版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/J080624/article/details/82725122
Java 5.0 在java.util.concurrent 提供了一个新的创建执行线程的方式:Callable 接口。
Callable 接口类似于Runnable,两者都是为那些其实例可能被另一个线程执行的类设计的。但是Runnable 不会返回结果,并且无法抛出经过检查的异常。
Callable接口示例如下:
public class TestCallable {
public static void main(String[] args){
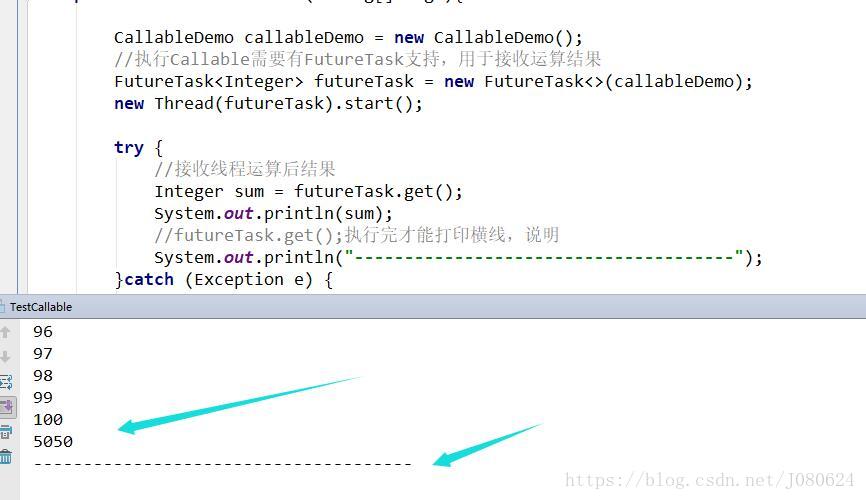
CallableDemo callableDemo = new CallableDemo();
//执行Callable需要有FutureTask支持,用于接收运算结果
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(callableDemo);
new Thread(futureTask).start();
try {
//接收线程运算后结果
Integer sum = futureTask.get();
System.out.println(sum);
//futureTask.get();执行完才能打印横线,说明
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class CallableDemo implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int sum=0;
for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){
System.out.println(i);
sum+=i;
}
return sum;
}
}
Callable 需要依赖FutureTask ,FutureTask 也可以用作闭锁。
如下图所示,只有获取到结果后才会打印横线:
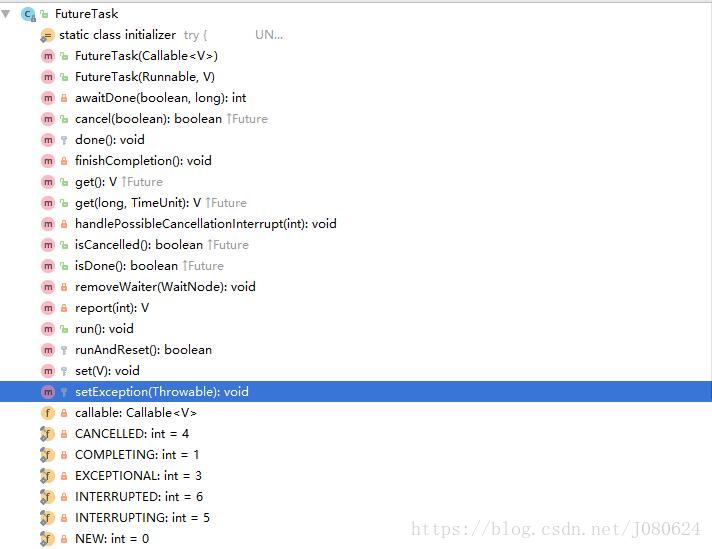
FutureTask拥有方法如下:
其实现了RunnableFuture接口:
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {
//...
}其中RunnableFuture接口又继承自Runnable和Future接口:
/**
* A {@link Future} that is {@link Runnable}. Successful execution of
* the {@code run} method causes completion of the {@code Future}
* and allows access to its results.
* @see FutureTask
* @see Executor
* @since 1.6
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> The result type returned by this Future's {@code get} method
*/
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {
/**
* Sets this Future to the result of its computation
* unless it has been cancelled.
*/
void run();
}
Future是什么,有什么用?
查看其javadoc如下:
/**
* A {@code Future} represents the result of an asynchronous
* computation. Methods are provided to check if the computation is
* complete, to wait for its completion, and to retrieve the result of
* the computation. The result can only be retrieved using method
* {@code get} when the computation has completed, blocking if
* necessary until it is ready. Cancellation is performed by the
* {@code cancel} method. Additional methods are provided to
* determine if the task completed normally or was cancelled. Once a
* computation has completed, the computation cannot be cancelled.
* If you would like to use a {@code Future} for the sake
* of cancellability but not provide a usable result, you can
* declare types of the form {@code Future<?>} and
* return {@code null} as a result of the underlying task.参考博文: