前言:(摘自Wikipedia)
Google Guice (pronounced “juice”) is an open source software framework for the Java platform released by Google under the Apache License. It provides support for dependency injection using annotations to configure Java objects.Dependency injection is a design pattern whose core principle is to separate behavior from dependency resolution.
Guice allows implementation classes to be bound programmatically to an interface, then injected into constructors, methods or fields using an @Inject annotation. When more than one implementation of the same interface is needed, the user can create custom annotations that identify an implementation, then use that annotation when injecting it.
维基百科中写道:Google Guice是一款轻量级的依赖注入框架,通过注解 @inject将实现类 注入constructors, methods or fields。那么,这款依赖注入又应如何剖析?
以下转自博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/zhaowen25/article/details/52927193
术语:
- Guice:整个框架的门面
- Injector:一个依赖的管理上下文
- Binder:一个接口和实现的绑定
- Module:一组Binder
- Provider:bean的提供者
- Key:Binder中对应一个Provider
- Scope:Provider的作用域
- Stage:运行方式(为了不同的要求)
使用示例
导入maven dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>guice</artifactId>
<version>3.0</version>
</dependency>main方法编写
public class FooApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Injector injector = Guice.createInjector(
new ModuleA(),
new ModuleB(),
. . .
new FooApplicationFlagsModule(args)
);
// Now just bootstrap the application and you're done
FooStarter starter = injector.getInstance(FooStarter.class);
starter.runApplication();
}
} 关于Stage以及如何选择?
stage分为三种,是三个不同场景下选择对应的值,Stage.TOOL时一些操作则不会支持,例如:
java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException:Injector.injectMembers(Object) is not supported in Stage.TOOL
- TOOL(最小代价,有些功能会无法使用)
- DEVELOPMENT(快速启动,但不会做校验)
- PRODUCTION(异常检查与性能,启动会比较慢)
Guice.createInjector(Stage.PRODUCTION, new ModuleA());
Guice.createInjector(new ModuleA());//默认DEVELOPMENT Module(模块)
Module内利用BindingBuilder生成Binder,如何实现一个Module?
public class EventModule extends AbstractModule {
@Override
protected void configure() {
// 绑定接口与实现
bind(EventBusManager.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("eventBusManager"))
.to(EventBusManager.class);
}
} 绑定时如果是实现类绑定实现类会报错,但如果加个别名的话就没问题
几种bind方式
bind(EventService.class).to(SpringEventService.class);
bind(EventService.class).toInstance(new SpringEventService());
bind(SpringEventService.class).asEagerSingleton();
bind(EventService.class).toProvider(new Provider<EventService>(){
@Override
public EventService get(){
return new SpringEventService();
}
});
bind(EventService.class)
.toConstructor((Constructor<SpringEventService>)SpringEventService.class.getConstructors()[0]);注意:第一个直接to(implemet)的方式是getProvider时new出的Provider,第二种是用Providers.of(instance)生成的ConstantProvider
注入依赖@Inject
@Singleton
public class MyHandler {
@Inject
@Named("springEventService")
private EventService eventService;
@Subscribe
public void handleEvent(MyEvent event) {
eventService.post("MyHandler",event);
}
} @Inject和@Named结合使用达到按名字注入,@Inject的optional默认为false,注入时如果依赖不存在,则报错停止,当使用@Inject(optional = true)时可达到忽然依赖是否存在的效果
实例创建
FooStarter starter = injector.getInstance(FooStarter.class); 如果injector已经有则直接返回已有对象,没有则创建一个(利用依赖注入,如果没有绑定过则不会被依赖注入),默认prototype模式(每次都新建一个),@Singleton可以指定singleton模式
getInstance的过程
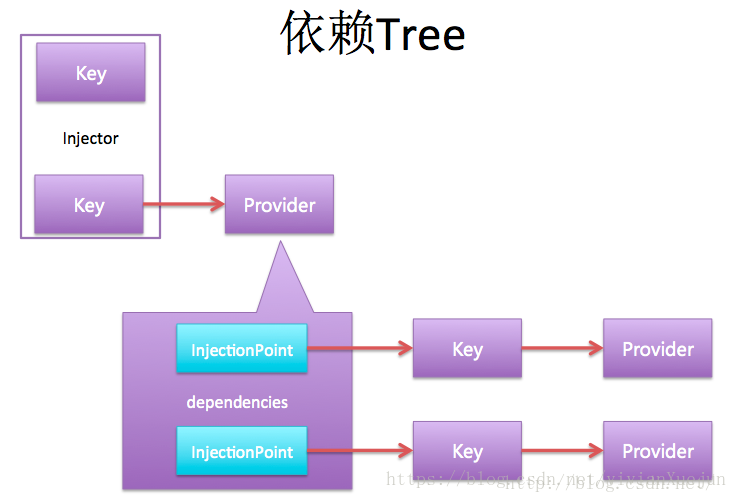
先根据指定的class类new Key(),Key包括class信息和注解信息,class的hashcode和注解的hashcode决定了Key的hashcode,getProvider时是根据Key的hashcode来判断是否是同一个Key,然后取到Provider,由Provider提供最终的instance
注意:无注解时会有一个默认的hashcode
Key的hashcode计算公式
class.hashcode * 31 + annotation.hashcode
会出现多个组合得到的hashcode是相同的情况么?
