二叉树的概念:
一棵二叉树是结点的一个有限集合,该集合或者为空,或者是由一个根节点加上两棵分别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成。
二叉树的特点:
- 每个结点最多有两棵子树,即二叉树不存在度大于2的结点
- 二叉树的子树有左右之分,其子树的次序不能颠倒
二叉树的五种形态:
实现代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int TDataType;
typedef struct BTreeNode{
TDataType data;
struct BTreeNode *left;
struct BTreeNode *right;
} BTreeNode;
BTreeNode *CreateNode(int data)
{
BTreeNode *node = (BTreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTreeNode));
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
/*
创建一棵二叉树
*/
BTreeNode *CreateTree(int preOrder[], int size, int *pUsedSize)
{
//考虑特殊情况,空
if (size == 0){
*pUsedSize = 0;
return NULL;
}
//正常情况
int leftUsed, rightUsed;
int rootValue = preOrder[0];
if (rootValue == -1){
*pUsedSize = 1;
return NULL;
}
BTreeNode *root = CreateNode(rootValue);
root->left = CreateTree(preOrder + 1, size - 1, &leftUsed);
root->right = CreateTree(preOrder + 1 + leftUsed, size - 1 - leftUsed, &rightUsed);
*pUsedSize = leftUsed + rightUsed + 1;
return root;
}
/*
遍历二叉树
*/
//前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTreeNode *root)
{
//考虑空树
if (root == NULL){
return;
}
printf(" %d ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTreeNode *root)
{
if (root == NULL){
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf(" %d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTreeNode *root)
{
if (root == NULL){
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf(" %d ", root->data);
}
/*
求树的总节点个数
*/
//方法一
int GetSize1(BTreeNode *root)
{
if (root == NULL){
return 0;
}
int left = GetSize1(root->left);
int right = GetSize1(root->right);
return left + right + 1;
}
//方法二
int count = 0;
void GetSize2(BTreeNode *root)
{
if (root == NULL){
return;
}
GetSize2(root->left);
GetSize2(root->right);
count++;
}
/*
求叶子节点个数
*/
int GetLeafSize(BTreeNode *root)
{
if (root == NULL){
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL){
return 1;
}
return GetLeafSize(root->left) + GetLeafSize(root->right);
}
//方法二
int num = 0;
void GetLeafSize2(BTreeNode *root)
{
if (root == NULL){
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL){
num++;
}
GetLeafSize2(root->left);
GetLeafSize2(root->right);
}
/*
求第k层的节点个数
*/
int GetLeafKSize(BTreeNode *root,int k)
{
if (root == NULL){
//空树,任意层都是0
return 0;
}
if (k == 1){
// 第一层只有根节点一个
return 1;
}
int left = GetLeafKSize(root->left, k - 1);
int right = GetLeafKSize(root->right, k - 1);
return left + right;
}
/*
求高度/深度
*/
#define MAX(a,b) ( (a)>(b) ? (a):(b) )
int GetHight(BTreeNode *root)
{
//树为空
if (root == NULL){
return 0;
}
//判断只有一个节点时
//可写也可不写,写的画可节省两次函数调用
if (root == 1){
return 1;
}
return MAX(GetHight(root->left), GetHight(root->right)) + 1;
}
/*
查找某一节点是否在给定的无重复节点的二叉树里
*/
BTreeNode *Find(BTreeNode *root, TDataType data)
{
if (root == NULL){
return NULL;
}
if (root->data == data){
return root;
}
BTreeNode *result = Find(root->left, data);
if (result != NULL){
//左子树找到了
return result;
}
result = Find(root->right,data);
if (result != NULL){
//右子树找到了
return result;
}
else{
//没有找到
return NULL;
}
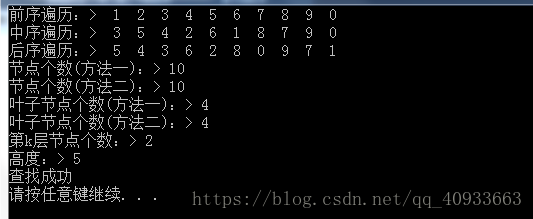
}测试函数与主函数:
void test()
{
int preOrder[] = { 1, 2, 3, -1, 4, 5, -1, -1, -1, 6, -1, -1, 7, 8, -1, -1, 9, -1, 0 };
int size = sizeof (preOrder) / sizeof(int);
int pUsedSize;
BTreeNode *root = CreateTree(preOrder, size, &pUsedSize);
printf("前序遍历:> ");
PreOrder(root);
printf("\n中序遍历:> ");
InOrder(root);
printf("\n后序遍历:> ");
PostOrder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("节点个数(方法一):> %d\n", GetSize1(root));
printf("节点个数(方法二):> ");
GetSize2(root);
printf("%d\n",count);
printf("叶子节点个数(方法一):> %d\n", GetLeafSize(root));
printf("叶子节点个数(方法二):> ");
GetLeafSize2(root);
printf("%d\n", num);
printf("第k层节点个数:> %d\n", GetLeafKSize(root, 4));
printf("高度:> %d\n", GetHight(root));
if (Find(root, 5) != NULL){
printf("查找成功\n");
}
else{
printf("查找失败\n");
}
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}实现效果: