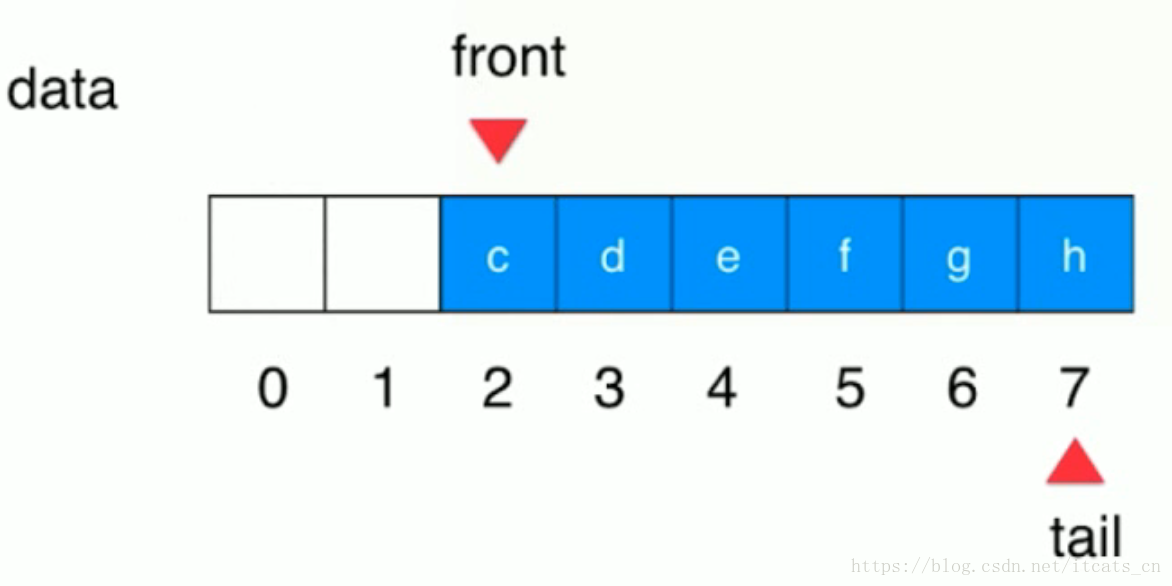
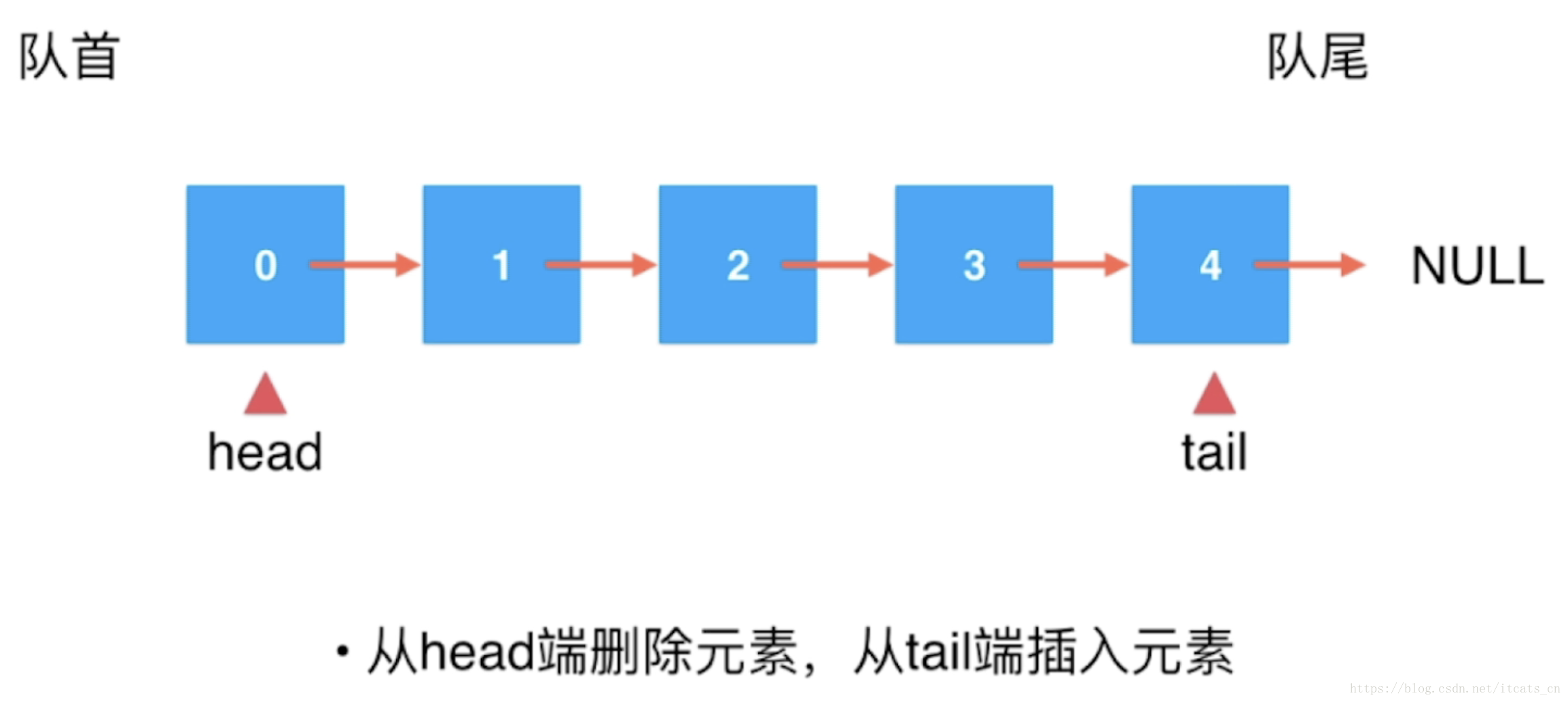
什么是队列?
队列是一种线性的数据结构【线性数据结构:数组、栈、队列】
相比数组,队列对应的数据操作是数组的子集。
只能从一端(队尾)添加元素,只能从另一端(队首)取出元素。
数组队列
代码实现
Array数组类
package cn.itcats.queue;
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
public Array(int capacity) {
data =(E[]) new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
public Array() {
//空参数构造默认的capacity为10
this(10);
}
//获取数组元素中元素个数
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
//获得数组容量
public int getCapacity() {
return data.length;
}
//判断数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
//向数组尾部添加元素
public void addLast(E e) {
add(size, e);
}
//向数组头部添加元素
public void addFirst(E e) {
add(0, e);
}
//向数组中index索引处插入某个元素
public void add(int index, E e) {
//检查数组中是否能容纳新的元素
if (size == data.length)
System.out.println("数组需要扩容");
resize(data.length * 2);
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index非法");
//移动元素
for (int i = size - 1; i >= index; i--) {
//后一个索引赋上前一个索引的元素,即每一个元素都向后挪了一个位置
data[i + 1] = data[i];
}
data[index] = e;
size++;
}
//获取数组中的值
E get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index非法");
return data[index];
}
//获取数组中的值
E getLast() {
return get(size - 1);
}
//获取数组中的值
E getFirst() {
return get(0);
}
//更新数组的值
E update(int index, E e) {
E oldValue = get(index);
data[index] = e;
return oldValue;
}
//数组中是否含有某元素,有返回true,无返回false
public boolean contains(E e) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
//查找数组中的某个元素,找到返回索引,找不到返回-1
public int find(E e) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (data[i].equals(e)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//删除数组中某个元素
public E remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index非法");
}
E ret = data[index];
for (int i = index + 1; i < size; i++) {
data[i - 1] = data[i];
}
size--;
data[size] = null;
if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0 )
resize(data.length /2);
return ret;
}
public E removeFirst() {
return remove(0);
}
public E removeLast() {
return remove(size - 1);
}
//删除指定元素,如果有则删除,删除成功返回true,删除失败返回false
public boolean removeElement(E e) {
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1){
remove(index);
return true;
}
return false;
}
//实现动态数组,动态扩容 size==data.lenngth 扩容2倍 和 缩容 size == data.length / 2
private void resize(int newCapacity){
//创建一个新的数组
E[] newData = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity];
//把原来的元素迁移到新的数组中
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++){
newData[i] = data[i];
}
data = newData;
}
//打印数组中的元素
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
//显示[1,2,3,4,5]
sb.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
sb.append(data[i]);
if (i != size - 1) {
sb.append(", ");
}
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}
Queue接口
package cn.itcats.queue;
public interface Queue<E> {
//入队操作
void enqueue(E e);
//出队操作
E dequeue();
//获取队首元素
E getFront();
//获取队列中元素个数
int getSize();
//判断队列是否为空
boolean isEmpty();
}
基于数组实现的Queue
package cn.itcats.queue;
public class ArrayQueue<E> implements Queue<E>{
private Array<E> array;
public ArrayQueue(int capacity){
array = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public ArrayQueue(){
array = new Array();
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e) {
array.addLast(e);
}
@Override
public E dequeue() {
return array.removeFirst();
}
@Override
public E getFront() {
return array.getFirst();
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return array.getSize();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return array.isEmpty();
}
public int getCapacity(){
return array.getCapacity();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("Queue: "));
sb.append("front [");
for (int i = 0; i < array.getSize(); i++) {
sb.append(array.get(i));
if (i != array.getSize() - 1) {
sb.append(", ");
}
}
sb.append("] tail");
return sb.toString();
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ;i ++){
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println("i:"+i +" "+queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println("i:"+i +" "+queue);
}
}
}
}
使用数组实现队列的复杂度分析:
可以看到,因为每次出队都调用removeFirst()方法,时间复杂度O(n),那么有没有什么方法可以实现入队和出队时间复杂度都是O(1)呢?答案是有的,下面我们就来说说循环队列
循环队列
由于数组队列的出队时间复杂度都为O(n),原因是每次出队时都需要移动元素进行赋值操作,那么循环队列便产生了。
循环队列内部维护了两个指针,front和tail。
1、在初始化时,front和tail都指向索引为0的位置,所以当front==tail时,队列为空。
2、每入队一个元素,tail++,每出队一个元素,front++。
3、到tail++到末尾时,若开头还有可利用的空间,则7之后的索引其实是0。 index = (7+1) % capacitySize == 0
3、如下图所示,如果在索引1处放置一个元素,tail++,此时tail==front,但此时队列并不为空,这并不是我们想看见的,所以数组中需要浪费一个索引空间。当(tail+1) % capacity ==front时,队列为满,所以索引1不放元素。有些人可能疑问为什么不是tail+1 == front呢?当tail==7时,再加入一个元素,靠的就是取模运算把下一个tail放在索引0位置的,当tail为0,front为7时,队列也是满的,而7+1 != front,不能判断队列是满的,所以需要(tail+1) % capacity ==front,判断队列为满。
