引言
spring做为java程序员必学的框架,从学校的课堂上,到实际工作中,都可以看到它的身影。之前看过一篇文章,说对于spring的源码只需要了解架构,不需要关注具体的实现,不敢苟同。如果对于java程序员最重要的框架都不关注具体实现,那么还有什么代码值得去关注呢?有人说spring让java程序员丧失了程序设计的能力,只需要关注service,dao这些东西,那么它给我们提供这些便利的背后到底做了什么工作,如果能窥之一二,想想还有点小兴奋呢。为了突出主题,就不介绍spring那些相关的概念了,看到spring,就提概念,真的很烦。QAQ
整体介绍
spring的IOC容器可以简单的看做一个map,当然实际要复杂的多。看做map有助于帮助我们理解spring的相关接口定义,spring中最重要的一个接口BeanFactory,BeanFactory定义了spring容器最基本也是最重要的能力。这么重要当然的分析一下。
顺便说一下,这里spring的版本是4.3.15.RELEASE,最新的spring版本已经到5.+了,但是重要的部分变化不大。
public interface BeanFactory {
/**
* Used to dereference a {@link FactoryBean} instance and distinguish it from
* beans <i>created</i> by the FactoryBean. For example, if the bean named
* {@code myJndiObject} is a FactoryBean, getting {@code &myJndiObject}
* will return the factory, not the instance returned by the factory.
*
* 如果通过通过名称去获取bean,如果名称以开头&将获取到FactoryBean本身而不是FactoryBean生产出的bean
* 顺便提一句,FactoryBean是spring的一个接口,可以通过实现FactoryBean来注册实例
*/
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* <p>This method allows a Spring BeanFactory to be used as a replacement for the
* Singleton or Prototype design pattern. Callers may retain references to
* returned objects in the case of Singleton beans.
* <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name.
* Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean definition
* with the specified name
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be obtained
*
*/
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* <p>Behaves the same as {@link #getBean(String)}, but provides a measure of type
* safety by throwing a BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException if the bean is not of the
* required type. This means that ClassCastException can't be thrown on casting
* the result correctly, as can happen with {@link #getBean(String)}.
* <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name.
* Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
* @param requiredType type the bean must match. Can be an interface or superclass
* of the actual class, or {@code null} for any match. For example, if the value
* is {@code Object.class}, this method will succeed whatever the class of the
* returned instance.
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no such bean definition
* @throws BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException if the bean is not of the required type
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
*/
<T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* <p>Allows for specifying explicit constructor arguments / factory method arguments,
* overriding the specified default arguments (if any) in the bean definition.
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
* @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments
* (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no such bean definition
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if arguments have been given but
* the affected bean isn't a prototype
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
* @since 2.5
*/
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
/**
* Return the bean instance that uniquely matches the given object type, if any.
* <p>This method goes into {@link ListableBeanFactory} by-type lookup territory
* but may also be translated into a conventional by-name lookup based on the name
* of the given type. For more extensive retrieval operations across sets of beans,
* use {@link ListableBeanFactory} and/or {@link BeanFactoryUtils}.
* @param requiredType type the bean must match; can be an interface or superclass.
* {@code null} is disallowed.
* @return an instance of the single bean matching the required type
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if no bean of the given type was found
* @throws NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException if more than one bean of the given type was found
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
* @since 3.0
* @see ListableBeanFactory
*/
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* <p>Allows for specifying explicit constructor arguments / factory method arguments,
* overriding the specified default arguments (if any) in the bean definition.
* <p>This method goes into {@link ListableBeanFactory} by-type lookup territory
* but may also be translated into a conventional by-name lookup based on the name
* of the given type. For more extensive retrieval operations across sets of beans,
* use {@link ListableBeanFactory} and/or {@link BeanFactoryUtils}.
* @param requiredType type the bean must match; can be an interface or superclass.
* {@code null} is disallowed.
* @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments
* (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no such bean definition
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if arguments have been given but
* the affected bean isn't a prototype
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
* @since 4.1
*/
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
/**
* Does this bean factory contain a bean definition or externally registered singleton
* instance with the given name?
