一、Tomcat的Pipeline-value管道实现
Pipeline管道的实现分为生命周期管理和处理请求。
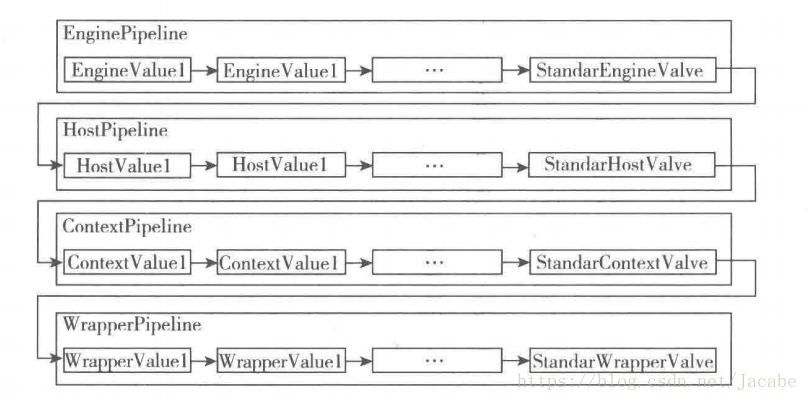
在Engin的管道中依次执行Engin的各个Value,最后执行StandardEnginValue,依次类推StandardWrapperValue.
(Filter用到的FilterChain就是这种模式,FilterChain相当于Pipeline,每个Filter相当于一个Value,Servlet相当于最后的BaseValue)
由于Container容器负责具体Servlet的处理,也就是负责处理请求(http请求),
而Container是使用Pipeline-value管道来处理请求的。
Pipeline-value是属于责任链模式。
责任链模式是指在一个请求处理过程中有多个处理者依次对请求进行处理,每个处理者负责处理自己的,处理完交给下一位处理。
Pipeline-value 特点:每个Pipeline都有特定的Value,而且是管道最后一个执行,这个Value叫BaseValue,BaseValue是不可删除的。上层的BaseValue会调用下层容器的管道。流程如上图所示,
四个容器的BaseValue分别是StandardEngineValue,StandardHostValue,StandardContextValue和StandardWrapperValue。
1、Pipeline管道的生命周期管理
Container的Pipeline在ContainerBase中定义,在生命周期的startInternal,stopInternal,destroyInternal调用相应的生命周期方法。管道不需要初始化无initInternal方法。
启动Container的同时也内部调用启动Pipeline管道。
在ConainerBase类的 startInternal()里面调用了 ((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();就会调用Lifecycle的start方法,
而Lifecycle接口的基本实现类是 LifecycleBase类,在LifecycleBase类里面执行了start()方法,然后在PipeLine的具体实现类StandardPipeLine实现startInternal()方法。
package org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase类:
/**
* The Pipeline object with which this Container is associated.
*/
protected final Pipeline pipeline = new StandardPipeline(this);
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements
* of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start our subordinate components, if any
logger = null;
getLogger();
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if ((cluster != null) && (cluster instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if ((realm != null) && (realm instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
// Start our child containers, if any
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(children[i])));
}
boolean fail = false;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
fail = true;
}
}
if (fail) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"));
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our thread
threadStart();
}
/**
* Stop this component and implement the requirements
* of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#stopInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Stop our thread
threadStop();
setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING);
// Stop the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle &&
((Lifecycle) pipeline).getState().isAvailable()) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).stop();
}
// Stop our child containers, if any
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StopChild(children[i])));
}
boolean fail = false;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStopFailed"), e);
fail = true;
}
}
if (fail) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStopFailed"));
}
// Stop our subordinate components, if any
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if ((realm != null) && (realm instanceof Lifecycle)) {
((Lifecycle) realm).stop();
}
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if ((cluster != null) && (cluster instanceof Lifecycle)) {
((Lifecycle) cluster).stop(); //停止了stop管道
}
}
开始启动pipeline 管道 --》 ((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();的pipeline是StandardPipeline类:
org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase类的startInternal方法:
/**
* The Pipeline object with which this Container is associated.
*/
protected final Pipeline pipeline = new StandardPipeline(this);
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start(); 
由于LifecycleBase继承自Lifecycle,所以 ((Lifecycle) pipeline).start(); start()方法在LifecycleBase类里面调用,也就是调用了LifecycleBase的start方法,由于Pipeline接口下的默认实现类是StandardPipeline,在StandardPipeline类里面具体实现了startInternal方法。
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardPipeline类
protected Valve basic = null;
protected Valve first = null;
/**
* Start {@link Valve}s) in this pipeline and implement the requirements
* of {@link LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
Valve current = first;
if (current == null) {
current = basic;
}
while (current != null) { //遍历Value链里的所有Value并调用start方法
if (current instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) current).start();
current = current.getNext();
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); //设置LifecycleState状态
}
Valve current = first;
if (current == null) {
current = basic;
}
在first为null的情况下,把basic赋值给current,那basic值是什么时候赋值的呢?
在StandardPipeline类里面有一个setBasic()方法。
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardPipeline类
@Override
public void setBasic(Valve valve) {
// Change components if necessary
Valve oldBasic = this.basic;
if (oldBasic == valve)
return;
// Stop the old component if necessary
if (oldBasic != null) {
if (getState().isAvailable() && (oldBasic instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) oldBasic).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("StandardPipeline.setBasic: stop", e);
}
}
if (oldBasic instanceof Contained) {
try {
((Contained) oldBasic).setContainer(null);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
}
}
}
// Start the new component if necessary
if (valve == null)
return;
if (valve instanceof Contained) {
((Contained) valve).setContainer(this.container);
}
if (getState().isAvailable() && valve instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) valve).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("StandardPipeline.setBasic: start", e);
return;
}
}
// Update the pipeline
Valve current = first;
while (current != null) {
if (current.getNext() == oldBasic) {
current.setNext(valve);
break;
}
current = current.getNext();
}
this.basic = valve;
}而调用setBasic(Value)方法的 分别是StandardContext,StandardEngine,StandardWrapper类,
StandardContext为例:
package org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext类
/**
* Create a new StandardContext component with the default basic Valve.
*/
public StandardContext() {
super();
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardContextValve());
broadcaster = new NotificationBroadcasterSupport();
// Set defaults
if (!Globals.STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE) {
// Strict servlet compliance requires all extension mapped servlets
// to be checked against welcome files
resourceOnlyServlets.add("jsp");
}
}pipeline.setBasic(new StandardContextValve()); 而
setBasic对应的对象正是 StandardEngineValue,StandardHostValue,StandardContextValue和StandardWrapperValue类。
而在serBasic方法中也 调用了启动管道的start方法.最后完成了赋值。setBasic方法设置的basicValue也是最后才执行。
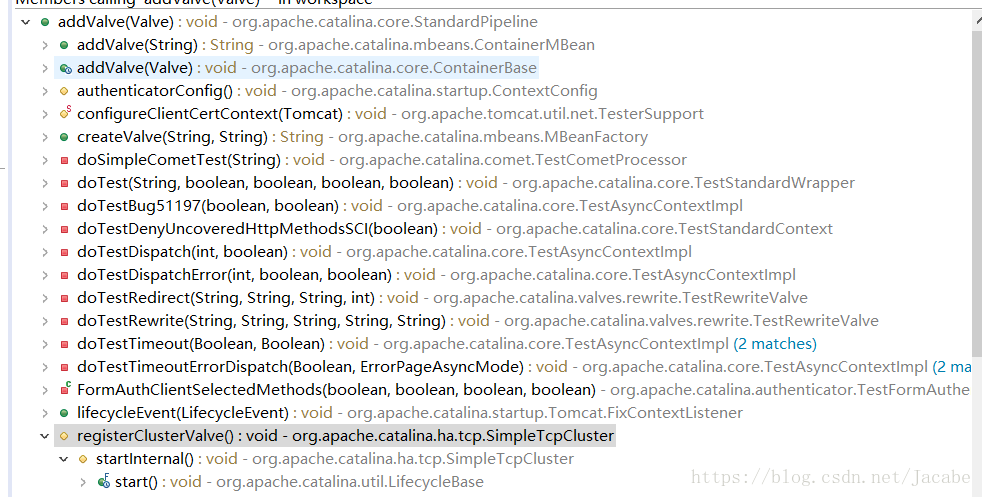
那在什么地方 添加value值,然后启动Pipeline的时候可以 迭代循环value呢?
while (current != null) { //遍历Value链里的所有Value并调用start方法
if (current instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) current).start();
current = current.getNext();
}
在org.apache.catalina.core.StandardPipeline类里有一个addValue方法 来添加value.
那什么时候 调用这个addValue方法呢?追踪查到:
也就是在注册Cluster的时候,也就是在启动LifecycleBase的生命周期方法 start方法的时候,会去调用SimpleTcpCluster类的
registerClusterValve()方法,代码如下:
org.apache.catalina.ha.tcp.SimpleTcpCluster类:
private final List<Valve> valves = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* register all cluster valve to host or engine
*/
protected void registerClusterValve() {
if(container != null ) {
for (Iterator<Valve> iter = valves.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
ClusterValve valve = (ClusterValve) iter.next();
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Invoking addValve on " + getContainer()
+ " with class=" + valve.getClass().getName());
if (valve != null) {
container.getPipeline().addValve(valve);
valve.setCluster(this);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Add cluster valve
* Cluster Valves are only add to container when cluster is started!
