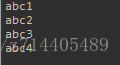集合框架
集合类
集合对象用于封装特有数据,对象多了需要存储,如果对象的个数不确定。
就使用集合容器进行存储。
集合特点:
1,用于存储对象的容器。
2,集合的长度是可变的。
3,集合中不可以存储基本数据类型值。
集合容器因为内部的数据结构不同,有多种具体容器。
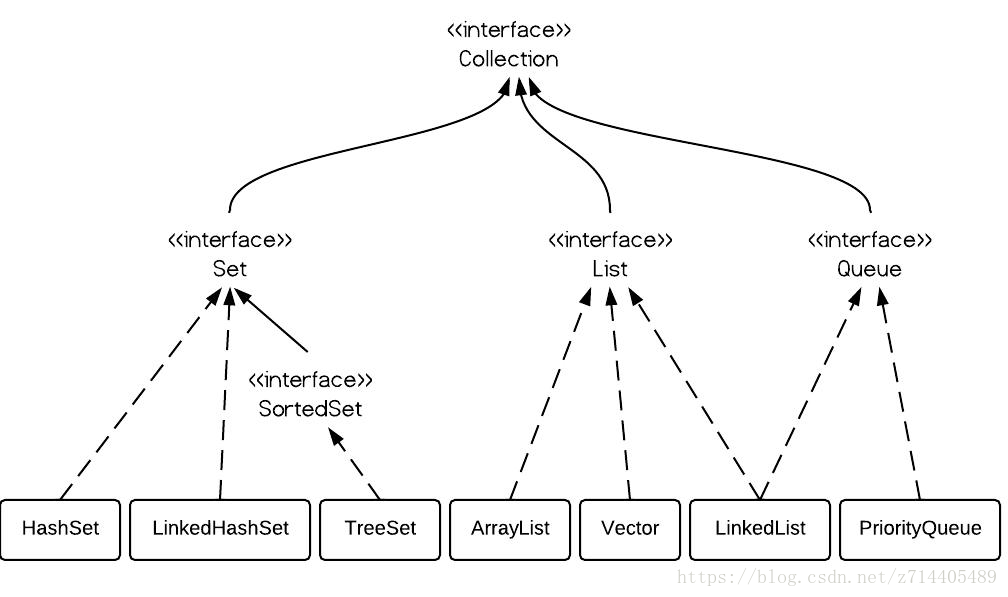
不断的向上抽取,就形成了集合框架。
框架的顶层Collection接口:
Collection的常见方法:
1,添加。
boolean add(Object obj):
boolean addAll(Collection coll):
2,删除。
boolean remove(object obj):
boolean removeAll(Collection coll);
void clear();
3,判断:
boolean contains(object obj):
boolean containsAll(Colllection coll);
boolean isEmpty():判断集合中是否有元素。
4,获取:
int size():
Iterator iterator():取出元素的方式:迭代器。
该对象必须依赖于具体容器,因为每一个容器的数据结构都不同。
所以该迭代器对象是在容器中进行内部实现的。
对于使用容器者而言,具体的实现不重要,只要通过容器获取到该实现的迭代器的对象即可,
也就是iterator方法。
Iterator接口就是对所有的Collection容器进行元素取出的公共接口。
其实就是抓娃娃游戏机中的夹子!
常用方法使用演示:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
// show(coll);
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
show(c1,c2);
}
public static void show(Collection c1,Collection c2){
//给c1添加元素。
c1.add("abc1");
c1.add("abc2");
c1.add("abc3");
c1.add("abc4");
//给c2添加元素。
c2.add("abc1");
c2.add("abc2");
c2.add("abc3");
c2.add("abc4");
c2.add("abc5");
System.out.println("c1:"+c1);
System.out.println("c2:"+c2);
//演示addAll
// c1.addAll(c2);//将c2中的元素添加到c1中。
//演示removeAll
// boolean b = c1.removeAll(c2);//将两个集合中的相同元素从调用removeAll的集合中删除。
// System.out.println("removeAll:"+b);
//演示containsAll
// boolean b = c1.containsAll(c2);
// System.out.println("containsAll:"+b);
//演示retainAll
boolean b = c1.retainAll(c2);//取交集,保留和指定的集合相同的元素,而删除不同的元素。
//和removeAll功能相反 。
System.out.println("retainAll:"+b);
System.out.println("c1:"+c1);
}
public static void show(Collection coll){
//1,添加元素。add.
coll.add("abc1");
coll.add("abc2");
coll.add("abc3");
System.out.println(coll);
//2,删除元素。remove
// coll.remove("abc2");//会改变集合的长度
//清空集合.