* <p>If the given name is an alias, it will be translated back to the corresponding
* canonical bean name.
* <p>If this factory is hierarchical, will ask any parent factory if the bean cannot
* be found in this factory instance.
* <p>If a bean definition or singleton instance matching the given name is found,
* this method will return {@code true} whether the named bean definition is concrete
* or abstract, lazy or eager, in scope or not. Therefore, note that a {@code true}
* return value from this method does not necessarily indicate that {@link #getBean}
* will be able to obtain an instance for the same name.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @return whether a bean with the given name is present
*/
boolean containsBean(String name);
/**
* Is this bean a shared singleton? That is, will {@link #getBean} always
* return the same instance?
* <p>Note: This method returning {@code false} does not clearly indicate
* independent instances. It indicates non-singleton instances, which may correspond
* to a scoped bean as well. Use the {@link #isPrototype} operation to explicitly
* check for independent instances.
* <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name.
* Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @return whether this bean corresponds to a singleton instance
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* @see #getBean
* @see #isPrototype
*/
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Is this bean a prototype? That is, will {@link #getBean} always return
* independent instances?
* <p>Note: This method returning {@code false} does not clearly indicate
* a singleton object. It indicates non-independent instances, which may correspond
* to a scoped bean as well. Use the {@link #isSingleton} operation to explicitly
* check for a shared singleton instance.
* <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name.
* Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @return whether this bean will always deliver independent instances
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* @since 2.0.3
* @see #getBean
* @see #isSingleton
*/
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Check whether the bean with the given name matches the specified type.
* More specifically, check whether a {@link #getBean} call for the given name
* would return an object that is assignable to the specified target type.
* <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name.
* Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @param typeToMatch the type to match against (as a {@code ResolvableType})
* @return {@code true} if the bean type matches,
* {@code false} if it doesn't match or cannot be determined yet
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* @since 4.2
* @see #getBean
* @see #getType
*/
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Check whether the bean with the given name matches the specified type.
* More specifically, check whether a {@link #getBean} call for the given name
* would return an object that is assignable to the specified target type.
* <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name.
* Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @param typeToMatch the type to match against (as a {@code Class})
* @return {@code true} if the bean type matches,
* {@code false} if it doesn't match or cannot be determined yet
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* @since 2.0.1
* @see #getBean
* @see #getType
*/
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Determine the type of the bean with the given name. More specifically,
* determine the type of object that {@link #getBean} would return for the given name.
* <p>For a {@link FactoryBean}, return the type of object that the FactoryBean creates,
* as exposed by {@link FactoryBean#getObjectType()}.
* <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name.
* Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @return the type of the bean, or {@code null} if not determinable
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* @since 1.1.2
* @see #getBean
* @see #isTypeMatch
*/
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Return the aliases for the given bean name, if any.
* All of those aliases point to the same bean when used in a {@link #getBean} call.
* <p>If the given name is an alias, the corresponding original bean name
* and other aliases (if any) will be returned, with the original bean name
* being the first element in the array.
* <p>Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the bean name to check for aliases
* @return the aliases, or an empty array if none
* @see #getBean
*/
String[] getAliases(String name);我也不想贴代码的QAQ,但这个接口很是重要,以后都要围绕它展开。如果要你给这个接口添加个实现类,是不是马上想到一个或者几个map就能搞定了?所以再有人问你能不能自己实现个spring,坚定告诉他可以!
