版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34928644/article/details/82687718
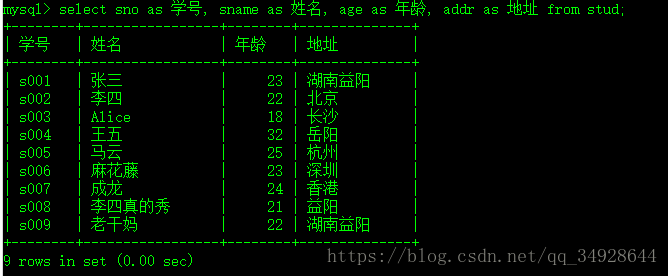
查询 取别名
select sno as 学号, sname as 姓名, age as 年龄, addr as 地址 from stud;as 可以省略
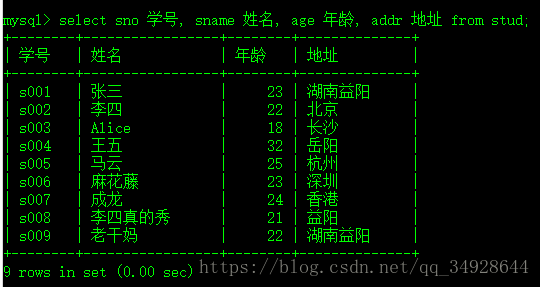
select sno 学号, sname 姓名, age 年龄, addr 地址 from stud;复杂查询
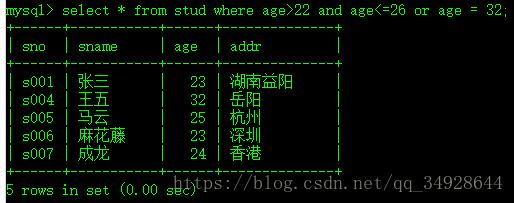
and 、or 、> 、< 、>= 、<= 、= 、 !=
select * from stud where age>22 and age<=26 or age = 32;between ... and ...
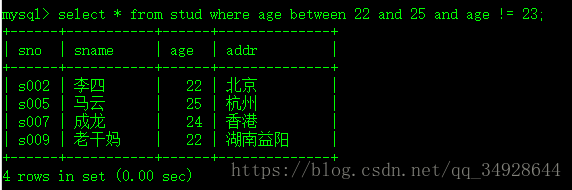
查询年龄在[22,25]之间(between 22 and 25) 并且(and) 年龄不等于23的学生
select * from stud where age between 22 and 25 and age != 23;
in(...)
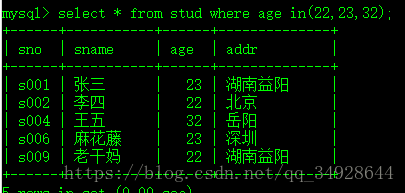
查询年龄为22、23、32的学生
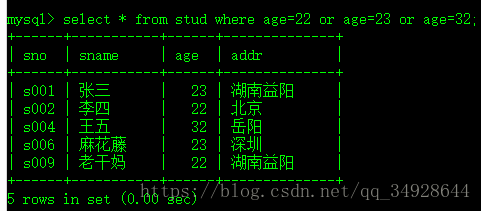
select * from stud where age in(22,23,32);等价于
select * from stud where age=22 or age=23 or age=32;not 与 !
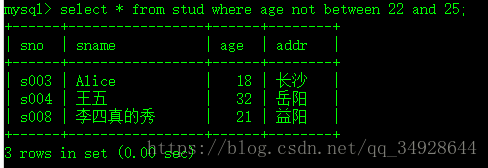
select * from stud where age not between 22 and 25;
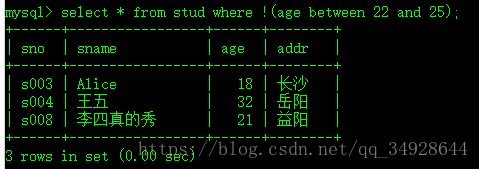
select * from stud where age ! between 22 and 25; #错误的!!!select * from stud where !(age between 22 and 25);
select * from stud where not(age between 22 and 25);因此,在boolean值前面用 not 和 ! 效果是一样的,但是在表达式中 使用 not 和 ! 是有语法区别的。
比如:age not between ... 、age not in(...)是正确的, age ! between ... 、age ! in(...) 是错误的;
age != 22 是正确的, age not= 22 是错误的。
判断为null ------ is null
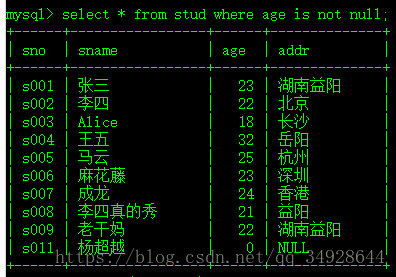
select * from stud where age is null;判断不为null ------ is not null
select * from stud where age is not null;还可以使用 boolean值取反。
select * from stud where not(age is null);
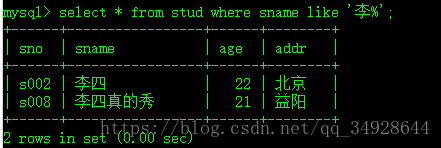
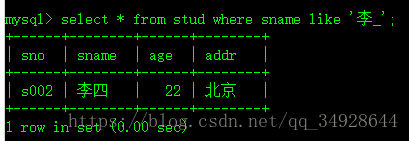
select * from stud where !(age is null);模糊查询--- LIKE 搭配通配符 '%' : 匹配多个、'_' : 匹配单个
select * from stud where sname like '李%';select * from stud where sname like '李_';创建视图
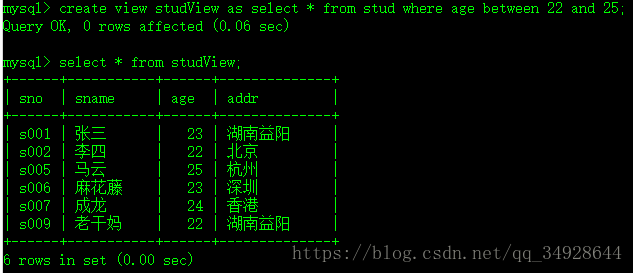
- 视图是保存在数据库中的选择查询,相当于从一个或多个数据表中派生出来的虚拟表。它兼有查询和表的双重功能。
- 查询功能:视图保存一个完整的SQL查询命令,相当于给一个查询起了一个名字。简化数据查询和数据处理操作。提高数据的安全性。
- 表的功能:视图可以和表一样使用,即操作表的所有命令都可以使用在视图中,但是要注意:视图本身不含有任何数据,每次使用相当于从数据库表中重新查询。
create view studView as select * from stud where age between 22 and 25;聚合函数
- Count(*)行数量—不包含空行 null
select count(*) as 总人数 from stud;- avg平均。
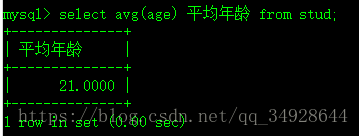
select avg(age) 平均年龄 from stud;- Sum求和。
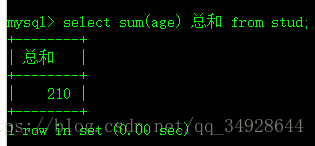
select sum(age) 总和 from stud;- Max最大。
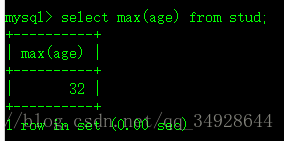
select max(age) from stud;- Min最小。
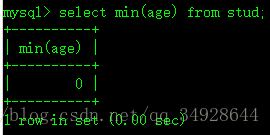
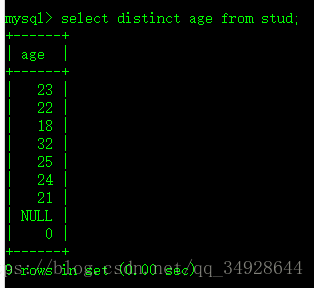
select min(age) from stud;- Distinct-去除相同的信息。
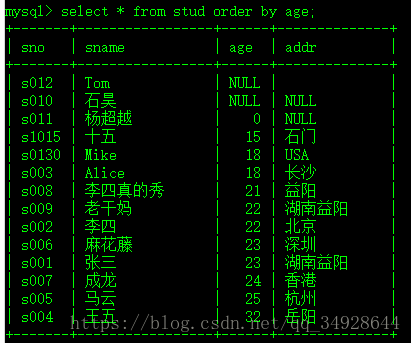
select distinct age from stud;排序---order by---必须放在SQL语句最后面。
默认 ASC 升序。
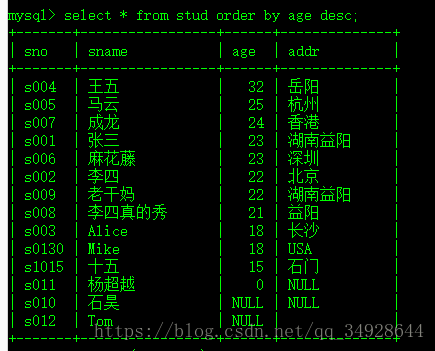
select * from stud order by age;降序 DESC
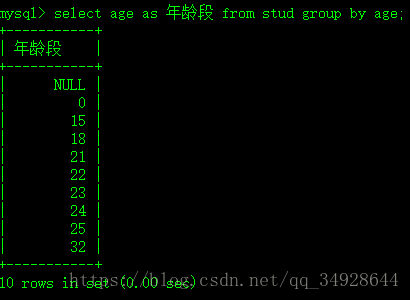
select * from stud order by age desc;分组---group by
需求1:查询stud中有几个年龄段。
select age as 年龄段 from stud group by age;需求2:查询具有相同年龄的学生。
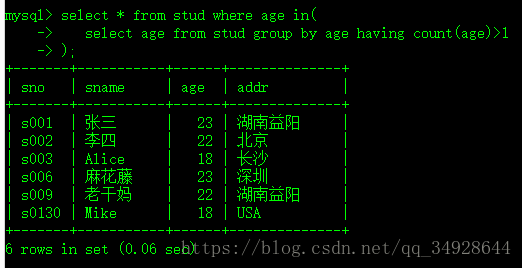
思路:先查询出相同年龄的年龄段有哪些,再把子查询的查询结果 作为主查询的查询条件,即可完成需求。
select * from stud where age in(
select age from stud group by age having count(age)>1
);case when then end
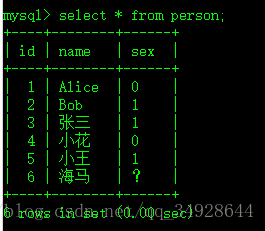
表数据
采用 case when then end 类似java中 if、else if、else 语法
select id,name,(case sex when '1' then '男' when '0' then '女' else '未知' end) as 性别 from person;有关字符串处理函数
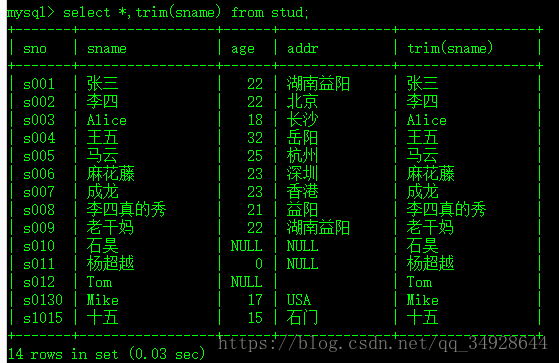
- trim(str) 、ltrim(str) 、rtrim(str)---减去前后空格、减去前空格、减去后空格
- length(str) 判断长度单位字节 一个汉字=一个字符=3个字节
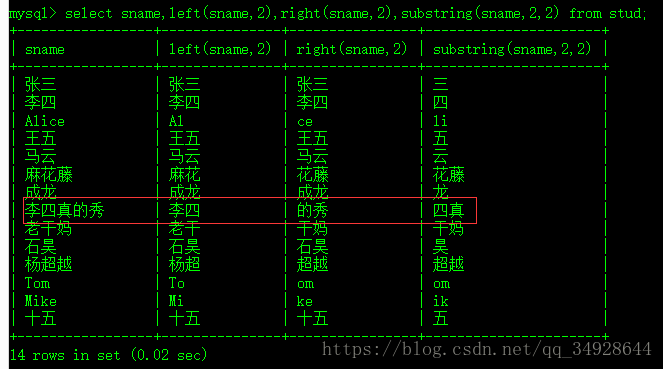
left(str,len) 、right(str,len) 、substring(srt,begin,len) 注意:begin从1开始
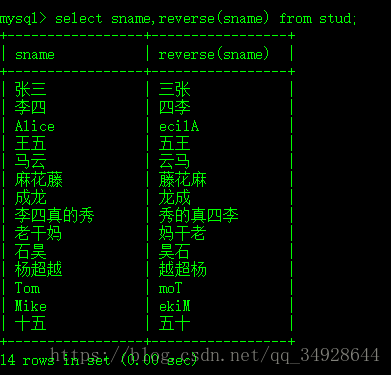
reverse(str) 反转字符串。
lower(str) upper(str) concat(str1,str2,...strn) 字母转换小写、大写,连接字符串。
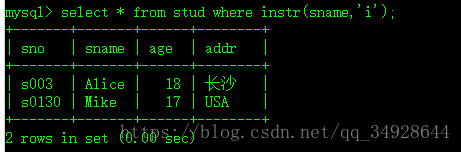
instr(str1,str2) 类似Java中indexOf函数 ,不同Java的是没找到返回0,找到返回对应的下标,从1开始。
查询数据库变量
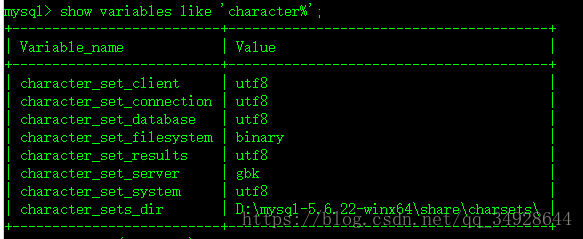
show variables;查询数据库编码
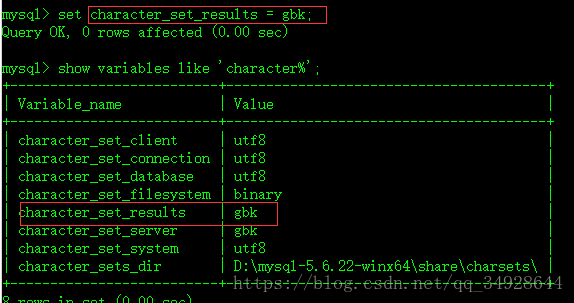
show variables like 'character%';修改 数据库编码
set character_set_results = gbk;