,Func<T,T,bool> compareMethod)//传入排序数组,以及自定义的比较方法
{
bool swapped = false;
do
{
swapped = false;
for (int i = 0; i < sortArray.Length - 1; i++)
{
if (compareMethod(sortArray[i],sortArray[i+1]))
{
T temp = sortArray[i];
sortArray[i] = sortArray[i + 1];
sortArray[i + 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
} while (swapped);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//int[] sortArray = new int[] { 123, 23, 12, 3, 345, 34, 565, 4 };
//Sort(sortArray);
//foreach(int temp in sortArray)
//{
// Console.Write(temp + " ");
//}
Employee[] employees = new Employee[]
{
new Employee("dsf",12),
new Employee("d",3),
new Employee("s",12),
new Employee("f",49),
new Employee("sf",5),
new Employee("ds",18),
new Employee("df",23)
};
CommonSort<Employee>(employees, Employee.Compare);
foreach(Employee em in employees)
{
Console.WriteLine(em.ToString());
//Console.WriteLine(em);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
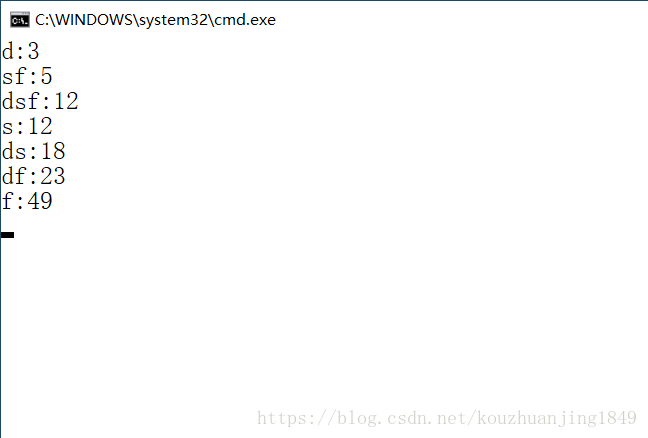
运行结果
多播委托
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _013_多播委托
{
class Program
{
static void Test1()
{
Console.WriteLine("test1");
}
static void Test2()
{
Console.WriteLine("test2");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//多播委托
Action a = Test1;
//a = Test2;
a += Test2;//表示添加一个委托的引用
//a -= Test1;
//if(a!=null)
// a();//当一个委托没有指向任何方法的时候,调用的话会出现异常null
//取得多播委托中所有方法的委托
Delegate[] delegates = a.GetInvocationList();
foreach(Delegate de in delegates)
{
de.DynamicInvoke();
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}匿名方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _014_匿名方法
{
class Program
{
static int Test1(int arg1,int arg2)
{
return arg1 + arg2;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Func<int, int, int> plus = Test1;
//修改成匿名方法的形式
Func<int, int, int> plus = delegate (int arg1, int arg2)
{
return arg1 + arg2;
};
//匿名方法本质上是一个方法,只是没有名字,任何使用委托变量的地方都可以使用匿名方法赋值
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Lambda表达式
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _015_Lambda表达式
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Lambda表达式用来代替匿名方法,所有一个Lambda表达式也是定义了一个方法
//Func<int, int, int> plus = delegate (int arg1, int arg2)
//{
// return arg1 + arg2;
//};
//Func<int, int, int> plus = (arg1, arg2) =>//lambda表达式的参数是不需要声明类型的
//{
// return arg1 + arg2;
//};
//Console.WriteLine(plus(90, 60));
Func<int, int> test2 = a => a + 1;//lambda表示的参数只有一个的时候,可以不加上括号
//当函数体的语句只有一句的时候,我们可以不加上大括号,也可以不加上return语句
Func<int, int> test3 = (a) =>
{
return a + 1;
};
Console.WriteLine(test2(32)); //33
Console.WriteLine(test3(32)); //33
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}事件
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _016_事件
{
class Program
{
public delegate void MyDelegate();
public event MyDelegate mydelegate;//声明事件只能放在类里边
//public MyDelegate mydelegate;//声明一个委托类型的变量,作为类的成员
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p = new Program();
p.mydelegate = Test1;
p.mydelegate();
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void Test1()
{
Console.WriteLine("test1");
}
}
}
观察者设计模式_猫捉老鼠
Cat.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _017_观察者设计模式_猫捉老鼠
{
//猫类
class Cat
{
private string name;
private string color;
public Cat(String name,string color)
{
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
//猫进屋(猫的状态发送改变)(被观察者的状态发送改变)
//public void CatComing(Mouse mouse1, Mouse mouse2, Mouse mouse3)
public void CatComing()
{
Console.WriteLine(color + "的猫" + name + "过来了,喵喵喵~");
//mouse1.RunAway();
//mouse2.RunAway();
//mouse3.RunAway();
if (catCome != null)
{
catCome();
}
}
public Action catCome;
}
}Mouse.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _017_观察者设计模式_猫捉老鼠
{
//观察者类(老鼠)
class Mouse
{
private string name;
private string color;
public Mouse(string name,string color)
{
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
//逃跑功能
public void RunAway()
{
Console.WriteLine(color+"的老鼠"+name+"说:老猫来了,赶紧跑,我跑,我使劲跑,我加速使劲跑!");
}
}
}program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _017_观察者设计模式_猫捉老鼠
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Cat cat = new Cat("加菲猫", "黄色");
Mouse mouse1 = new Mouse("米奇", "黑色");
cat.catCome += mouse1.RunAway;
Mouse mouse2 = new Mouse("唐老鸭", "红色");
cat.catCome += mouse2.RunAway;
Mouse mouse3 = new Mouse("xx", "红色");
cat.catCome += mouse3.RunAway;
Mouse mouse4 = new Mouse("贝塔", "红色");
cat.catCome += mouse4.RunAway;
//cat.CatComing(mouse1,mouse2,mouse3);//猫的状态发送改变,在cat中调用了观察者的方法,当观察者发送改变的时候
//需要同时修改被观察者的代码
cat.CatComing();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}