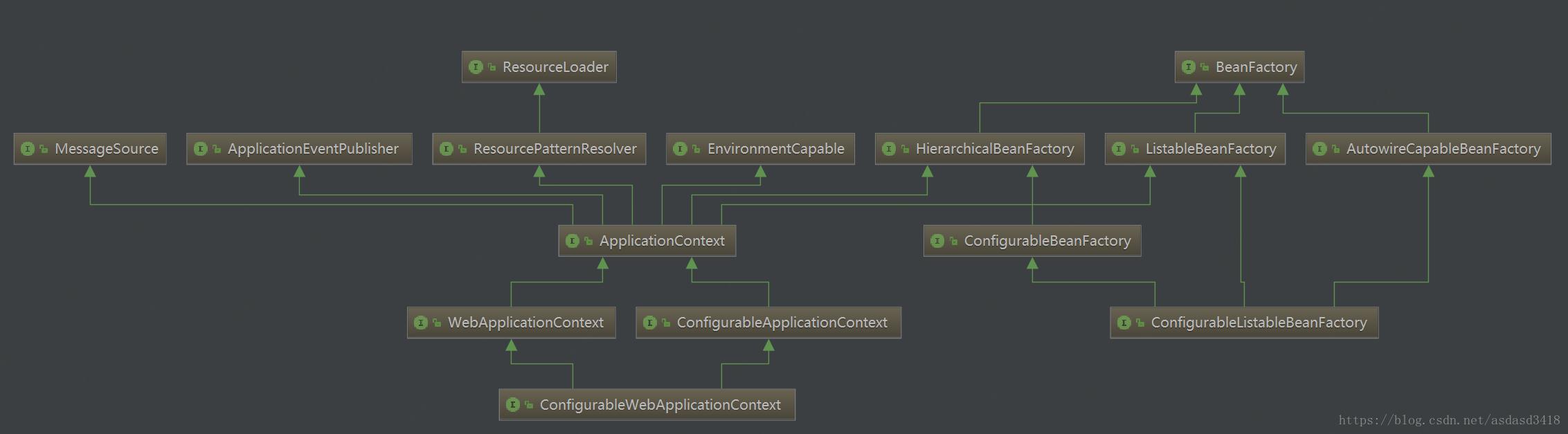
有了源头BeanFactory,很自然的出现了很多“目的地”,可以看出,BeanFactory大致“流”向了两个方向。一个是Factory方向,一个ApplicationContext方向。Factory方向关注的更多的是bean创建的加强,而applicationContext方向更多的关注的是一些额外的“装饰”,比如国际化MessageSource,事件的分发ApplicationEventPublisher。就像程序员常常需要面对的一个问题:“往深度发展还是往广度发展?”。程序是人写出来的,肯定处处包含人类社会发展的规律,扯远了……
下面先看下spring是如何对BeanFactory进行增强的:
- HierarchicalBeanFactory
public interface HierarchicalBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
/**
* Return the parent bean factory, or {@code null} if there is none.
*
* 获取父容器
*/
BeanFactory getParentBeanFactory();
/**
* 当前容器是否包含某个实例
*/
boolean containsLocalBean(String name);
}- ListableBeanFactory
public interface ListableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
/**
* 是否包含bean的BeanDefinition
*/
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
/**
* 获取bean的BeanDefinition的数量
*/
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
/**
* 获取BeanDefinition的names
*/
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
/**
* 获取指定类型的bean的名称
*/
String[] getBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type);
/**
* 获取指定类型bean的名称
*/
String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type);
/**
* 获取指定类型bean的名称
*/
String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit);
/**
* 获取指定类型的bean的实例
*/
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type) throws BeansException;
/**
* 获取指定类型的bean的实例
*/
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit)
throws BeansException;
/**
* 获取类上含有指定注解类型的类名称
*/
String[] getBeanNamesForAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType);
/**
* 获取类上含有指定注解类型的实例
*/
Map<String, Object> getBeansWithAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType) throws BeansException;
/**
* 获取指定名称类上的注解实例
*/
<A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean(String beanName, Class<A> annotationType)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;可以看出ListableBeanFactory是相当重要的一个接口,赋予了beanFactory将解析的Bean的信息存储及获取的能力。
- AutowireCapableBeanFactory
public interface AutowireCapableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
/**
* 默认值 不进行自动注入
*/
int AUTOWIRE_NO = 0;
/**
* 根据名字自动注入
*/
int AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME = 1;
/**
* 根据类型自动注入
*/
int AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE = 2;
/**
* 构造器注入
*/
int AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR = 3;
@Deprecated
int AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT = 4;
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Typical methods for creating and populating external bean instances
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 根据类型创建bean
*/
<T> T createBean(Class<T> beanClass) throws BeansException;
/**
* 触发指定的bean的依赖注入
*/
void autowireBean(Object existingBean) throws BeansException;
/**
* 配置指定的bean,包括自动注入属性,设置属性的值,调用beanFactory的回调,例如 setBeanFactory,
* 执行相关后置处理器
*/
Object configureBean(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Specialized methods for fine-grained control over the bean lifecycle
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 创建bean的实例
*/
Object createBean(Class<?> beanClass, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck) throws BeansException;
/**
* 创建指定类型的bean实例,并进行依赖注入
*/
Object autowire(Class<?> beanClass, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck) throws BeansException;
/**
* 设置指定bean实例的属性
*/
