The Closest M Points
Time Limit: 16000/8000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 98304/98304 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 7118 Accepted Submission(s): 2176
Problem Description
The course of Software Design and Development Practice is objectionable. ZLC is facing a serious problem .There are many points in K-dimensional space .Given a point. ZLC need to find out the closest m points. Euclidean distance is used as the distance metric between two points. The Euclidean distance between points p and q is the length of the line segment connecting them.In Cartesian coordinates, if p = (p1, p2,..., pn) and q = (q1, q2,..., qn) are two points in Euclidean n-space, then the distance from p to q, or from q to p is given by:
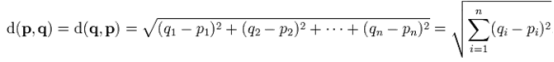
Can you help him solve this problem?
Input
In the first line of the text file .there are two non-negative integers n and K. They denote respectively: the number of points, 1 <= n <= 50000, and the number of Dimensions,1 <= K <= 5. In each of the following n lines there is written k integers, representing the coordinates of a point. This followed by a line with one positive integer t, representing the number of queries,1 <= t <=10000.each query contains two lines. The k integers in the first line represent the given point. In the second line, there is one integer m, the number of closest points you should find,1 <= m <=10. The absolute value of all the coordinates will not be more than 10000.
There are multiple test cases. Process to end of file.
Output
For each query, output m+1 lines:
The first line saying :”the closest m points are:” where m is the number of the points.
The following m lines representing m points ,in accordance with the order from near to far
It is guaranteed that the answer can only be formed in one ways. The distances from the given point to all the nearest m+1 points are different. That means input like this:
2 2
1 1
3 3
1
2 2
1
will not exist.
Sample Input
3 2 1 1 1 3 3 4 2 2 3 2 2 3 1
Sample Output
the closest 2 points are: 1 3 3 4 the closest 1 points are: 1 3
Author
HIT
Source
2012 Multi-University Training Contest 5
Recommend
zhuyuanchen520
题意:求最近邻K点
解题思路:KDTree模板,在搜索过程当中,用优先队列存储前K近即可。然后用KDTree去剪枝搜索。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 200050;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
int nowD;//当前排序的维度
struct node{
int Min[10],Max[10];//这个点所维护的块内,离这个点最远的值和最近的值
int d[10];//这个点的坐标
int l,r;//这个块所维护的点的区间
int id;
friend bool operator <(const node &a,const node &b){
return a.d[nowD] < b.d[nowD];
}
}t[MAXN];
int DIM=2;//维度数
void pushup(int now) //由子节点控制范围来更新now点的控制范围
{
for(int i =0;i<DIM;i++){
if(t[now].l)
{
if(t[t[now].l].Max[i]>t[now].Max[i]) t[now].Max[i]=t[t[now].l].Max[i];
if(t[t[now].l].Min[i]<t[now].Min[i]) t[now].Min[i]=t[t[now].l].Min[i];
}
if(t[now].r)
{
if(t[t[now].r].Max[i]>t[now].Max[i]) t[now].Max[i]=t[t[now].r].Max[i];
if(t[t[now].r].Min[i]<t[now].Min[i]) t[now].Min[i]=t[t[now].r].Min[i];
}
}
}
int build(int l,int r,int D) //kd树的建立
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
nowD=D;
nth_element(t+l,t+mid,t+r+1);//类似快排,快排后,左边的都比mid小,右边的都比mid大,这样就可以正确的递归了
if(l!=mid) t[mid].l=build(l,mid-1,(D+1)%DIM);else t[mid].l=0;//递归
if(r!=mid) t[mid].r=build(mid+1,r,(D+1)%DIM);else t[mid].r=0;
for(int i=0;i<DIM;i++)
t[mid].Max[i]=t[mid].Min[i]=t[mid].d[i];//初始化
pushup(mid);//更新
return mid;
}
//计算x到p这一块的最短距离,用于A*剪枝
ll getdist_min(int p,node x){
ll dis=0;
for(int i=0;i<DIM;i++){
if(x.d[i]<t[p].Min[i]) dis+=ll(t[p].Min[i]-x.d[i])*ll(t[p].Min[i]-x.d[i]);
if(x.d[i]>t[p].Max[i]) dis+=ll(x.d[i]-t[p].Max[i])*ll(x.d[i]-t[p].Max[i]);
}
return dis;
}
int M;
priority_queue<pair<ll,node> > que;
void query_min(int p, node x)
{
/***计算x到p这个点的距离***/
ll dis=0;
for(int i=0;i<DIM;i++)
dis+=ll(x.d[i]-t[p].d[i])*ll(x.d[i]-t[p].d[i]);
//入队
if(que.size()==M){
if(dis<que.top().first){
que.pop();
que.push(make_pair(dis,t[p]));
}
}
else
que.push(make_pair(dis,t[p]));
ll ld=t[p].l ? getdist_min(t[p].l,x):INF;
ll rd=t[p].r ? getdist_min(t[p].r,x):INF;
if(min(ld,rd)>que.top().first&&que.size()==M)//剪枝
return;
if(ld<rd){
if(ld<que.top().first||que.size()<M)//剪枝
query_min(t[p].l,x);
if(rd<que.top().first||que.size()<M)
query_min(t[p].r,x);
}
else{
if(ld<que.top().first||que.size()<M)//剪枝
query_min(t[p].l,x);
if(rd<que.top().first||que.size()<M)
query_min(t[p].r,x);
}
}
int ans[15][10];
int main()
{
int N;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&N,&DIM)){
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
for(int j=0;j<DIM;j++)
scanf("%d",&t[i].d[j]);
int rt=build(1,N,0);
int Q;
scanf("%d",&Q);
node tmp;
while(Q--){
for(int i=0;i<DIM;i++)
scanf("%d",&tmp.d[i]);
scanf("%d",&M);
query_min(rt,tmp);
printf("the closest %d points are:\n",M);
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
pair<ll,node> tp = que.top();
que.pop();
for(int j=0;j<DIM;j++)
ans[M-i-1][j]=tp.second.d[j];
}
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
for(int j=0;j<DIM-1;j++)
printf("%d ",ans[i][j]);
printf("%d\n",ans[i][DIM-1]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}