// coll.clear();
System.out.println(coll.contains("abc3"));
System.out.println(coll);
}
}
迭代器使用演示:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class IteratorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("abc1");
coll.add("abc2");
coll.add("abc3");
coll.add("abc4");
// System.out.println(coll);
//使用了Collection中的iterator()方法。 调用集合中的迭代器方法,是为了获取集合中的迭代器对象。
// Iterator it = coll.iterator();
// while(it.hasNext()){
// System.out.println(it.next());
// }
for(Iterator it = coll.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ){ //常用
System.out.println(it.next());
}
// System.out.println(it.next());
// System.out.println(it.next());
// System.out.println(it.next());
// System.out.println(it.next());
// System.out.println(it.next());//java.util.NoSuchElementException
}
}
运行结果
小结:it.next();用来取出集合中的下一个元素(it为某个集合对象)
it.hasNext();用来判断集合中是否还有下一个元素
Collection框架
|–List:有序(存入和取出的顺序一致),元素都有索引(角标),元素可以重复。
|–Set:元素不能重复,无序。
List集合
特有的常见方法
有一个共性特点就是都可以操作角标
1,添加
void add(index,element);
void add(index,collection);
2,删除;
Object remove(index): //返回值是被删除的元素
3,修改:
Object set(index,element);
4,获取:
Object get(index);
int indexOf(object);
int lastIndexOf(object);
List subList(from,to);//包头不包尾
由上看出,list集合可以完成对元素的增删改查。
listIterator类
列表迭代器,它可以实现在迭代过程中完成对元素的增删改查
举例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class ListDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
// show(list);
list.add("abc1");
list.add("abc2");
list.add("abc3");
System.out.println("list:"+list);
ListIterator it = list.listIterator();//获取列表迭代器对象
//它可以实现在迭代过程中完成对元素的增删改查。
//注意:只有list集合具备该迭代功能.
while(it.hasNext()){
Object obj = it.next();
if(obj.equals("abc2")){
it.set("abc9");
//it.add("abc9");
}
}
// System.out.println("hasNext:"+it.hasNext());
// System.out.println("hasPrevious:"+it.hasPrevious());
while(it.hasPrevious()){ //逆序
System.out.println("previous:"+it.previous());
}
System.out.println("list:"+list);
/*Iterator it = list.iterator(); //这是异常举例
while(it.hasNext()){
Object obj = it.next();//java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
//在迭代器过程中,不要使用集合操作元素,容易出现异常。
//可以使用Iterator接口的子接口ListIterator来完成在迭代中对元素进行更多的操作。
if(obj.equals("abc2")){
list.add("abc9");
}
else
System.out.println("next:"+obj);
}
System.out.println(list);
*/
}
public static void show(List list) {
list.add("abc1");
list.add("abc2");
list.add("abc3");
list.add("abc4");
Iterator it = list.iterator(); // 通用的取出方式
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println("next:"+it.next());
}
//list特有的取出元素的方式之一。
for(int x=0; x<list.size(); x++){
System.out.println("get:"+list.get(x));
}
}
}
List常用子类的特点
List:
|–Vector:内部是数组数据结构,是同步的。增删,查询都很慢!
|–ArrayList:内部是数组数据结构,是不同步的。替代了Vector。查询的速度快。
|–LinkedList:内部是链表数据结构,是不同步的。增删元素的速度很快。
Vector集合
数组数据结构。增删,查询都很慢。
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Vector;
public class VectorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector v = new Vector();
v.addElement("abc1");
v.addElement("abc2");
v.addElement("abc3");
v.addElement("abc4");
Enumeration en = v.elements(); //返回此向量的枚举 此接口的功能与迭代器是重复的
while(en.hasMoreElements()){
System.out.println("nextelment:"+en.nextElement());
}
Iterator it = v.iterator(); //优先考虑Iterator接口,保证了阅读性和简单
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println("next:"+it.next());
}
}
}
LinkedList
链表数据结构,增删元素的速度很快。
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList link = new LinkedList();
link.addFirst("abc1"); //添加到表头位置
link.addFirst("abc2");
link.addFirst("abc3");
link.addFirst("abc4");
// System.out.println(link);
// System.out.println(link.getFirst());//获取第一个但不删除。
// System.out.println(link.getFirst());
// System.out.println(link.removeFirst());//获取元素但是会删除。
// System.out.println(link.removeFirst());
while(!link.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(link.removeLast());
}
System.out.println(link);
// Iterator it = link.iterator();
// while(it.hasNext()){
// System.out.println(it.next());
// }
}
}
练习:堆栈与队列
-
请使用LinkedList来模拟一个堆栈或者队列数据结构。
-
堆栈:先进后出 First In Last Out FILO
-
队列:先进先出 First In First Out FIFO
-
我们应该描述这样一个容器,给使用提供一个容器对象完成这两种结构中的一种。
package cn.itcast.p2.linkedlist.test;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class DuiLie { //先进先出
private LinkedList link;
public DuiLie() {
link = new LinkedList(); //使用构造函数来进行初始化
}
/**
* 队列的添加元素的功能。若改成栈,则addFirst即可
*/
public void myAdd(Object obj) {
link.addLast(obj);
}
public Object myGet() {
return link.removeFirst();
}
public boolean isNull() {
return link.isEmpty();
}
}
package cn.itcast.p2.linkedlist.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class LinkedTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DuiLie dl = new DuiLie();
dl.myAdd("abc1");
dl.myAdd("abc2");
dl.myAdd("abc3");
dl.myAdd("abc4");
while(!dl.isNull()){
System.out.println(dl.myGet());
}
}
}
1.6版本新特性
LinkedList:
addFirst();
addLast():
jdk1.6
offerFirst();
offetLast();
getFirst();.//获取但不移除,如果链表为空,抛出NoSuchElementException.