void autowireBeanProperties(Object existingBean, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck)
throws BeansException;
/**
* 设置指定bean实例的属性,并不触发依赖注入
*/
void applyBeanPropertyValues(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* 初始化指定bean实例,包括调用beanFactory相关回调,处理后置处理器等。
*/
Object initializeBean(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* 在bean实例化之前触发指定bean实例的处理器
*/
Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException;
/**
* 在bean实例化之后触发指定bean实例的处理器
*/
Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException;
/**
* 销毁指定bean实例
*/
void destroyBean(Object existingBean);
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Delegate methods for resolving injection points
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 根据类型解析成为相应的NamedBeanHolder
*/
<T> NamedBeanHolder<T> resolveNamedBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
/**
* 根据DependencyDescriptor 解析注入的类实例
*/
Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, String requestingBeanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* 根据DependencyDescriptor 解析注入的类实例
*/
Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, String requestingBeanName,
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException;AutowireCapableBeanFactory赋予了BeanFactory依赖注入的能力。
- ConfigurableBeanFactory
public interface ConfigurableBeanFactory extends HierarchicalBeanFactory, SingletonBeanRegistry {
/**
* 单例标志
*/
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = "singleton";
/**
* 原型标志
*/
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = "prototype";
/**
* 设置父BeanFactory
*/
void setParentBeanFactory(BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 设置ClassLoader
*/
void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader);
/**
* 获取ClassLoader
*/
ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader();
/**
* 设置临时的ClassLoader用作类型匹配
*/
void setTempClassLoader(ClassLoader tempClassLoader);
/**
* 获取临时的ClassLoader
*/
ClassLoader getTempClassLoader();
/**
* 设置是否缓存Bean的元数据
*/
void setCacheBeanMetadata(boolean cacheBeanMetadata);
/**
* 获取是否缓存Bean的元数据
*/
boolean isCacheBeanMetadata();
/**
*
* 指定bean表达式解析器,默认没有,ApplicationContext会默认指定一个标准的策略,支持el表达式
*/
void setBeanExpressionResolver(BeanExpressionResolver resolver);
/**
* 获取bean表达式解析器
*/
BeanExpressionResolver getBeanExpressionResolver();
/**
* 指定bean属性的转化service
*/
void setConversionService(ConversionService conversionService);
/**
* 获取bean属性转化service
*/
ConversionService getConversionService();
void addPropertyEditorRegistrar(PropertyEditorRegistrar registrar);
/**
* 注册属性Editor
*/
void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, Class<? extends PropertyEditor> propertyEditorClass);
/**
* Initialize the given PropertyEditorRegistry with the custom editors
* that have been registered with this BeanFactory.
* @param registry the PropertyEditorRegistry to initialize
*/
void copyRegisteredEditorsTo(PropertyEditorRegistry registry);
/**
* 设置类型转换器
*/
void setTypeConverter(TypeConverter typeConverter);
/**
* 获取类型转换器
*/
TypeConverter getTypeConverter();
/**
* Add a String resolver for embedded values such as annotation attributes.
* @param valueResolver the String resolver to apply to embedded values
* @since 3.0
*/
void addEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver valueResolver);
/**
* Determine whether an embedded value resolver has been registered with this
* bean factory, to be applied through {@link #resolveEmbeddedValue(String)}.
