Collector常见用法
| 常用形式为: .collect(Collectors.toList()) collect()是Stream的方法 Collectors 是收集器Collector 的工厂方法,提供了一些常用的收集器 |
比如
常用收集器概要
| 收集器 | 行为 |
|---|---|
toList() |
将元素收集到一个 List 中。 |
toSet() |
将元素收集到一个 Set 中。 |
toCollection() |
将元素收集到一个 Collection 中。 |
toMap(...) |
将元素收集到一个 Map 中,依据提供的映射函数将元素转换为键/值。 |
summingInt(ToIntFunction<? super T>) |
给定值序列进行求和(还有 long 和 double 版本) |
summarizingInt(ToIntFunction<T>) |
给定值序列计算统计信息 sum、 min、 max、 count 和 average (还有 long 和 double 版本) |
reducing(...) |
用于归约计算(通常用作下游收集器,比如用于 groupingBy 或者partitioningBy 下游) |
partitioningBy(...) |
按照predicate分为两组 |
groupingBy(...) |
将元素分组 |
| maxBy(Comparator<? super T> comparator) | 最大值 |
minBy(Comparator<? super T> comparator) |
最小值 |
mapping(Function<T,U>, Collector) |
将提供的映射函数应用于每个元素,并使用指定的下游收集器(通常用作下游收集器本身,比如用于 groupingBy)进行处理。 |
joining() |
假设元素为 String 类型,将这些元素联结到一个字符串中(或许使用分隔符、前缀和后缀)。 |
counting() |
计算元素数量。(通常用作下游收集器。) |
| averagingInt(ToIntFunction<? super T>) | 平均数 (还有 long 和 double 版本) |
收集器参数列表
| toList() |
| toSet() |
| toCollection(Supplier<C>) |
| counting() |
| collectingAndThen(Collector<T, A, R>, Function<R, RR>) |
| summingInt(ToIntFunction<? super T>) summingLong(ToLongFunction<? super T>) summingDouble(ToDoubleFunction<? super T>) |
| maxBy(Comparator<? super T>) |
| minBy(Comparator<? super T>) |
| reducing(BinaryOperator<T>) reducing(T, BinaryOperator<T>) reducing(U, Function<? super T, ? extends U>, BinaryOperator<U>) |
| joining() joining(CharSequence) joining(CharSequence, CharSequence, CharSequence) |
| mapping(Function<? super T, ? extends U>, Collector<? super U, A, R>) |
| toMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K>, Function<? super T, ? extends U>) toMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K>, Function<? super T, ? extends U>, BinaryOperator<U>) toMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K>, Function<? super T, ? extends U>, BinaryOperator<U>, Supplier<M>) toConcurrentMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K>, Function<? super T, ? extends U>) toConcurrentMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K>, Function<? super T, ? extends U>, BinaryOperator<U>) toConcurrentMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K>, Function<? super T, ? extends U>, BinaryOperator<U>, Supplier<M>) |
| groupingBy(Function<? super T, ? extends K>) groupingBy(Function<? super T, ? extends K>, Supplier<M>, Collector<? super T, A, D>) groupingBy(Function<? super T, ? extends K>, Collector<? super T, A, D>) groupingByConcurrent(Function<? super T, ? extends K>) groupingByConcurrent(Function<? super T, ? extends K>, Supplier<M>, Collector<? super T, A, D>) groupingByConcurrent(Function<? super T, ? extends K>, Collector<? super T, A, D>) |
| partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T>) partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T>, Collector<? super T, A, D>) |
| averagingDouble(ToDoubleFunction<? super T>) averagingInt(ToIntFunction<? super T>) averagingLong(ToLongFunction<? super T>) |
| summarizingDouble(ToDoubleFunction<? super T>) summarizingInt(ToIntFunction<? super T>) summarizingLong(ToLongFunction<? super T>) |
收集器详解
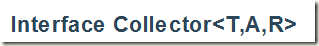
Collector
T - 输入类型
A - 在收集过程中用于累积部分结果的对象类型
R - 返回类型
| mutable reduction的一些场景: 将元素聚集到集合中 使用StringBuilder连接字符串 计算有关元素的汇总信息,如sum、min、max或平均值 计算“主表”摘要,如“卖方的最大价值交易”等 类Collectors提供了许多常见的reduce实现 |
收集器构成
收集器是由四个函数约定构成,它们一起工作,将条目汇集到一个可变的结果容器中,并可选择性地对结果执行最终转换。
| 1. 创建一个新的结果容器(supplier()) 2. 将一个新的数据元素合并到一个结果容器中(accumulator()) 3. 将两个结果容器合并成一个(combiner()) (非必然运行 可能在并行流且Collector不具备CONCURRENT 时执行的 ) 4. 在容器上执行一个可选的最终转换 (finisher()) (非必然运行 中间结果与最终结果类型是否一致决定是否运行 IDENTITY_FINISH用来标志 ) |
属性特征字段
| 特征值是Collector的特征值,用于描述Collecto本身r的,不是其他含义 |
| Set<Characteristics> characteristics() 方法可以访问 |
| Collector.Characteristics CONCURRENT 表示中间结果只有一个,即使在并行流的情况下 所以只有在并行流且收集器不具备CONCURRENT特性时,combiner方法返回的lambda表达式才会执行 如果收集器没有标为UNORDERED,那它仅在用于无序数据源时才可以并行归约 |
