转载地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/armlinux/archive/2012/02/29/2396756.html
这周抽空研究了一下SurfaceFlinger,发现真正复杂的并不是SurfaceFlinger本身,而是android的display显示系统,网上关于这部分的介绍有不少,本不打算写的,但是发现还是记录一下研究代码的过程比较好,一是能够帮助自己理清思路,另一个原因就是以后当这块内容忘记的时候,能快速的通过这个记录捡起来。
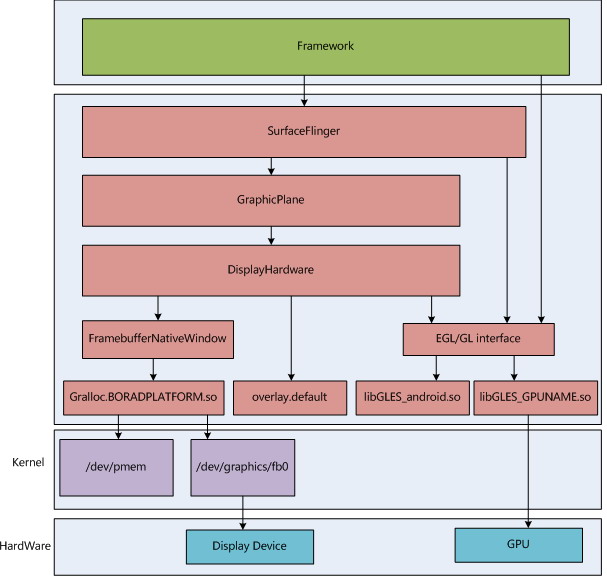
一. android显示系统的建立
SurfaceFlinger对于显示的管理是通过一个或多个GraphicPlane对象(目前android只实现了一个)来管理的,
@SurfaceFlinger.h
- GraphicPlane mGraphicPlanes[1];
- GraphicPlane mGraphicPlanes[1];
1. FrameBuffer的建立
framebuffer,确切的是说是linux下的framebuffer,,它是linux图形显示系统中一个与图形硬件无关的抽象层,user完全不用考虑我们的硬件设备,而仅仅使用framebuffer就可以实现对屏幕的操作。
android的framebuffer并没有被SurfaceFlinger直接使用,而是在framebuffer外做了一层包装,这个包装就是FramebufferNativeWindow,我们来看一下FramebufferNativeWindow的创建过程。
我们的framebuffer是由一个设备符fbDev来表示的,它是FramebufferNativeWindow的一个成员,我们来分析一下对fbDev的处理过程。
1.1. fbDev设备符
1.1.1 gralloc library
在这之前,先介绍一下gralloc library,它的形态如grallocBOARDPLATFORM.so, BOARDPLATFORM可以从属性ro.board.platform中获得,这篇文章中我们以Qualcommmsmx7x30为例,也就是gralloc.msm7x30.so中,它的源路径在hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k。
framebuffer的初始化需要通过HAL gralloc.msm7x30.so 来完成与底层硬件驱动的适配,但是gralloc library并不是平台无关的,不同的vendor可能会实现自己的gralloc library,因此为了保证在创建framebuffer时能够平台无关,android只能是动态的判断并使用当前的gralloc library,android通过从gralloc library中再抽象出一个hw_module_t结构来供使用,它为framebuffer的初始化提供了需要的gralloc.msm7x30.so业务。因此通过这个hw_module_t结构我们就不需要知道当前系统使用的到底是哪个gralloc library。按规定,所有gralloc library中的这个结构体被命名为HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM(HMI)。当前分析的系统中,HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM在hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k/galloc.cpp。
1.1.2 打开fbDev设备符
下面看如何打开 打开fbDev设备符。通过HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM提供的gralloc.msm7x30.so的接口我们调用到了fb_device_open()@hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8kframebuffer.cpp。
- int fb_device_open(hw_module_tconst* module, constchar* name,
- hw_device_t** device)
- {
- int status = -EINVAL;
- if (!strcmp(name, GRALLOC_HARDWARE_FB0)) {
- alloc_device_t* gralloc_device;
- status = gralloc_open(module, &gralloc_device);
- /* initialize our state here */
- fb_context_t *dev = (fb_context_t*)malloc(sizeof(*dev));
- memset(dev, 0, sizeof(*dev));
- /* initialize the procs */
- dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
- private_module_t* m = (private_module_t*)module;
- status = mapFrameBuffer(m);
- }
- int fb_device_open(hw_module_t const* module, const char* name,
- hw_device_t** device)
- {
- int status = -EINVAL;
- if (!strcmp(name, GRALLOC_HARDWARE_FB0)) {
- alloc_device_t* gralloc_device;
- status = gralloc_open(module, &gralloc_device);
- /* initialize our state here */
- fb_context_t *dev = (fb_context_t*)malloc(sizeof(*dev));
- memset(dev, 0, sizeof(*dev));
- /* initialize the procs */
- dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
- private_module_t* m = (private_module_t*)module;
- status = mapFrameBuffer(m);
- }
在这个函数中,主要为fbDev设备符指定一个fb_context_t实例,并通过函数mapFrameBuffer()对设备节点/dev/graphics/fb0进行操作,操作的目的有:
1.获得屏幕设备的信息,并将屏幕信息保存在HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM(上面代码中的module)中。
2. 向/dev/graphics/fb0请求page flip模式,page
flip模式需要至少2个屏幕大小的buffer,page flip模式在后面介绍。目前android系统中设置为2个屏幕大小的buffer。当然屏幕设备可能不支持page flip模式。
mapFrameBufferLocked()@hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k/framebuffer.cpp
- /*
- * Request NUM_BUFFERS screens (at lest 2 for page flipping)
- */
- info.yres_virtual = info.yres * NUM_BUFFERS;
- uint32_t flags = PAGE_FLIP;
- if (ioctl(fd, FBIOPUT_VSCREENINFO, &info) == -1) {
- info.yres_virtual = info.yres;
- flags &= ~PAGE_FLIP;
- LOGW("FBIOPUT_VSCREENINFO failed, page flipping not supported");
- }
- /*
- * Request NUM_BUFFERS screens (at lest 2 for page flipping)
- */
- info.yres_virtual = info.yres * NUM_BUFFERS;
- uint32_t flags = PAGE_FLIP;
- if (ioctl(fd, FBIOPUT_VSCREENINFO, &info) == -1) {
- info.yres_virtual = info.yres;
- flags &= ~PAGE_FLIP;
- LOGW("FBIOPUT_VSCREENINFO failed, page flipping not supported");
- }
3. 映射屏幕设备缓存区给fbDev设备符。
mapFrameBufferLocked()@hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k/framebuffer.cpp
- /*
- * map the framebuffer
- */
- int err;
- size_t fbSize = roundUpToPageSize(finfo.line_length * info.yres_virtual);
- module->framebuffer = new private_handle_t(dup(fd), fbSize,
- private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_USES_PMEM);
- module->numBuffers = info.yres_virtual / info.yres;
- module->bufferMask = 0;
- void* vaddr = mmap(0, fbSize, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
- if (vaddr == MAP_FAILED) {
- LOGE("Error mapping the framebuffer (%s)", strerror(errno));
- return -errno;
- }
- module->framebuffer->base = intptr_t(vaddr);
- memset(vaddr, 0, fbSize);
- /*
- * map the framebuffer
- */
- int err;
- size_t fbSize = roundUpToPageSize(finfo.line_length * info.yres_virtual);
- module->framebuffer = new private_handle_t(dup(fd), fbSize,
- private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_USES_PMEM);
- module->numBuffers = info.yres_virtual / info.yres;
- module->bufferMask = 0;
- void* vaddr = mmap(0, fbSize, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
- if (vaddr == MAP_FAILED) {
- LOGE("Error mapping the framebuffer (%s)", strerror(errno));
- return -errno;
- }
- module->framebuffer->base = intptr_t(vaddr);
- memset(vaddr, 0, fbSize);
1.2 grDev设备符
在为framebuffer,也就是FramebufferNativeWindow申请内存之前,我们还要介绍一个概念,就是grDev设备符。它虽然也叫设备符,但是它和具体的设备没有直接关系,我们看它的类型就是知道了alloc_device_t,没错,grDev设备符就是为了FramebufferNativeWindow管理内存使用的。为FramebufferNativeWindow提供了申请/释放内存的接口。
1.3 FramebufferNativeWindow内存管理
- sp<NativeBuffer> buffers[2];
- sp<NativeBuffer> buffers[2];
1.3.1 屏幕设备支持page filp模式
- // create a "fake" handles for it
- intptr_t vaddr = intptr_t(m->framebuffer->base);
- private_handle_t* hnd = new private_handle_t(dup(m->framebuffer->fd), size,
- private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_USES_PMEM |
- private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_FRAMEBUFFER);
- // find a free slot
- for (uint32_t i=0 ; i<numBuffers ; i++) {
- if ((bufferMask & (1LU<<i)) == 0) {
- m->bufferMask |= (1LU<<i);
- break;
- }
- vaddr += bufferSize;
- }
- hnd->base = vaddr;
- hnd->offset = vaddr - intptr_t(m->framebuffer->base);
- *pHandle = hnd;
- // create a "fake" handles for it
- intptr_t vaddr = intptr_t(m->framebuffer->base);
- private_handle_t* hnd = new private_handle_t(dup(m->framebuffer->fd), size,
- private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_USES_PMEM |
- private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_FRAMEBUFFER);
- // find a free slot
- for (uint32_t i=0 ; i<numBuffers ; i++) {
- if ((bufferMask & (1LU<<i)) == 0) {
- m->bufferMask |= (1LU<<i);
- break;
- }
- vaddr += bufferSize;
- }
- hnd->base = vaddr;
- hnd->offset = vaddr - intptr_t(m->framebuffer->base);
- *pHandle = hnd;
1.3.2 屏幕设备不支持page flip模式
gralloc_alloc_framebuffer_locked()@hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k/gpu.cpp
- const uint32_t bufferMask = m->bufferMask;
- const uint32_t numBuffers = m->numBuffers;
- const size_t bufferSize = m->finfo.line_length * m->info.yres;
- if (numBuffers == 1) {
- // If we have only one buffer, we never use page-flipping. Instead,
- // we return a regular buffer which will be memcpy'ed to the main
- // screen when post is called.
- int newUsage = (usage & ~GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_FB) | GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_2D;
- return gralloc_alloc_buffer(bufferSize, newUsage, pHandle);
- }
- const uint32_t bufferMask = m->bufferMask;
- const uint32_t numBuffers = m->numBuffers;
- const size_t bufferSize = m->finfo.line_length * m->info.yres;
- if (numBuffers == 1) {
- // If we have only one buffer, we never use page-flipping. Instead,
- // we return a regular buffer which will be memcpy'ed to the main
- // screen when post is called.