* @since 4.3
*/
boolean hasEmbeddedValueResolver();
/**
* Resolve the given embedded value, e.g. an annotation attribute.
* @param value the value to resolve
* @return the resolved value (may be the original value as-is)
* @since 3.0
*/
String resolveEmbeddedValue(String value);
/**
* 添加bean后置处理器
*/
void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor);
/**
* 获取bean后置处理器的数量
*/
int getBeanPostProcessorCount();
/**
* Register the given scope, backed by the given Scope implementation.
*/
void registerScope(String scopeName, Scope scope);
/**
* Return the names of all currently registered scopes.
* <p>This will only return the names of explicitly registered scopes.
* Built-in scopes such as "singleton" and "prototype" won't be exposed.
*/
String[] getRegisteredScopeNames();
/**
* Return the Scope implementation for the given scope name, if any.
* <p>This will only return explicitly registered scopes.
* Built-in scopes such as "singleton" and "prototype" won't be exposed.
*/
Scope getRegisteredScope(String scopeName);
/**
* Provides a security access control context relevant to this factory.
*/
AccessControlContext getAccessControlContext();
/**
* 从其他beanFactory复制配置值
*/
void copyConfigurationFrom(ConfigurableBeanFactory otherFactory);
/**
* 配置别名
*/
void registerAlias(String beanName, String alias) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
/**
* 解析别名
*/
void resolveAliases(StringValueResolver valueResolver);
/**
* Return a merged BeanDefinition for the given bean name,
* merging a child bean definition with its parent if necessary.
* Considers bean definitions in ancestor factories as well.
*/
BeanDefinition getMergedBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Determine whether the bean with the given name is a FactoryBean.
*/
boolean isFactoryBean(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* 设置指定名称的bean是否是正在创建的状态
*/
void setCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName, boolean inCreation);
/**
* Determine whether the specified bean is currently in creation.
*/
boolean isCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName);
/**
* 设置指定的bean依赖的bean的名称
*
*/
void registerDependentBean(String beanName, String dependentBeanName);
/**
* Return the names of all beans which depend on the specified bean, if any.
*/
String[] getDependentBeans(String beanName);
/**
* Return the names of all beans that the specified bean depends on, if any.
*/
String[] getDependenciesForBean(String beanName);
/**
* Destroy the given bean instance (usually a prototype instance
* obtained from this factory) according to its bean definition.
* <p>Any exception that arises during destruction should be caught
* and logged instead of propagated to the caller of this method.
*/
void destroyBean(String beanName, Object beanInstance);
/**
* Destroy the specified scoped bean in the current target scope, if any.
* <p>Any exception that arises during destruction should be caught
* and logged instead of propagated to the caller of this method.
*/
void destroyScopedBean(String beanName);
/**
* Destroy all singleton beans in this factory, including inner beans that have
* been registered as disposable. To be called on shutdown of a factory.
* <p>Any exception that arises during destruction should be caught
* and logged instead of propagated to the caller of this method.
*/
void destroySingletons();
}ConfigurableBeanFactory定义了BeanFactory的各种配置项。
- ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
public interface ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
extends ListableBeanFactory, AutowireCapableBeanFactory, ConfigurableBeanFactory {
/**
* 需要忽略依赖注入的类型
*/
void ignoreDependencyType(Class<?> type);
/**
* 需要忽略依赖注入的接口
*/
void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc);
/**
* Register a special dependency type with corresponding autowired value.
* <p>This is intended for factory/context references that are supposed
* to be autowirable but are not defined as beans in the factory:
* e.g. a dependency of type ApplicationContext resolved to the
* ApplicationContext instance that the bean is living in.
* <p>Note: There are no such default types registered in a plain BeanFactory,
* not even for the BeanFactory interface itself.
*
* 将指定类型和指定类型的bean的实例化对象注册进beanFactory,为了需要依赖注入此bean但是beanFactory并没有此种
* 类型的情况下
*/
void registerResolvableDependency(Class<?> dependencyType, Object autowiredValue);
/**
* Determine whether the specified bean qualifies as an autowire candidate,
* to be injected into other beans which declare a dependency of matching type.
