this 关键字
成员变量与局部变量同名
class Person {
private int age = 10;
public Person(){
System.out.println("初始化年龄:"+age);
}
public int GetAge(int age){
this.age = age;
return this.age;
}
}
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person Harry = new Person();
System.out.println("Harry's age is "+Harry.GetAge(12));
}
}
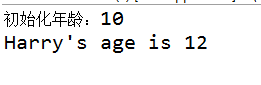
可以看到,这里age是GetAge成员方法的形参,this.age是Person类的成员变量。
调用构造方法
public class Student1 {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student1() {
// this()在构造方法中调用本类的其他构造方法
// this()在构造方法第一行
this("张三");
age = 18;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Student1(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student1 s2 = new Student1();
System.out.println(s2.getName()+"..."+s2.getAge());
}
}

this(参数):调用本类中另一种形式的构造函数(应该为构造函数中的第一条语句)。
super
子父类中构造方法的默认调用隐式语句:super();
调用父类中的有参数构造方法:super(实参列表);
子类会继承父类中的内容,所以子类在初始化时,必须先到父类中去执行父类的初始化动作。
当父类中没有空参数构造方法时,子类的构造方法必须有显示的super语句,指定要访问的父类有参数构造方法。
public class Person {
public Person(String name,int age){
System.out.println("父类");
}
}
public class Student extends Person{
String name;
int age;
public Student() {
this("lili",12);
System.out.println("子类");
}
public Student(String name,int age){
super(name, age);
}
}
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
}
}

super()和this()均需放在构造方法内第一行。this和super不能同时出现在一个构造函数里面,只能this间接调用。
final
final修饰的类不能被继承,但可以继承其他类
public final class Fu extends Object{
}

final修饰的成员方法不能重写,但是不修饰的重写的可以加final修饰
public class Fu2 {
public final void xiuche() {
System.out.println("试穿的修车手艺");
}
public void sale() {
System.out.println("祖传买车方法");
}
}

被final修饰的成员变量没有系统默认初始值,需要在创建对象前赋值

被final修饰的局部变量是常量,不能改变,如果是引用数据类型,可以对其属性进行修改。
static
被static修饰的成员变量属于类,不属于这个类的某个对象
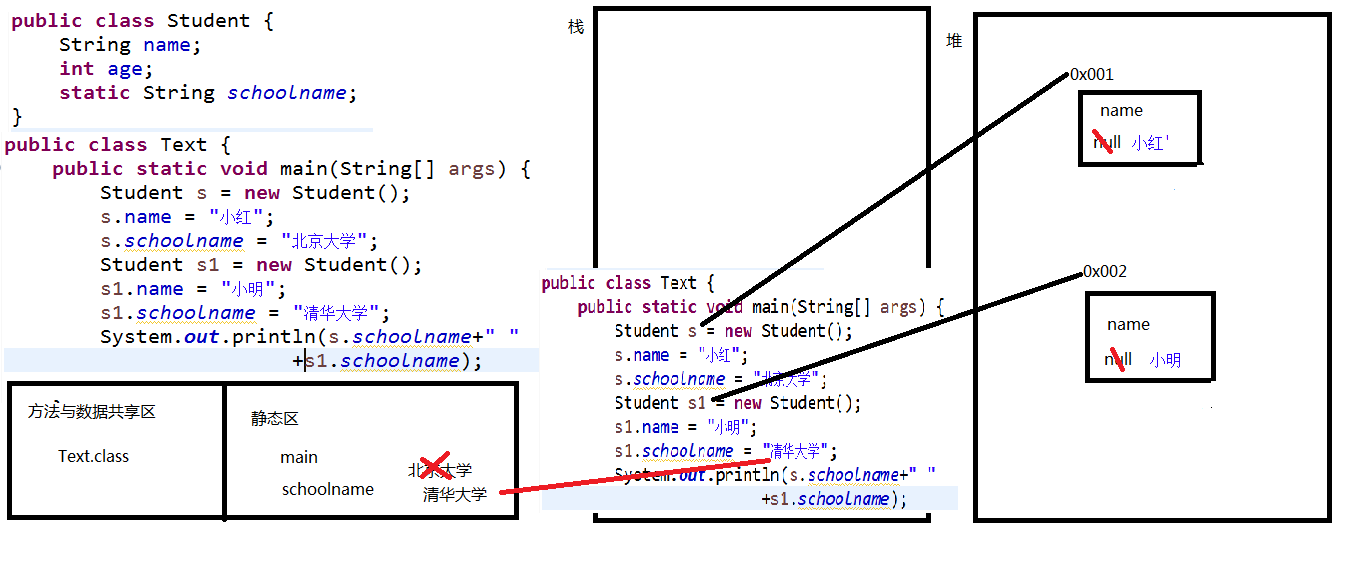
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
static String schoolname;
}
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.name = "小红";
s.schoolname = "北京大学";
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.name = "小明";
s1.schoolname = "清华大学";
System.out.println(s.schoolname+" "+s1.schoolname);
}
}

静态成员只能调用静态成员,不能调用非静态成员,非静态成员可以调用静态成员
package com.oracle.demo05;
public class ceshi {
static int a = 1;
int b = 2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//静态成员可以调用静态成员方法
eat();
//静态成员不可以调用非静态成员方法
//study();
/*Cannot make a static reference to
the non-static method study() from the
type ceshi*/
//静态成员方法可以调用静态成员变量
System.out.println(a);
//静态成员方法不可以调用非静态成员变量
//System.out.println(b);
}
public static void eat(){
}
public void study(){
//非静态成员方法可以调用静态成员方法
eat();
//非静态成员方法可以调用静态成员变量
System.out.println(a);
}
}
不能使用this/super【this、super属于对象,而静态属于类】
图解