代码实现:
package cn.itcats.queue;
/**
* 循环队列 基于数组
* @param <E>
*/
public class LoopQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private E[] data;
private int front , tail;
private int size;
public LoopQueue(int capacity){
//因为循环队列我们有意识的浪费一个空间,所以长度+1
data = (E[]) new Object[capacity + 1];
front = 0;
tail = 0;
size = 0;
}
public LoopQueue(){
this(10);
}
//入队操作
@Override
public void enqueue(E e) {
//入队之前判断队列是否为满
if(front == (tail+1) % data.length){
//队列满了,扩容
resize(getCapacity() * 2);
}
data[tail] = e;
tail = (tail + 1) % data.length;
size++;
}
//出队操作
@Override
public E dequeue() {
//队列为空
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("队列为空,无法出队");
//队列不为空,出队元素
E e = data[front];
//出队后把元素置空
data[front] = null;
front = (front + 1) % data.length;
size -- ;
//若出队到一定数量时,动态缩小容量
if(size == getCapacity() / 4 && getCapacity() / 2 != 0 ){
resize(getCapacity() / 2);
}
return e;
}
//扩容过程
private void resize(int newCapacity){
//构建一个新的数组 长度为原来可用空间的两倍
E[] newData = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity + 1];
//迁移数组
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++){
//把原来front位置的元素依次迁移到新数组0开始的位置,存在偏移量front
newData[i] = data[(i+front) % data.length];
}
//改变引用
data = newData;
//front和tail归位
front = 0 ;
tail = size;
}
//查看队首元素,但不出队
@Override
public E getFront() {
//队列为空
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("队列为空,无法查看队首元素");
return data[front];
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == tail;
}
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length - 1;
}
//打印数组中的元素
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("LoopQueue: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, getCapacity()));
//显示[1,2,3,4,5]
sb.append("front [");
for (int i = front; i != tail; i = (i+1) % data.length) {
sb.append(data[i]);
//如果当前索引不是最后一个元素
if ( (i+1) % data.length != tail) {
sb.append(", ");
}
}
sb.append("] tail");
return sb.toString();
}
//测试方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
LoopQueue<Integer> queue = new LoopQueue<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ;i ++){
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println("i:"+i +" "+queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println("i:"+i +" "+queue);
}
}
}
}
数组队列与循环队列的比较