* <p>This method checks ancestor factories as well.
*/
boolean isAutowireCandidate(String beanName, DependencyDescriptor descriptor)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* 获取值定名称的BeanDefinition
*/
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
Iterator<String> getBeanNamesIterator();
void clearMetadataCache();
/**
* 冻结所有的beanDefifition
*/
void freezeConfiguration();
/**
* Return whether this factory's bean definitions are frozen,
* i.e. are not supposed to be modified or post-processed any further.
*/
boolean isConfigurationFrozen();
/**
* 初始化所有的单例bean
*/
void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException;
}接下来我们再看下spring是如何对beanFactory进行”装饰”的:
- ResourceLoader
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
/**
* 获取指定路径的资源信息
*/
Resource getResource(String location);
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}- ResourcePatternResolver
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
/**
* 根据匹配表达式获取规则
*/
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}-EnvironmentCapable
public interface EnvironmentCapable {
/**
* 获取环境信息
*/
Environment getEnvironment();
}-MessageSource
public interface MessageSource {
/**
* 获取国际化消息
*/
String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, String defaultMessage, Locale locale);
/**
* 获取国际化消息
*/
String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException;
/**
* 获取国际化消息
*/
String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException;
}- ApplicationEventPublisher
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
/**
* 发布事件
*/
void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event);
void publishEvent(Object event);
}接下来就是重量级的接口ApplicationContext
-ApplicationContext
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
/**
* 容器标识
*/
String getId();
String getApplicationName();
String getDisplayName();
long getStartupDate();
/**
* 获取父类容器
*/
ApplicationContext getParent();
/**
* 获取BeanFactory,通过这个方法可以看出ApplicationContext的实现类不是通过继承BeanFatory来扩展功能的,
* 而是通过持有BeanFatory的实例来扩展功能的。
*/
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
- WebApplicationContext
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
/**
* Scope identifier for request scope: "request".
*/
String SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
/**
* Scope identifier for session scope: "session".
*/
String SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
/**
* Scope identifier for global session scope: "globalSession".
*/
String SCOPE_GLOBAL_SESSION = "globalSession";
/**
* Scope identifier for the global web application scope: "application".
*/
String SCOPE_APPLICATION = "application";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext environment bean in the factory.
*/
String SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME = "servletContext";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext/PortletContext init-params environment bean in the factory.
*/
String CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME = "contextParameters";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext/PortletContext attributes environment bean in the factory.
*/
String CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME = "contextAttributes";
/**
* 获取servlet上下文信息
*/
ServletContext getServletContext();
}
WebApplicationContext是对ApplicationContext的扩展
- ConfigurableApplicationContext
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable {
/**
* 路径分隔符
*/
String CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS = ",; \t\n";
/**
* 类型转换服务名字
*/
String CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME = "conversionService";
/**
* 默认代码织入名字
*/
String LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME = "loadTimeWeaver";
String ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = "environment";
String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME = "systemProperties";
String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
void setId(String id);
void setParent(ApplicationContext parent);
@Override
ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment();
void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);
/**
* 添加beanFactory后置处理器
*/
void addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor beanFactoryPostProcessor);
/**
* 添加容器的监听器
*/
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
/**
* 刷新容器
*/
void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
/**
* 注册jvm关闭时的钩子函数
*/
void registerShutdownHook();
/**
* 关闭容器
*/
@Override
void close();
/**
* 容器是否正在运行
*/
boolean isActive();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}- ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
public interface ConfigurableWebApplicationContext extends WebApplicationContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext {
String APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ":";
String SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME = "servletConfig";
void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext);
void setServletConfig(ServletConfig servletConfig);
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
/**
* 设置命名空间
*/
void setNamespace(String namespace);
String getNamespace();
/**
* 设置配置文件的路径
*/
void setConfigLocation(String configLocation);
void setConfigLocations(String... configLocations);
String[] getConfigLocations();
}通过分析接口我们大概可以看出整个spring容器的结构,接口中出现的类有些可能不认识,我们之后再一一分析。