桶排序介绍
桶排序(Bucket Sort)的原理很简单,它是将数组分到有限数量的桶子里。
假设待排序的数组a中共有N个整数,并且已知数组a中数据的范围[0, MAX)。在桶排序时,创建容量为MAX的桶数组r,并将桶数组元素都初始化为0;将容量为MAX的桶数组中的每一个单元都看作一个"桶"。
在排序时,逐个遍历数组a,将数组a的值,作为"桶数组r"的下标。当a中数据被读取时,就将桶的值加1。例如,读取到数组a[3]=5,则将r[5]的值+1。
桶排序图文说明
bucketSort(a, n, max)是作用是对数组a进行桶排序,n是数组a的长度,max是数组中最大元素所属的范围[0,max)。
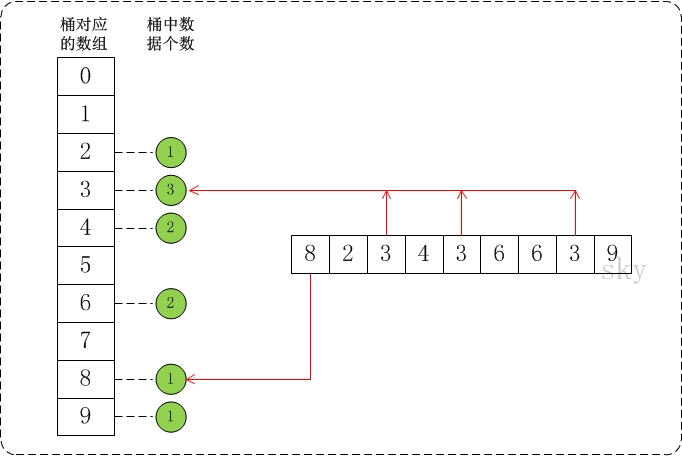
假设a={8,2,3,4,3,6,6,3,9}, max=10。此时,将数组a的所有数据都放到需要为0-9的桶中。如下图:
在将数据放到桶中之后,再通过一定的算法,将桶中的数据提出出来并转换成有序数组。就得到我们想要的结果了。
桶排序实现
/**
* 桶排序:Java
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2014/03/13
*/
public class BucketSort {
/*
* 桶排序
*
* 参数说明:
* a -- 待排序数组
* max -- 数组a中最大值的范围
*/
public static void bucketSort(int[] a, int max) {
int[] buckets;
if (a==null || max<1)
return ;
// 创建一个容量为max的数组buckets,并且将buckets中的所有数据都初始化为0。
buckets = new int[max];
// 1. 计数
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
buckets[a[i]]++;
// 2. 排序
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < max; i++) {
while( (buckets[i]--) >0 ) {
a[j++] = i;
}
}
buckets = null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
int a[] = {8,2,3,4,3,6,6,3,9};
System.out.printf("before sort:");
for (i=0; i<a.length; i++)
System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]);
System.out.printf("\n");
bucketSort(a, 10); // 桶排序
System.out.printf("after sort:");
for (i=0; i<a.length; i++)
System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]);
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}before sort:8 2 3 4 3 6 6 3 9 after sort:2 3 3 3 4 6 6 8 9