2 * 31 + 3 = 65
1 * 31 + 34 = 65
为什么用这样的公式?(java中String是如何计算hashcode的?)
Joshua Bloch’s Effective Java中是这样解释的:
The value 31 was chosen because it is an odd prime. If it were even and the multiplication overflowed, information would be lost, as multiplication by 2 is equivalent to shifting. The advantage of using a prime is less clear, but it is traditional. A nice property of 31 is that the multiplication can be replaced by a shift and a subtraction for better performance: 31 * i == (i << 5) - i. Modern VMs do this sort of optimization automatically.(from Chapter 3, Item 9: Always override hashcode when you override equals, page 48)
选择值31是因为它是奇数。 如果是偶数并且乘法溢出,则信息将丢失,因为乘以2等效于移位。 使用素数的优点不太清楚,但它是传统的。 31的一个好的属性是乘法可以由移位和减法替换以获得更好的性能:31 * i ==(i << 5) - i。 现代虚拟机自动进行这种优化。(从第3章,项9:覆盖equals时始终覆盖hashcode,第48页)
参考:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/299304/why-does-javas-hashcode-in-string-use-31-as-a-multiplier
https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~adamchik/15-121/lectures/Hashing/hashing.html
Guice对于classloader的依赖有多重要?
由于一个class被加载后是否唯一由加载的classloader决定,所以不同的classloader加载同一个class会生成两个class实例(反射中一个class也会有一个实例),两个不同的class生成的Key的hashcode则不同,所以在Guice中根据Key来获取时必须要用同一个classloader加载的类,否则获取不到,所以在OSGI方式下用Guice需要注意。
injector.injectMembers(instance)
Injector injectorBase = Guice.createInjector(new EventModule());
Injector injector = injectorBase.createChildInjector(new SpringModule());
MyHandler handler = new MyHandler();// eventService is null
injector.injectMembers(handler);// eventService use instance 用一个已经有的实例,但依赖的对象为null,这时可以用injector注入依赖对象,但这个实例不会有绑定关系,所以如果其他有需要依赖这个实例的也无法注入这个实例
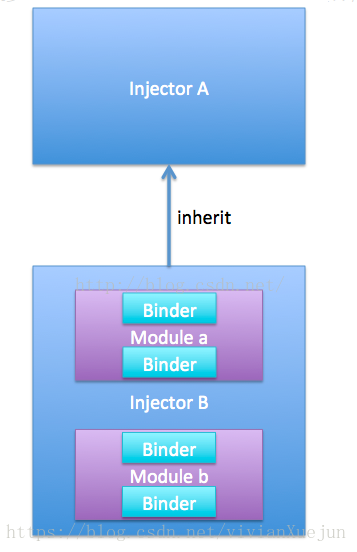
Injector继承
Injector parent = Guice.createInjector(new EventModule());
Injector child = parent.createChildInjector(new SpringModule());child 可以依赖parent ,但反过来则不可以
依赖范围
一个Injector中如果包含了多个Module,各Module中的是可以相互使用的,也就是可以相互依赖
如果一个Injector想依赖另一个Injector中的实例,那就要通过继承了,例如功能模块想要依赖基础模块,那功能模块可以继承基础模块
依赖Tree
AOP in Guice
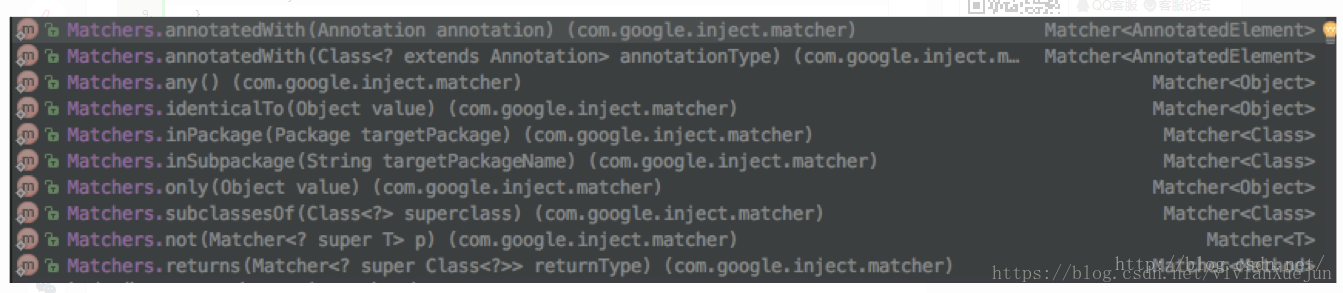
Binder#bindInterceptor(Matcher<? super Class<?>> classMatcher, Matcher<? super Method> methodMatcher, org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor... interceptors)
bindInterceptor(Matchers.any(),Matchers.annotatedWith(Named.class),new MethodInterceptor(){
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("do something before...");
Object result = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("do something after...");
return result;
}
}); Matcher通过Matchers来生成
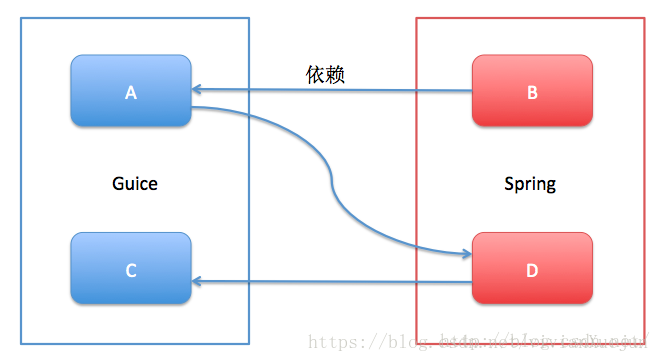
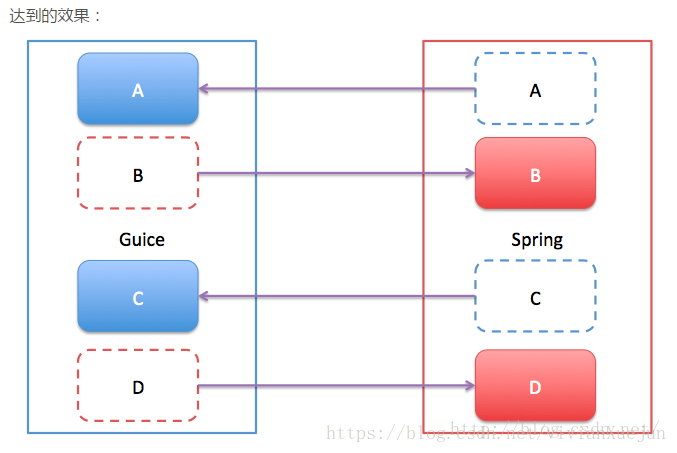
与spring整合
如何解决这种相互依赖?