* @param valve The new cluster Valve.
*/
@Override
public void addValve(Valve valve) {
if (valve instanceof ClusterValve && (!valves.contains(valve)))
valves.add(valve);
}
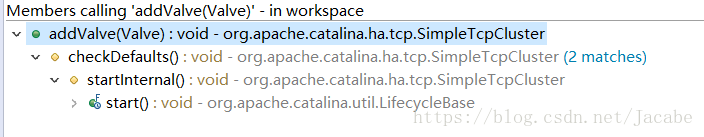
那registerClusterValve()方法里面的values又是从哪里添加的呢?SimpleTcpCluster有一个addValue()方法,
那SimpleTcpCluster的addValue方法什么时候调用呢
org.apache.catalina.ha.tcp.SimpleTcpCluster类:
protected void checkDefaults() {
if ( clusterListeners.size() == 0 && managerTemplate instanceof DeltaManager ) {
addClusterListener(new ClusterSessionListener());
}
if ( valves.size() == 0 ) {
addValve(new JvmRouteBinderValve());
addValve(new ReplicationValve());
}
if ( clusterDeployer != null ) clusterDeployer.setCluster(this);
if ( channel == null ) channel = new GroupChannel();
if ( channel instanceof GroupChannel && !((GroupChannel)channel).getInterceptors().hasNext()) {
channel.addInterceptor(new MessageDispatchInterceptor());
channel.addInterceptor(new TcpFailureDetector());
}
if (heartbeatBackgroundEnabled) channel.setHeartbeat(false);
}
/**
* Start Cluster and implement the requirements
* of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) log.info(sm.getString("simpleTcpCluster.start"));
try {
checkDefaults();
registerClusterValve();
channel.addMembershipListener(this);
channel.addChannelListener(this);
if (channel instanceof GroupChannel)
((GroupChannel)channel).setName(getClusterName() + "-Channel");
channel.start(channelStartOptions);
if (clusterDeployer != null) clusterDeployer.start();
registerMember(channel.getLocalMember(false));
} catch (Exception x) {
log.error(sm.getString("simpleTcpCluster.startUnable"), x);
throw new LifecycleException(x);
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}
也就是在SimpleTcpCluster类里面有一个checkDefaults方法调用了addValue方法分别把ValueBase下的
addValve(new JvmRouteBinderValve());
addValve(new ReplicationValve());
添加JvmRouteBinderValve和ReplicationValve 入value集合中。也就是添加了ClusterValue下的value进入集合中。
从而也调用JvmRouteBinderValve和ReplicationValve这两个的start方法(在StandardPipeline类中)
而在SimpleTcpCluster的startInternal方法中分别调用了 checkDefaults();,registerClusterValve();方法。
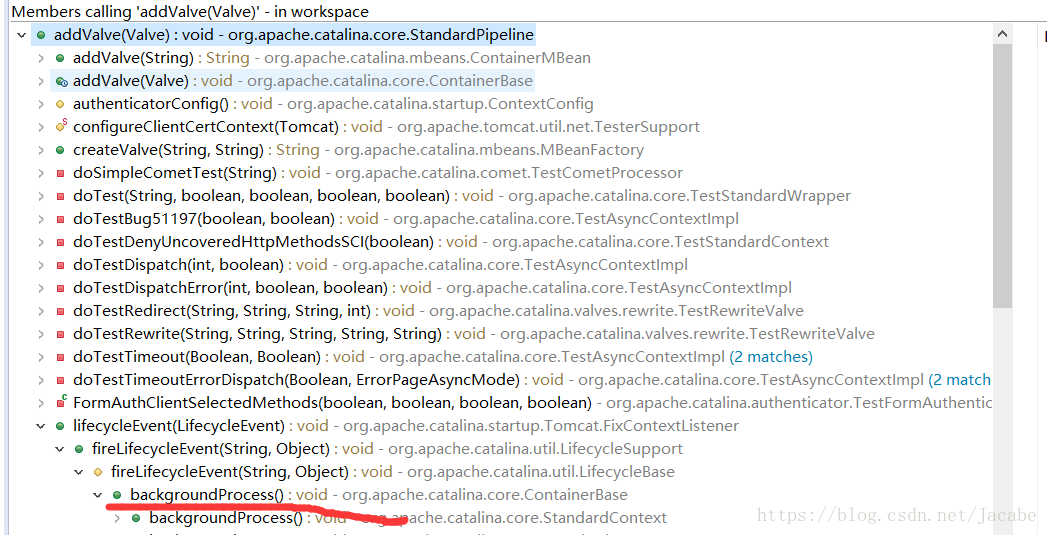
而backgroudProcess方法也最后调用了StandardPipeline类的addValue方法
而lifecycleEvent方法代码如下:
org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat类:
/**
* Fix startup sequence - required if you don't use web.xml.
*
* <p>
* The start() method in context will set 'configured' to false - and
* expects a listener to set it back to true.
*/
public static class FixContextListener implements LifecycleListener {
@Override
public void lifecycleEvent(LifecycleEvent event) {
try {
Context context = (Context) event.getLifecycle();
if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.CONFIGURE_START_EVENT)) {
context.setConfigured(true);
// Process annotations
WebAnnotationSet.loadApplicationAnnotations(context);
// LoginConfig is required to process @ServletSecurity
// annotations
if (context.getLoginConfig() == null) {
context.setLoginConfig(new LoginConfig("NONE", null, null, null));
context.getPipeline().addValve(new NonLoginAuthenticator());
}
}
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
return;
}
}
}2、Pipeline管道处理请求
Pipeline调用所包含的invoke方法来处理请求,并在BaseValue里又调用了子容器Pipeline所包含Value的invoke方法,最后调用Wrapper的Pipeline所包含的BaseValue。
上面也就是 前面那一章Connector介绍的CoyoteAdapter类中:
CoyoteAdapter接收到请求,调用invoke方法。
org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter类:
// Calling the container
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
Conector在接收到请求后 会获取到Service,然后获取Container,然后调用pipeline的firstValue 的invoke方法。
Engin的BaseValue是StandardEnginValue.invoke代码如下:
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngineValve类:
/**
* Select the appropriate child Host to process this request,
* based on the requested server name. If no matching Host can
* be found, return an appropriate HTTP error.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Host to be used for this Request
Host host = request.getHost();
if (host == null) {
response.sendError
(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST,
sm.getString("standardEngine.noHost",
request.getServerName()));
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
// Ask this Host to process this request
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}Host在调用invoke之前就已设置到request中,从request获取到Host后将请求传递到Host的管道。
Host的BaseValue会调用Context的Pipeline,Context的BaseValue调用Wrapper的Pipeline,
Wrapper的Pipeline最后在BaseValue(StandardWrapperValue)中创建FilterChain并调用doFilter方法来处理请求。
FilterChain包含着我们配置的与请求相匹配的Filter和Servlet,doFilter方法会依次调用所有的doFilter方法和Servlet的service方法。
代码如下:
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve类:
/**
* Invoke the servlet we are managing, respecting the rules regarding
* servlet lifecycle and SingleThreadModel support.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Initialize local variables we may need
boolean unavailable = false;
Throwable throwable = null;
// This should be a Request attribute...
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
requestCount.incrementAndGet();
StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer();
Servlet servlet = null;
Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent();
// Check for the application being marked unavailable
if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardContext.isUnavailable"));
unavailable = true;
}
// Check for the servlet being marked unavailable
if (!unavailable && wrapper.isUnavailable()) {
container.getLogger().info(sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
long available = wrapper.getAvailable();
if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
} else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound",
wrapper.getName()));
}
unavailable = true;
}
// Allocate a servlet instance to process this request
try {
if (!unavailable) {
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
}
} catch (UnavailableException e) {
container.getLogger().error(
sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
long available = wrapper.getAvailable();
if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
} else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound",
wrapper.getName()));
}
} catch (ServletException e) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException",
wrapper.getName()), StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e));
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
servlet = null;
}
// Identify if the request is Comet related now that the servlet has been allocated
boolean comet = false;
if (servlet instanceof CometProcessor && Boolean.TRUE.equals(request.getAttribute(
Globals.COMET_SUPPORTED_ATTR))) {
comet = true;
request.setComet(true);
}
MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB();
DispatcherType dispatcherType = DispatcherType.REQUEST;
if (request.getDispatcherType()==DispatcherType.ASYNC) dispatcherType = DispatcherType.ASYNC;
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR,dispatcherType);
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR,
requestPathMB);
// Create the filter chain for this request
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain =
ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
// Call the filter chain for this request
// NOTE: This also calls the servlet's service() method
try {
if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
// Swallow output if needed
if (context.getSwallowOutput()) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else if (comet) {
filterChain.doFilterEvent(request.getEvent());
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(),
response.getResponse());
}
} finally {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
context.getLogger().info(log);
}
}
} else {
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else if (comet) {
filterChain.doFilterEvent(request.getEvent());
} else {
filterChain.doFilter
(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
}
}
} catch (ClientAbortException e) {
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (IOException e) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(),
context.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (UnavailableException e) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(),
context.getName()), e);
// throwable = e;
// exception(request, response, e);
wrapper.unavailable(e);
long available = wrapper.getAvailable();
if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
} else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound",
wrapper.getName()));
}
// Do not save exception in 'throwable', because we
// do not want to do exception(request, response, e) processing
} catch (ServletException e) {
Throwable rootCause = StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e);
if (!(rootCause instanceof ClientAbortException)) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardWrapper.serviceExceptionRoot",
wrapper.getName(), context.getName(), e.getMessage()),
rootCause);
}
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString(
"standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(),
context.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
// Release the filter chain (if any) for this request
if (filterChain != null) {
if (request.isComet()) {
// If this is a Comet request, then the same chain will be used for the
// processing of all subsequent events.
filterChain.reuse();
} else {
filterChain.release();
}
}
// Deallocate the allocated servlet instance
try {
if (servlet != null) {
wrapper.deallocate(servlet);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.deallocateException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
if (throwable == null) {
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
}
// If this servlet has been marked permanently unavailable,
// unload it and release this instance
try {
if ((servlet != null) &&
(wrapper.getAvailable() == Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
wrapper.unload();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloadException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
if (throwable == null) {
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
}
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
long time=t2-t1;
processingTime += time;
if( time > maxTime) maxTime=time;
if( time < minTime) minTime=time;
}
调用doFilter,然后实现代码如下:
org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain类:
/**
* Invoke the next filter in this chain, passing the specified request
* and response. If there are no more filters in this chain, invoke
* the <code>service()</code> method of the servlet itself.
*
* @param request The servlet request we are processing
* @param response The servlet response we are creating
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs
* @exception ServletException if a servlet exception occurs
*/
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
try {
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction<Void>() {
@Override
public Void run()
throws ServletException, IOException {
internalDoFilter(req,res);
return null;
}
}
);
} catch( PrivilegedActionException pe) {
Exception e = pe.getException();
if (e instanceof ServletException)
throw (ServletException) e;
else if (e instanceof IOException)
throw (IOException) e;
else if (e instanceof RuntimeException)
throw (RuntimeException) e;
else
throw new ServletException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
} else {
internalDoFilter(request,response);
}
}联合Container部分--》分析:
org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase类:
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start our subordinate components, if any
logger = null;
getLogger();
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if ((cluster != null) && (cluster instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if ((realm != null) && (realm instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
// Start our child containers, if any
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(children[i])));
}
boolean fail = false;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
fail = true;
}
}
if (fail) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"));
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our thread
threadStart();
}
// Start our child containers, if any
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(children[i])));
}//启动Container下的四个子容器start启动。
findChildren();方法实现代码如下:
org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase类:
/**
* The child Containers belonging to this Container, keyed by name.
*/
protected final HashMap<String, Container> children = new HashMap<>();
/**
* Return the set of children Containers associated with this Container.
* If this Container has no children, a zero-length array is returned.
*/
@Override
public Container[] findChildren() {
synchronized (children) {
Container results[] = new Container[children.size()];
return children.values().toArray(results);
}
}那上面 HashMap<String, Container> children = new HashMap<>();的children 是在哪里添加的呢?
是通过ContainerBase类的addChild方法:代码如下:
org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase类:
@Override
public void addChild(Container child) {
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction<Void> dp =
new PrivilegedAddChild(child);
AccessController.doPrivileged(dp);
} else {
addChildInternal(child);
}
}
private void addChildInternal(Container child) {
if( log.isDebugEnabled() )
log.debug("Add child " + child + " " + this);
synchronized(children) {
if (children.get(child.getName()) != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("addChild: Child name '" +
child.getName() +
"' is not unique");
child.setParent(this); // May throw IAE
children.put(child.getName(), child);
}
// Start child
// Don't do this inside sync block - start can be a slow process and
// locking the children object can cause problems elsewhere
try {
if ((getState().isAvailable() ||
LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(getState())) &&
startChildren) {
child.start();
}
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("ContainerBase.addChild: start: ", e);
throw new IllegalStateException("ContainerBase.addChild: start: " + e);
} finally {
fireContainerEvent(ADD_CHILD_EVENT, child);
}
}:
后续再补充