getLast();
jdk1.6
peekFirst();//获取但不移除,如果链表为空,返回null.
peekLast():
removeFirst();//获取并移除,如果链表为空,抛出NoSuchElementException.
removeLast();`
jdk1.6
pollFirst();//获取并移除,如果链表为空,返回null.
pollLast();
ArrayList
package cn.itcast.p3.arraylist.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import cn.itcast.p.bean.Person; //这是一个已经定义过的类
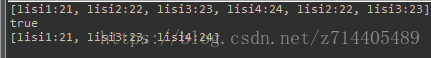
public class ArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("lisi1",21);
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(p1);
al.add(new Person("lisi2",22));
al.add(new Person("lisi3",23));
al.add(new Person("lisi4",24));
Iterator it = al.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
// System.out.println(((Person) it.next()).getName()+"::"+((Person) it.next()).getAge()); //不能在一次循环语句中用两次next
Person p = (Person) it.next();
System.out.println(p.getName()+"--"+p.getAge());
}
// al.add(5);//al.add(new Integer(5)); //自动装箱
}
}
Set集合
Set:元素不可以重复,是无序。 Set接口中的方法和Collection一致。
常用子类特点:
|–HashSet: 内部数据结构是哈希表 ,是不同步的。
|–TreeSet:可以对Set集合中的元素进行排序。是不同步的。
HashSet
内部数据结构是哈希表 ,是不同步的。
如何保证该集合的元素唯一性呢? 是通过对象的hashCode和equals方法来完成对象唯一性的。
如果对象的hashCode值不同,那么不用判断equals方法,就直接存储到哈希表中。
如果对象的hashCode值相同,那么要再次判断对象的equals方法是否为true。
如果为true,视为相同元素,不存。如果为false,那么视为不同元素,就进行存储。
记住:如果元素要存储到HashSet集合中,必须覆盖hashCode方法和equals方法。 一般情况下,如果定义的类会产生很多对象,比如人,学生,书,通常都需要覆盖equals,hashCode方法。
建立对象判断是否相同的依据。
演示:
package cn.itcast.p4.hashset.demo;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class HashSetDemo {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
hs.add("hehe");
// hs.add("heihei");
hs.add("hahah");
hs.add("xixii");
hs.add("hehe"); //由于元素唯一性,无法再存入
Iterator it = hs.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next()); 不保证有序性
}
}
}
HashSet存储自定义对象
往hashSet集合中存储Person对象(带有姓名和年龄参数)。如果姓名和年龄相同,视为同一个人。视为相同元素。这需要让Person对象自定义一个hashCode方法。
@Override
public int hashCode() { //自定义
return name.hashCode()+age*27;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this == obj)
return true;
if(!(obj instanceof Person))
throw new ClassCastException("类型错误");
// System.out.println(this+"....equals....."+obj);
Person p = (Person)obj;
return this.name.equals(p.name) && this.age == p.age;
}
test部分
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import cn.itcast.p.bean.Person;
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
/*
* HashSet集合数据结构是哈希表,所以存储元素的时候,
* 使用的元素的hashCode方法来确定位置,如果位置相同,在通过元素的equals来确定是否相同。
*
*/
hs.add(new Person("lisi4",24));
hs.add(new Person("lisi7",27));
hs.add(new Person("lisi1",21));
hs.add(new Person("lisi9",29));
hs.add(new Person("lisi7",27)); //同一个人
Iterator it = hs.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Person p = (Person)it.next();
System.out.println(p);
// System.out.println(p.getName()+"...."+p.getAge());
}
}
}
练习
定义功能去除ArrayList中的重复元素。
public class ArrayListTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(new Person("lisi1",21));
al.add(new Person("lisi2",22));
al.add(new Person("lisi3",23));
al.add(new Person("lisi4",24));
al.add(new Person("lisi2",22));
al.add(new Person("lisi3",23));
System.out.println(al);
al = getSingleElement(al);
System.out.println(al.remove(new Person("lisi2",22)));
System.out.println(al);
}