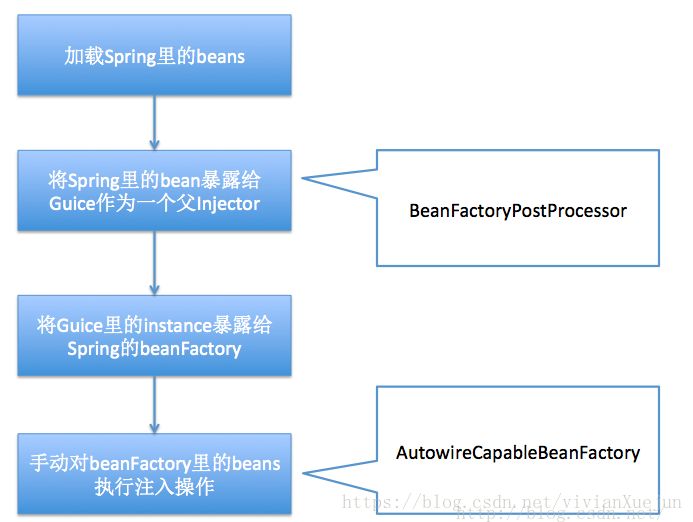
处理过程:
代码:
将spring中的bean暴露给Guice:
public class SpringModule extends AbstractModule {
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
public SpringModule(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory){
this.beanFactory = beanFactory; }
@Override
protected void configure() {
bind(BeanFactory.class).toInstance(this.beanFactory);
String[] names = this.beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
try {
Object instance = this.beanFactory.getBean(name);
Class clazz = instance.getClass();
bind(clazz).toInstance(instance);
Class[] intefaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
for (Class inteface: intefaces) {
if (!inteface.getName().contains("com.xxxxxx")) {
continue;
}
bind(inteface).annotatedWith(Names.named(name)).toInstance(instance);
}
bind(clazz).annotatedWith(Names.named(name)).toInstance(instance);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
} 将Guice里的beans暴露给spring:
@Component
public class PbfInitProcesser implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
// map injector to spring beanFactory
Injector spring = Guice.createInjector(new SpringModule(beanFactory));
Injector injector = spring.createChildInjector(new ProductModule());
PbfEnvInitUtil.shareGuiceToSpring("injector", beanFactory, injector);
}
} public class PbfEnvInitUtil {
public static final void refresh(ApplicationContext context) {
// refresh inject bean to autowire
String names[] = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
context.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().autowireBean(context.getBean(name));
}
}
public static void shareGuiceToSpring(String bizName, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, Injector injector) {
Map<Key<?>, Binding<?>> map = injector.getAllBindings();
Iterator<Map.Entry<Key<?>, Binding<?>>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Key<?>, Binding<?>> entry = iterator.next();
Binding<?> binding = entry.getValue();
Object listener = binding.getProvider().get();
Annotation annotation = entry.getKey().getAnnotation();
if (null != annotation && annotation instanceof Named) {
String name = ((Named)annotation).value();
try {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(name, listener);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
beanFactory.registerSingleton(bizName, injector);
}
} springboot中使用:
ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
PbfEnvInitUtil.refresh(context); 转其他博文作参考:
http://www.importnew.com/15947.html
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-guice.html
http://hao.jobbole.com/guice/