1、循环队列相比数组队列底层都是基于数组,但循环队列编码更复杂一些,它引入了front和tail指针。
2、数组队列出队时间复杂度为O(n),而循环队列出队时间复杂度为O(1)。【均摊复杂度】,因为可能触发缩容操作。
为此,我们可以对二者进行性能测试。
package cn.itcats.queue;
import java.util.Random;
public class SpeedTest {
//模拟执行count次入队和出队所需时间,单位: s 秒
public static double speedTest(Queue<Integer> queue, int count){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random();
for(int i = 0 ; i < count ; i++)
queue.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
for(int i = 0 ; i < count ; i++)
queue.dequeue();
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) /1000000000.0 ;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//进行入队和出队的次数
int count = 2000000;
//使用数组队列ArrayQueue
Queue arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue();
System.out.println("ArrayQueue数组队列执行的时间: "+speedTest(arrayQueue,count)+" s");
//使用循环队列LoopQueue
Queue loopQueue = new LoopQueue();
System.out.println("LoopQueue循环队列执行的时间: " + speedTest(loopQueue,count)+" s");
}
}
发现loopQueue要比arrayQueue快上百倍。
基于链表实现队列
因为我设计的链表为单向链表,若在tail删除元素不容易获得tail的前一个元素,故在head端进行删除操作
package cn.itcats.queue;
import cn.itcats.linkedlist.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListQueue<E> implements Queue<E>{
//创建内部类Node
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e ,Node next){
this.e = e ;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e,null);
}
public Node(){
this(null,null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node head,tail;
private int size;
public LinkedListQueue(){
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e) {
if(tail == null){
tail = new Node(e);
head = tail;
}else{
tail.next = new Node(e);
tail = tail.next;
}
size++;
}
@Override
public E dequeue() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("队列为空");
}
Node retNode = head;
head = head.next;
retNode.next = null;
if(head == null){
tail = null;
}
size -- ;
return retNode.e;
}
@Override
public E getFront() {
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("队列为空");
return head.e;
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Queue: front ");
for(Node cur = head; cur != null ; cur = cur.next)
sb.append(cur+" -->");
sb.append("NULL tail");
return sb.toString();
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkedListQueue<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ;i ++){
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
}