public static ArrayList getSingleElement(ArrayList al) {
//1,定义一个临时容器。
ArrayList temp = new ArrayList();
//2,迭代al集合。
Iterator it = al.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object obj = it.next();
//3,判断被迭代到的元素是否在临时容器存在。
if(!temp.contains(obj)){
temp.add(obj);
}
}
return temp;
}
}
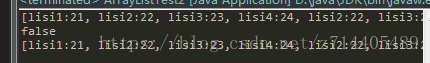
当Person类中的equals方法没有进行覆盖时,运行结果如下:
当对Person类中的equals方法覆盖时——
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this == obj)
return true;
if(!(obj instanceof Person))
throw new ClassCastException("类型错误");
Person p = (Person)obj; //对于该对象,应该比较的是姓名与年龄
return this.name.equals(p.name) && this.age == p.age; }
运行结果如下:
由此可以得出结论:使用contains与remove方法时,都是依赖于该对象的equals方法去判断是否存在相同对象的。
当Person的equals方法没有被覆盖时,那么就继承了Object类的equals方法,则比较的是引用类型的变量所指向的对象的地址,在本例下,即使两个对象的参数相同,但是由于地址不同,则并不会被判定为相同对象。
LinkedHashSet
当需要保证唯一与有序兼顾时,使用这个子类就行了。
TreeSet
可以对Set集合中的元素进行排序。是不同步的。
判断元素唯一性的方式:就是根据比较方法的返回结果是否是0,是0,就是相同元素,不存。
TreeSet对元素进行排序的方式一: 让元素自身具备比较功能,就需要实现Comparable接口。覆盖compareTo方法(自然排序)。
如果不按照对象中具备的自然顺序进行排序,或对象中不具备自然顺序。怎么办?
可以使用TreeSet集合第二种排序方式二: 让集合自身具备比较功能,定义一个类实现Comparator接口,覆盖compare方法。将该类对象作为参数传递给TreeSet集合的构造函数。
方式一:实现Comparable接口,覆盖compareTo方法
//这是Person类的一部分
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Person p = (Person)o;
int temp = this.age-p.age;
return temp==0?this.name.compareTo(p.name):temp;
/* if(this.age>p.age) //有强转,健壮性判断
return 1;
if(this.age<p.age)
return -1;
else{
return this.name.compareTo(p.name);
}*/ 这是另一种写法
Demo
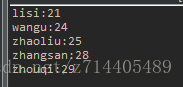
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet();
/*
以Person对象年龄进行从小到大的排序。
*/
ts.add(new Person("zhangsan",28));
ts.add(new Person("lisi",21));
ts.add(new Person("zhouqi",29));
ts.add(new Person("zhaoliu",25));
ts.add(new Person("wangu",24));
Iterator it = ts.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Person p = (Person)it.next();
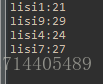
System.out.println(p.getName()+":"+p.getAge());
}
}
}
运行结果
方式二:Comparator比较器
覆盖compare方法。
import java.util.Comparator;
import cn.itcast.p.bean.Person;
/**
* 创建了一个根据Person类的name进行排序的比较器。
*/
public class ComparatorByName implements Comparator {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
Person p1 = (Person)o1;
Person p2 = (Person)o2;
int temp = p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());
return temp==0?p1.getAge()-p2.getAge(): temp;
// return 1;//有序。
}
}
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(new ComparatorByName());
将比较器类对象作为参数传递给TreeSet集合的构造函数。
示例:对字符串进行长度排序
这种情况是不能使用字符串的自然排序,所以要用到比较器。
import java.util.Comparator;
public class ComparatorByLength implements Comparator { //比较器
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
String s1 = (String)o1;
String s2 = (String)o2;
int temp = s1.length()-s2.length();
return temp==0? s1.compareTo(s2): temp;
}
}
/*
- 对字符串进行长度排序。
*/
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import cn.itcast.p5.comparator.ComparatorByLength;
public class TreeSetTest {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(new ComparatorByLength());
ts.add("aaaaa");
ts.add("zz");
ts.add("nbaq");
ts.add("cba");
ts.add("abc");
Iterator it = ts.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}