- int newUsage = (usage & ~GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_FB) | GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_2D;
- return gralloc_alloc_buffer(bufferSize, newUsage, pHandle);
- }
2. 打开Overlay
- if (hw_get_module(OVERLAY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module) == 0) {
- overlay_control_open(module, &mOverlayEngine);
- }
- if (hw_get_module(OVERLAY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module) == 0) {
- overlay_control_open(module, &mOverlayEngine);
- }
3. 选择OpenGL ES library(也即软/硬件加速)
- 0 0 android
- 0 1 adreno200
- 0 0 android
- 0 1 adreno200
- libGLESv1_CM_adreno200.so
- libGLESv2_adreno200.so
- libEGL_adreno200.so
- libGLESv1_CM_adreno200.so
- libGLESv2_adreno200.so
- libEGL_adreno200.so
3.1 OpenGL初始化
frameworks/base/opengl/libs/EGL/egl.cpp
- static egl_connection_t gEGLImpl[IMPL_NUM_IMPLEMENTATIONS];
- static egl_connection_t gEGLImpl[IMPL_NUM_IMPLEMENTATIONS];
- enum {
- IMPL_HARDWARE = 0,
- IMPL_SOFTWARE,
- IMPL_NUM_IMPLEMENTATIONS
- };
- enum {
- IMPL_HARDWARE = 0,
- IMPL_SOFTWARE,
- IMPL_NUM_IMPLEMENTATIONS
- };
gEGLImpl[IMPL_HARDWARE]中保存着硬件图形设备的OpenGL api地址,从
- libGLESv1_CM_adreno200.so
- libGLESv2_adreno200.so
- libEGL_adreno200.so
- libGLESv1_CM_adreno200.so
- libGLESv2_adreno200.so
- libEGL_adreno200.so
3.2 EGL和GLES api
- enum {
- EGL = 0x01,
- GLESv1_CM = 0x02,
- GLESv2 = 0x04
- };
- enum {
- EGL = 0x01,
- GLESv1_CM = 0x02,
- GLESv2 = 0x04
- };

3.3 OpenGL config
3.3.1 系统默认pixel format
- if(info.bits_per_pixel == 32) {
- /*
- * Explicitly request RGBA_8888
- */
- /* Note: the GL driver does not have a r=8 g=8 b=8 a=0 config, so if we do
- * not use the MDP for composition (i.e. hw composition == 0), ask for
- * RGBA instead of RGBX. */
- if (property_get("debug.sf.hw", property, NULL) > 0 && atoi(property) == 0)
- module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBX_8888;
- else if(property_get("debug.composition.type", property, NULL) > 0 && (strncmp(property,"mdp", 3) == 0))
- module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBX_8888;
- else
- module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888;
- } else {
- /*
- * Explicitly request 5/6/5
- */
- module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565;
- }
- if(info.bits_per_pixel == 32) {
- /*
- * Explicitly request RGBA_8888
- */
- /* Note: the GL driver does not have a r=8 g=8 b=8 a=0 config, so if we do
- * not use the MDP for composition (i.e. hw composition == 0), ask for
- * RGBA instead of RGBX. */
- if (property_get("debug.sf.hw", property, NULL) > 0 && atoi(property) == 0)
- module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBX_8888;
- else if(property_get("debug.composition.type", property, NULL) > 0 && (strncmp(property, "mdp", 3) == 0))
- module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBX_8888;
- else
- module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888;
- } else {
- /*
- * Explicitly request 5/6/5
- */
- module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565;
- }
3.3.2 config初始化
所有的OpenGL库提供的config,同样需要将软硬两种模式的各自的OpenGL config提取出来供系统使用,如同OpenGL api地址一样。OpenGL config提取出来后保存在另外一个全局变量- static egl_display_t gDisplay[NUM_DISPLAYS];
- static egl_display_t gDisplay[NUM_DISPLAYS];
- // EGLDisplay are global, not attached to a given thread
- const unsigned int NUM_DISPLAYS = 1;
- // EGLDisplay are global, not attached to a given thread
- const unsigned int NUM_DISPLAYS = 1;
- <strong> </strong> // sort our configurations so we can do binary-searches
- qsort( dp->configs,
- dp->numTotalConfigs,
- sizeof(egl_config_t), cmp_configs);<strong>
- </strong>
- <strong> </strong> // sort our configurations so we can do binary-searches
- qsort( dp->configs,
- dp->numTotalConfigs,
- sizeof(egl_config_t), cmp_configs);<strong>
- </strong>
3.3.3 config选择
3.3.3.1 满足属性要求
- // initialize EGL
- EGLint attribs[] = {
- EGL_SURFACE_TYPE, EGL_WINDOW_BIT,
- EGL_NONE, 0,
- EGL_NONE
- };
- // initialize EGL
- EGLint attribs[] = {
- EGL_SURFACE_TYPE, EGL_WINDOW_BIT,
- EGL_NONE, 0,
- EGL_NONE
- };
3.3.3.2 满足RGBA要求
- static GGLFormat const gPixelFormatInfos[] =
- { // Alpha Red Green Blue
- { 0, 0, {{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }}, 0 }, // PIXEL_FORMAT_NONE
- { 4, 32, {{32,24, 8, 0, 16, 8, 24,16 }}, GGL_RGBA }, // PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888
