版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请告知一声 https://blog.csdn.net/zmdsjtu/article/details/53454071
//女票被学妹约出去看电影了,所以有点无聊的我来写博客了。主要在官网给的Demo基础之上用Opencv把特征点描绘出来了。
很早之前写过一篇配置Dlib环境的博客,现在来稍微梳理下提取特征点的使用方法。
上一篇配置环境博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zmdsjtu/article/details/52422847
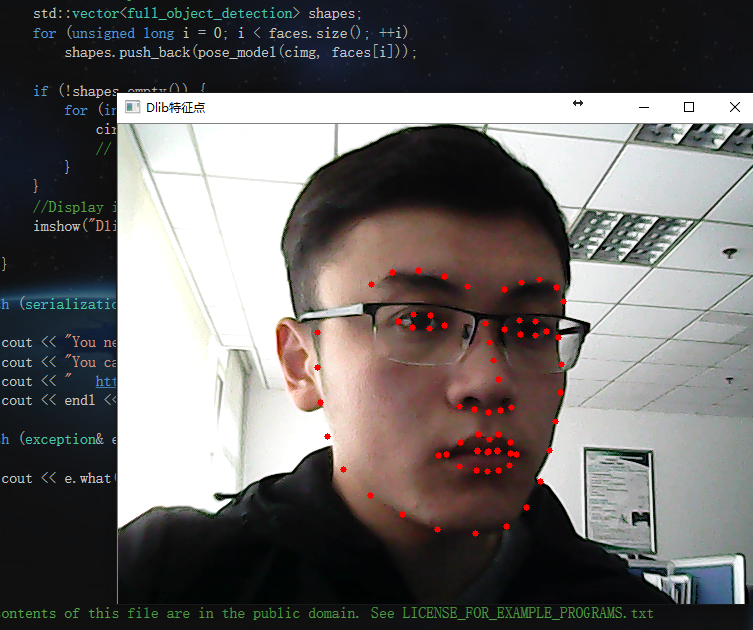
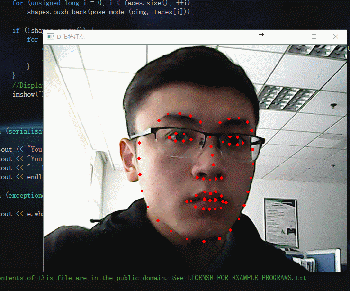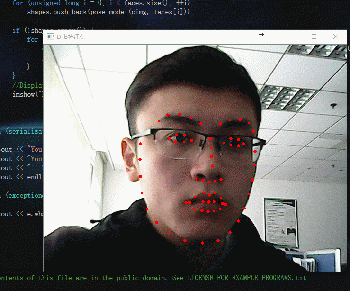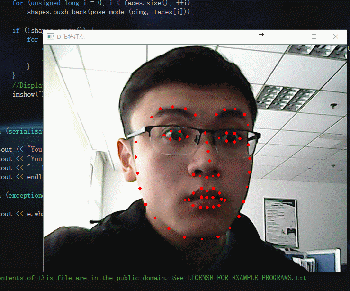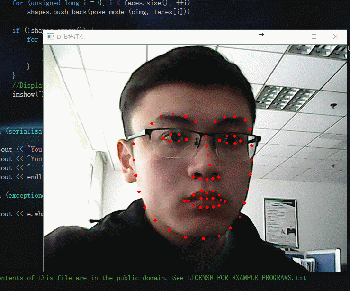
惯例先放效果图吧:
动图如下:
接着就是简单粗暴的代码:
//@[email protected]
//2016-12-4
//http://blog.csdn.net/zmdsjtu/article/details/53454071
#include <dlib/opencv.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <dlib/image_processing/frontal_face_detector.h>
#include <dlib/image_processing/render_face_detections.h>
#include <dlib/image_processing.h>
#include <dlib/gui_widgets.h>
using namespace dlib;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
try
{
cv::VideoCapture cap(0);
if (!cap.isOpened())
{
cerr << "Unable to connect to camera" << endl;
return 1;
}
//image_window win;
// Load face detection and pose estimation models.
frontal_face_detector detector = get_frontal_face_detector();
shape_predictor pose_model;
deserialize("shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat") >> pose_model;
// Grab and process frames until the main window is closed by the user.
while (cv::waitKey(30) != 27)
{
// Grab a frame
cv::Mat temp;
cap >> temp;
cv_image<bgr_pixel> cimg(temp);
// Detect faces
std::vector<rectangle> faces = detector(cimg);
// Find the pose of each face.
std::vector<full_object_detection> shapes;
for (unsigned long i = 0; i < faces.size(); ++i)
shapes.push_back(pose_model(cimg, faces[i]));
if (!shapes.empty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < 68; i++) {
circle(temp, cvPoint(shapes[0].part(i).x(), shapes[0].part(i).y()), 3, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), -1);
// shapes[0].part(i).x();//68个
}
}
//Display it all on the screen
imshow("Dlib特征点", temp);
}
}
catch (serialization_error& e)
{
cout << "You need dlib's default face landmarking model file to run this example." << endl;
cout << "You can get it from the following URL: " << endl;
cout << " http://dlib.net/files/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2" << endl;
cout << endl << e.what() << endl;
}
catch (exception& e)
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
}来看下上面那段代码,所有的需要的特征点都存储在Shapes里。仔细看看下面这行代码:
circle(temp, cvPoint(shapes[0].part(i).x(), shapes[0].part(i).y()), 3, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), -1);
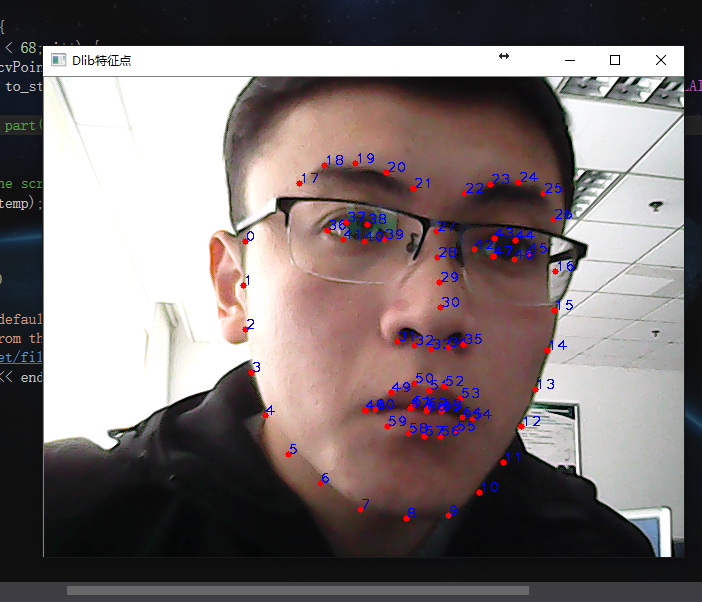
每个特征点的编号如下:
在上述画图的基础上加了如下一行代码:
putText(temp, to_string(i), cvPoint(shapes[0].part(i).x(), shapes[0].part(i).y()), CV_FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0),1,4);
对照着上图,比如说想获取鼻尖的坐标,那么横坐标就是shapes[0].part[30].x(),其余的类似。
在这个的基础上就可以做很多有意思的事情啦,2333
最后祝大家开发愉快:)
//顺便祝女票大人和学妹看电影愉快(摊手)