| Collector.Characteristics UNORDERED 表示不承诺按照操作顺序排列 |
| Collector.Characteristics IDENTITY_FINISH 表示中间结果容器类型与最终结果类型一致,此时finiser方法不会被调用 |
静态工厂方法
根据提供的给定条件创建 Collector
Collector 就是归约运算操作的一种抽象
首先要理解归约reduce的含义 也就是归纳转换成另外一种形式
| 想要进行归约运算,你先给出一个初始容器,作为中间结果容器 然后再给出迭代运算逻辑 也就是要如何归约 归约的逻辑 就是在这里 结果计算到中间结果容器中 针对于并行计算还需要一个合并的方式 中间结果肯定是为了方便计算,如果你最终想要的不是这种类型,我还可以给你转换下 |
Collector用 类型TAR 和四个方法将归约的过程逻辑化
| T - 输入类型 A - 在收集过程中用于累积部分结果的对象类型 R - 返回类型 |
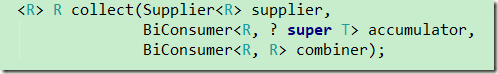
| Supplier<A> supplier(); 所以此方法提供了一个保存中间结果的对象 类型是A BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator(); 不断迭代运算操作结果累计到中间结果上 类型为A 流类型为T Function<A, R> finisher(); 最终的结果为A 还要根据实际情况是否转换为R BinaryOperator<A> combiner(); 用于合并计算 |
Collector工厂Collectors
提供了Collector的一些常用实现 比如
// 获取所有的name转换到List<String>中
List<String> list = people.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 获取所有的name转换到Set<String>中
Set<String> set = people.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new));
// 元素转换为String 并且将他们通过", " 连接起来
String joined = things.stream()
.map(Object::toString)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
//计算员工薪水之和
int total = employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summingInt(Employee::getSalary)));
// 按照部门对员工进行分组
Map<Department, List<Employee>> byDept
= employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDepartment));
// 计算部门薪资和
Map<Department, Integer> totalByDept
= employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDepartment,
Collectors.summingInt(Employee::getSalary)));
// 按照成绩是否通过把学生分为两组
Map<Boolean, List<Student>> passingFailing =
students.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.getGrade() >= PASS_THRESHOLD));Collectors 中有一个静态内部类CollectorImpl 实现了CollectorImpl
预置的一些收集器都是通过CollectorImpl 返回的
/**
* Simple implementation class for {@code Collector}.
*
* @param <T> the type of elements to be collected
* @param <R> the type of the result
*/
static class CollectorImpl<T, A, R> implements Collector<T, A, R> {
private final Supplier<A> supplier;
private final BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator;
private final BinaryOperator<A> combiner;
private final Function<A, R> finisher;
private final Set<Characteristics> characteristics;
CollectorImpl(Supplier<A> supplier,
BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator,
BinaryOperator<A> combiner,
Function<A,R> finisher,
Set<Characteristics> characteristics) {
this.supplier = supplier;
this.accumulator = accumulator;
this.combiner = combiner;
this.finisher = finisher;
this.characteristics = characteristics;
}
CollectorImpl(Supplier<A> supplier,
BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator,
BinaryOperator<A> combiner,
Set<Characteristics> characteristics) {
this(supplier, accumulator, combiner, castingIdentity(), characteristics);
}
@Override
public BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator() {
return accumulator;
}
@Override
public Supplier<A> supplier() {
return supplier;
}
@Override
public BinaryOperator<A> combiner() {
return combiner;
}
@Override
public Function<A, R> finisher() {
return finisher;
}
@Override
public Set<Characteristics> characteristics() {
return characteristics;
}
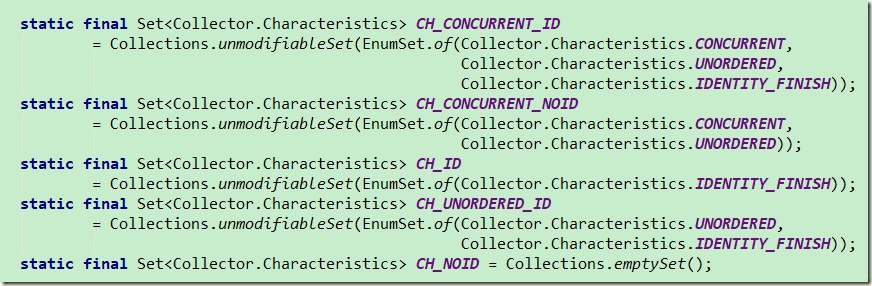
}Collectors中内置的 关于Collector characteristics 特性的组合值
看一个例子
Collector<T, ?, List<T>> toList() {
return new CollectorImpl<>( (Supplier<List<T>>) ArrayList::new,
List::add,
(left, right) -> { left.addAll(right); return left; },
CH_ID);
}TAR分别是 T ? List<T> 也就是处理元素为T类型 返回结果为List<T> 中间结果随意
ArrayList::new 返回List<T> 作为中间结果,显然,跟返回结果一样,不需要调用finisher了
归约方式为 使用List.add方法不断地将集合中的元素添加到中间结果中
合并方式为直接将一个List addAll到另一个list 并且返回最终结果
因为不需要调用finisher 设置下特征 CH_ID
所以说只要按规矩实现了四个方法以及设置characteristics 就可以实现一个Collector
你可以使用Stream中
调用Collectors 提供的一些Collector 或者你自己定义的
你还可以使用Stream中
直接传递参数,显然并不是很直观 建议能不用就别用了