- static GGLFormat const gPixelFormatInfos[] =
- { // Alpha Red Green Blue
- { 0, 0, {{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }}, 0 }, // PIXEL_FORMAT_NONE
- { 4, 32, {{32,24, 8, 0, 16, 8, 24,16 }}, GGL_RGBA }, // PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888
format信息,去和openGL的config比较,得到想要的config。
- EGLConfig* const configs = (EGLConfig*)malloc(sizeof(EGLConfig)*numConfigs);
- if (eglChooseConfig(dpy, attrs, configs, numConfigs, &n) == EGL_FALSE) {
- free(configs);
- return BAD_VALUE;
- }
- const int fbSzA = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_ALPHA);
- const int fbSzR = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_RED);
- const int fbSzG = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_GREEN);
- const int fbSzB = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_BLUE);
- int i;
- EGLConfig config = NULL;
- for (i=0 ; i<n ; i++) {
- EGLint r,g,b,a;
- EGLConfig curr = configs[i];
- eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_RED_SIZE, &r);
- eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_GREEN_SIZE, &g);
- eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_BLUE_SIZE, &b);
- eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_ALPHA_SIZE, &a);
- if (fbSzA <= a && fbSzR <= r && fbSzG <= g && fbSzB <= b) {
- config = curr;
- break;
- }
- }
- EGLConfig* const configs = (EGLConfig*)malloc(sizeof(EGLConfig)*numConfigs);
- if (eglChooseConfig(dpy, attrs, configs, numConfigs, &n) == EGL_FALSE) {
- free(configs);
- return BAD_VALUE;
- }
- const int fbSzA = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_ALPHA);
- const int fbSzR = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_RED);
- const int fbSzG = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_GREEN);
- const int fbSzB = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_BLUE);
- int i;
- EGLConfig config = NULL;
- for (i=0 ; i<n ; i++) {
- EGLint r,g,b,a;
- EGLConfig curr = configs[i];
- eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_RED_SIZE, &r);
- eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_GREEN_SIZE, &g);
- eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_BLUE_SIZE, &b);
- eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_ALPHA_SIZE, &a);
- if (fbSzA <= a && fbSzR <= r && fbSzG <= g && fbSzB <= b) {
- config = curr;
- break;
- }
- }
4. 创建main surface
5. 创建 OpenGL ES 上下文
AnOpenGL context represents many things. A context stores all of the state associated with this instance of OpenGL. It represents the (potentially visible)default framebufferthat rendering commands will draw to when not drawing to aframebuffer object. Think of a context as an object that holds all of OpenGL; when a context is destroyed, OpenGL is destroyed.
http://www.opengl.org/wiki/OpenGL_context
具体的创建过程专业术语太多,也没有仔细研究不再介绍。
6. 绑定context和surface
6.1 多线程支持
- ogles_context_t* current = (ogles_context_t*)getGlThreadSpecific();
- if (gl) {
- egl_context_t* c = egl_context_t::context(gl);
- if (c->flags & egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT) {
- if (current != gl) {
- // it is an error to set a context current, if it's already
- // current to another thread
- return -1;
- }
- } else {
- if (current) {
- // mark the current context as not current, and flush
- glFlush();
- egl_context_t::context(current)->flags &= ~egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT;
- }
- }
- if (!(c->flags & egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT)) {
- // The context is not current, make it current!
- setGlThreadSpecific(gl);
- c->flags |= egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT;
- }
- ogles_context_t* current = (ogles_context_t*)getGlThreadSpecific();
- if (gl) {
- egl_context_t* c = egl_context_t::context(gl);
- if (c->flags & egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT) {
- if (current != gl) {
- // it is an error to set a context current, if it's already
- // current to another thread
- return -1;
- }
- } else {
- if (current) {
- // mark the current context as not current, and flush
- glFlush();
- egl_context_t::context(current)->flags &= ~egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT;
- }
- }
- if (!(c->flags & egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT)) {
- // The context is not current, make it current!
- setGlThreadSpecific(gl);
- c->flags |= egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT;
- }
- // cur_c has to be valid here (but could be terminated)
- if (ctx != EGL_NO_CONTEXT) {
- setGlThreadSpecific(c->cnx->hooks[c->version]);
- setContext(ctx);
- _c.acquire();
- } else {
- setGlThreadSpecific(&gHooksNoContext);
- setContext(EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
- }
- // cur_c has to be valid here (but could be terminated)
- if (ctx != EGL_NO_CONTEXT) {
- setGlThreadSpecific(c->cnx->hooks[c->version]);
- setContext(ctx);
- _c.acquire();
- } else {
- setGlThreadSpecific(&gHooksNoContext);
- setContext(EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
- }
尽管openGL 实现了多线程的支持,目前我从代码中别没有找到多线程的使用。
6.2 设置surface和context之间的关系
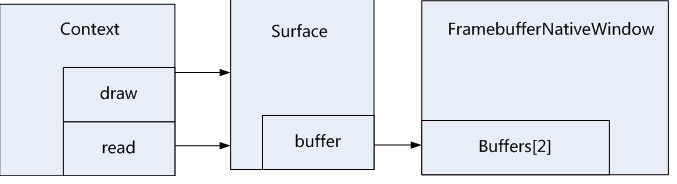
- // Unbind the context from this thread
- eglMakeCurrent(display, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
- // Unbind the context from this thread
- eglMakeCurrent(display, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
- // initialize primary screen
- // (other display should be initialized in the same manner, but
- // asynchronously, as they could come and go. None of this is supported
- // yet).
- const GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
- const DisplayHardware& hw = plane.displayHardware();
- const uint32_t w = hw.getWidth();
- const uint32_t h = hw.getHeight();
- const uint32_t f = hw.getFormat();
- hw.makeCurrent();
- // initialize primary screen
- // (other display should be initialized in the same manner, but
- // asynchronously, as they could come and go. None of this is supported
- // yet).
- const GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
- const DisplayHardware& hw = plane.displayHardware();
- const uint32_t w = hw.getWidth();
- const uint32_t h = hw.getHeight();
- const uint32_t f = hw.getFormat();
- hw.makeCurrent();
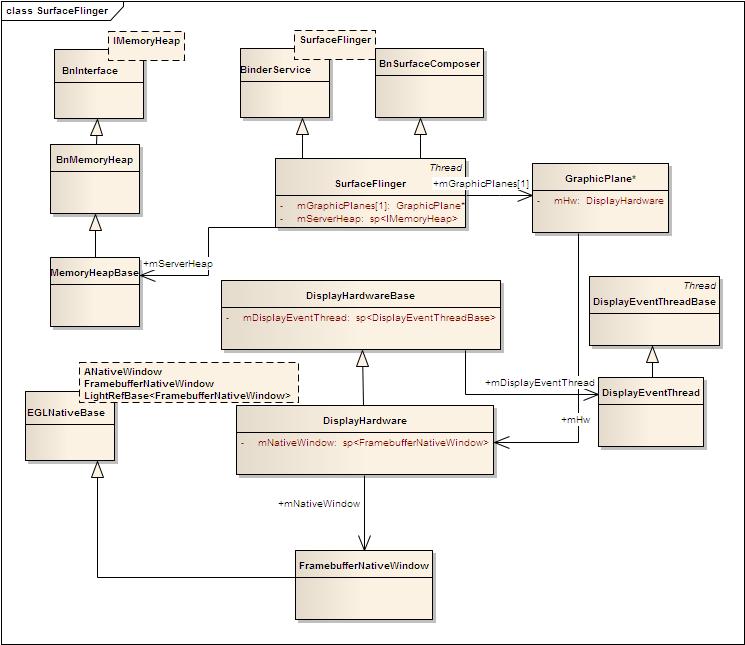
下图为这个图形系统的类图结构。